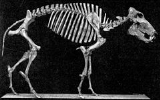
Platygonus
Encyclopedia
Platygonus is an extinct genus of herbivorous peccary
of the family
Tayassuidae, endemic to North America
from the Miocene
through Pleistocene
epochs (10.3 mya—11,000 years ago), existing for approximately .
Platygonus was a gregarious animal and, like modern peccaries, possibly traveled in packs. It ranged from southern Canada
to Mexico
and from California
to Pennsylvania
. Stratigraphically, it occurs throughout the Pleistocene
(Calabrian), and as early as the Blancan
in the Gelasian
of the Pliocene
.
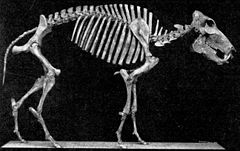 Platygonus was larger than modern peccaries, at around 1 metres (3.3 ft) in body length, and had long legs, allowing it to run well. It also had a pig
Platygonus was larger than modern peccaries, at around 1 metres (3.3 ft) in body length, and had long legs, allowing it to run well. It also had a pig
-like snout and long, carnivore-like tusk
s which were probably used to fend off predators. It had a complex digestive system, similar to that of a modern ruminant
.
Peccary
A peccary is a medium-sized mammal of the family Tayassuidae, or New World Pigs. Peccaries are members of the artiodactyl suborder Suina, as are the pig family and possibly the hippopotamus family...
of the family
Family (biology)
In biological classification, family is* a taxonomic rank. Other well-known ranks are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, genus, and species, with family fitting between order and genus. As for the other well-known ranks, there is the option of an immediately lower rank, indicated by the...
Tayassuidae, endemic to North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
from the Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
through Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
epochs (10.3 mya—11,000 years ago), existing for approximately .
Platygonus was a gregarious animal and, like modern peccaries, possibly traveled in packs. It ranged from southern Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
to Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
and from California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
to Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
. Stratigraphically, it occurs throughout the Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
(Calabrian), and as early as the Blancan
Blancan
The Blancan North American Stage on the geologic timescale is the North American faunal stage according to the North American Land Mammal Ages chronology , typically set from 4,750,000 to 1,808,000 years BP, a period of .. It is usually considered to start in the early-mid Pliocene epoch and end...
in the Gelasian
Gelasian
The Gelasian is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest or lowest subdivision of the Quaternary period/system and Pleistocene epoch/series. It spans the time between 2.588 ± 0.005 Ma and 1.806 ± 0.005 Ma...
of the Pliocene
Pliocene
The Pliocene Epoch is the period in the geologic timescale that extends from 5.332 million to 2.588 million years before present. It is the second and youngest epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch...
.
Taxonomy
Platygonus was named by Leconte (1848). It was assigned to Tayassuidae by Le Conte (1848), Hoare et al. (1964) and Carroll (1988).Morphology

Pig
A pig is any of the animals in the genus Sus, within the Suidae family of even-toed ungulates. Pigs include the domestic pig, its ancestor the wild boar, and several other wild relatives...
-like snout and long, carnivore-like tusk
Tusk
Tusks are elongated, continuously growing front teeth, usually but not always in pairs, that protrude well beyond the mouth of certain mammal species. They are most commonly canines, as with warthogs, wild boar, and walruses, or, in the case of elephants and narwhals, elongated incisors...
s which were probably used to fend off predators. It had a complex digestive system, similar to that of a modern ruminant
Ruminant
A ruminant is a mammal of the order Artiodactyla that digests plant-based food by initially softening it within the animal's first compartment of the stomach, principally through bacterial actions, then regurgitating the semi-digested mass, now known as cud, and chewing it again...
.
Body mass
Four specimens were examined by M. Mendoza for body mass with the following estimations on weight:- Specimen 1: 133.1 kg (293.4 lb)
- Specimen 2: 162 kg (357.1 lb)
- Specimen 3: 131 kg (288.8 lb)
- Specimen 4: 116.6 kg (257.1 lb)

