
Phragmoplast
Encyclopedia
Plant cell
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that differ in several key respects from the cells of other eukaryotic organisms. Their distinctive features include:...
specific structure that forms during late cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the late stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a binucleate cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation...
. It serves as a scaffold for cell plate
Cell plate
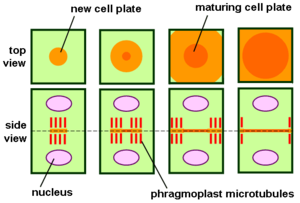
thumb|300px|Phragmoplast and cell plate formation in a plant cell during cytokinesis. Left side: Phragmoplast forms and cell plate starts to assemble in the center of the cell. Toawards the right: Phragmoplast enlarges in a donut-shape towards the outside of the cell, leaving behind mature cell...
assembly and subsequent formation of a new cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
separating the two daughter cells.
The phragmoplast is a complex assembly of microtubules (MTs), microfilaments (MFs), and endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle of cells in eukaryotic organisms that forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae...
(ER) elements, that assemble in two opposing sets perpendicular to the plane of the future cell plate
Cell plate
thumb|300px|Phragmoplast and cell plate formation in a plant cell during cytokinesis. Left side: Phragmoplast forms and cell plate starts to assemble in the center of the cell. Toawards the right: Phragmoplast enlarges in a donut-shape towards the outside of the cell, leaving behind mature cell...
during anaphase
Anaphase
Anaphase, from the ancient Greek ἀνά and φάσις , is the stage of mitosis or meiosis when chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell....
and telophase
Telophase
Telophase from the ancient Greek "τελος" and "φασις" , is a stage in both meiosis and mitosis in a eukaryotic cell. During telophase, the effects of prophase and prometaphase events are reversed. Two daughter nuclei form in the cell. The nuclear envelopes of the daughter cells are formed from the...
. It is initially barrel-shaped and forms from the mitotic spindle
Mitotic spindle
In cell biology, the spindle fibers are the structure that separates the chromosomes into the daughter cells during cell division. It is part of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells...
between the two daughter nuclei while nuclear envelope
Nuclear envelope
A nuclear envelope is a double lipid bilayer that encloses the genetic material in eukaryotic cells. The nuclear envelope also serves as the physical barrier, separating the contents of the nucleus from the cytosol...
s reassemble around them. The cell plate initially forms as a disc between the two halves of the phragmoplast structure. While new cell plate material is added to the edges of the growing plate, the phragmoplast microtubules disappear in the center and regenerate at the edges of the growing cell plate. The two structures grow outwards until they reach the outer wall of the dividing cell. If a phragmosome
Phragmosome
The phragmosome is a sheet of cytoplasm forming in highly vacuolated plant cells in preparation for mitosis. In contrast to animal cells, plant cells often contain large central vacuoles occupying up to 90% of the total cell volume and pushing the nucleus against the cell wall. In order for mitosis...
was present in the cell, the phragmoplast and cell plate will grow through the space occupied by the phragmosome. They will reach the parent cell wall exactly at the position formerly occupied by the preprophase band
Preprophase band
The preprophase band is a microtubule array found in plant cells that are about to undergo cell division and enter the preprophase stage of the plant cell cycle. Besides the phragmosome, it is the first microscopically visible sign that a plant cell is about to enter mitosis...
.
The microtubules and actin filaments within the phragmoplast serve to guide vesicles
Vesicle (biology)
A vesicle is a bubble of liquid within another liquid, a supramolecular assembly made up of many different molecules. More technically, a vesicle is a small membrane-enclosed sack that can store or transport substances. Vesicles can form naturally because of the properties of lipid membranes , or...
with cell wall material to the growing cell plate. Actin filaments are also possibly involved in guiding the phragmoplast to the site of the former preprophase band location at the parent cell wall. While the cell plate is growing, segments of smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle of cells in eukaryotic organisms that forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae...
are trapped within it, later forming the plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata are microscopic channels which traverse the cell walls of plant cells and some algal cells, enabling transport and communication between them. Species that have plasmodesmata include members of the Charophyceae, Charales and Coleochaetales , as well as all embryophytes, better known...
connecting the two daughter cells.
The phragmoplast can only be observed in bryophyte
Bryophyte
Bryophyte is a traditional name used to refer to all embryophytes that do not have true vascular tissue and are therefore called 'non-vascular plants'. Some bryophytes do have specialized tissues for the transport of water; however since these do not contain lignin, they are not considered to be...
s and vascular plant
Vascular plant
Vascular plants are those plants that have lignified tissues for conducting water, minerals, and photosynthetic products through the plant. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, Equisetum, ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms...
s and a few algae
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
. Some algae use another type of microtubule array, a phycoplast
Phycoplast
thumb|Schematic representation of types of cytokinesis in the green algae: 1) Phycoplast formation with cleavage furrow ; 2) Cleavage furrow and persistent telophase spindle ; 3) Phycoplast and cell plate formation ; 4) Persistent telophase spindle/phragmoplast with cell plate formation...
, during cytokinesis.

