
Phycobilisome
Encyclopedia
Photosystem II
Photosystem II is the first protein complex in the Light-dependent reactions. It is located in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. The enzyme uses photons of light to energize electrons that are then transferred through a variety of coenzymes and cofactors to reduce...
in cyanobacteria, red algae
Red algae
The red algae are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae, and also one of the largest, with about 5,000–6,000 species of mostly multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds...
and glaucophytes.
General structure
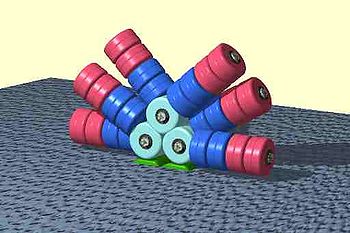
Phycobilisomes are protein complexes (up to 600 polypeptides) anchored to thylakoidThylakoid
A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as...
membranes. They are made of stacks of chromophorylated
Chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color arises when a molecule absorbs certain wavelengths of visible light and transmits or reflects others. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two different molecular orbitals falls...
proteins, the phycobiliprotein
Phycobiliprotein
Phycobiliproteins are water-soluble proteins present in cyanobacteria and certain algae that capture light energy, which is then passed on to chlorophylls during photosynthesis. Phycobiliproteins are formed of a complex between proteins and covalently bound phycobilins that act as chromophores...
s, and their associated linker polypeptides. Each phycobilisome consists of a core made of allophycocyanin
Allophycocyanin
Allophycocyanin is a protein from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, along with phycocyanin, phycoerythrin and phycoerythrocyanin. It is an accessory pigment to chlorophyll...
, from which several outwardly oriented rods made of stacked disks of phycocyanin
Phycocyanin
Phycocyanin is a pigment from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, along with allophycocyanin and phycoerythrin. It is an accessory pigment to chlorophyll. All phycobiliproteins are water-soluble and therefore cannot exist within the membrane as do carotenoids, but aggregate forming...
and (if present) phycoerythrin
Phycoerythrin
Phycoerythrin is a red protein from the light-harvesting phycobiliprotein family, present in cyanobacteria, red algae and cryptomonads.Like all phycobiliproteins, phycoerythrin is composed of a protein part, organised in a hexameric structure of alpha and beta chains, covalently binding...
(s) or phycoerythrocyanin
Phycoerythrocyanin
Phycoerythrocyanin is a kind of phycobiliproteins, magenta chromoprotein involved in photosynthesis of some Cyanobacteria. This chromoprotein consists of alpha- and beta-subunits, generally aggregated as hexamer...
. The spectral property of phycobiliproteins are mainly dictated by their prosthetic groups, which are linear tetrapyrrole
Tetrapyrrole
Tetrapyrroles are compounds containing four pyrrole rings. With the exception of corrin, the four pyrrole rings are interconnected through one-carbon bridges, in either a linear or a cyclic fashion...
s known as phycobilin
Phycobilin
Phycobilins are chromophores found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae, glaucophytes and some cryptomonads...
s including phycocyanobilin
Phycocyanobilin
Phycocyanobilin is a blue phycobilin, i.e., a tetrapyrrole chromophore found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae, glaucophytes, and some cryptomonads. Phycocyanobilin is present only in the phycobiliproteins allophycocyanin and phycocyanin, of which it is the terminal acceptor of...
, phycoerythrobilin
Phycoerythrobilin
Phycoerythrobilin is a red phycobilin, i.e. an open tetrapyrrole chromophore found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae, glaucophytes and some cryptomonads. Phycoerythrobilin is present in the phycobiliprotein phycoerythrin, of which it is the terminal acceptor of energy. The...
, phycourobilin
Phycourobilin
Phycourobilin is a tetrapyrrole orange molecule involved in photosynthesis in cyanobacteria and red algae. This chromophore is bound to the phycobiliprotein phycoerythrin, the distal component of the light-harvesting system of cyanobacteria and red algae .When bound to phycoerythrin, phycourobilin...
and phycobiliviolin. The spectral properties of a given phycobilin is influenced by its protein environment.
Function
Each phycobiliprotein has a specific absorption and fluorescence emission maximum in the visible range of light. Therefore, their presence and the particular arrangement within the phycobilisomes allow absorption and unidirectional transfer of light energy to chlorophyllChlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in almost all plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. Its name is derived from the Greek words χλωρος, chloros and φύλλον, phyllon . Chlorophyll is an extremely important biomolecule, critical in photosynthesis, which allows plants to obtain energy from light...
a of the photosystem II. In this way, the cells take advantage of the available wavelengths of light (in the 500-650 nm range), which are inaccessible to chlorophyll, and utilize their energy for photosynthesis. This is particularly advantageous deeper in the water column, where light with longer wavelengths is less transmitted and therefore less available directly to chlorophyll.
The geometrical arrangement of a phycobilisome is very elegant and results in 95% efficiency of energy transfer
Stopping power (particle radiation)
In passing through matter, fast charged particles ionize the atoms or molecules which they encounter. Thus, the fast particles gradually lose energy in many small steps. Stopping power is defined as the average energy loss of the particle per unit path length, measured for example in MeV/cm...
.
Evolution and diversity
There are many variations to the general phycobilisomes structure. Their shape can be hemidiscoidal (in cyanobacteria) or hemiellipsoidal (in red algae).The phycobiliproteins themselves show little sequence evolution due to their highly constrained function (absorption and transfer of specific wavelengths).
In some species of cyanobacteria, when both phycocyanin and phycoerythrin is present, the phycobilisome can undergo significant restructuring as response to light color. In green light the distal portions of the rods are made of red colored phycoerythrin, which absorbs green light better. In red light, this is replaced by blue colored phycocyanin, which absorbs red light better. This reversible process is known as complementary chromatic adaptation.

