
Planck current
Encyclopedia
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
, denoted by Ip, in the system of natural units
Natural units
In physics, natural units are physical units of measurement based only on universal physical constants. For example the elementary charge e is a natural unit of electric charge, or the speed of light c is a natural unit of speed...
known as Planck units
Planck units
In physics, Planck units are physical units of measurement defined exclusively in terms of five universal physical constants listed below, in such a manner that these five physical constants take on the numerical value of 1 when expressed in terms of these units. Planck units elegantly simplify...
.
 ≈
≈3.479 × 1025 A
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
where:
 is the Planck charge
is the Planck chargePlanck charge
In physics, the Planck charge , is one of the base units in the system of natural units called Planck units. It is a quantity of electric charge defined in terms of fundamental physical constants.The Planck charge is defined as:...
 is the Planck time
is the Planck timePlanck time
In physics, the Planck time, , is the unit of time in the system of natural units known as Planck units. It is the time required for light to travel, in a vacuum, a distance of 1 Planck length...
 = permittivity
= permittivityPermittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
in vacuum
 is the reduced Planck constant
is the reduced Planck constantG is the gravitational constant
Gravitational constant
The gravitational constant, denoted G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of the gravitational attraction between objects with mass. It appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is also known as the universal...
c is the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
in vacuum.
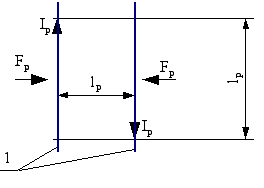
The Planck current is that current which, in a conductor, carries a Planck charge in Planck time.
Alternatively, the Planck current is that constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite
Infinity
Infinity is a concept in many fields, most predominantly mathematics and physics, that refers to a quantity without bound or end. People have developed various ideas throughout history about the nature of infinity...
length and negligible circular cross-section, and placed a Planck length apart in vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
, would produce between these conductors a force
Force
In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
equal to a Planck force per Planck length.

