
Peripheral vision
Encyclopedia
Visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret information and surroundings from the effects of visible light reaching the eye. The resulting perception is also known as eyesight, sight, or vision...
that occurs outside the very center of gaze. There is a broad set of non-central points in the field of view
Field of view
The field of view is the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment....
that is included in the notion of peripheral vision. "Far peripheral" vision exists at the edges of the field of view, "mid-peripheral" vision exists in the middle of the field of view, and "near-peripheral", sometimes referred to as "para-central" vision, exists adjacent to the center of gaze.
The loss of peripheral vision while retaining central vision is known as tunnel vision
Tunnel vision
Tunnel vision is the loss of peripheral vision with retention of central vision, resulting in a constricted circular tunnel-like field of vision.- Medical / biological causes :Tunnel vision can be caused by:...
, and the loss of central vision while retaining peripheral vision is known as central scotoma.
Peripheral vision is weaker in human
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
s, compared with other animals, especially at distinguishing color
Color vision
Color vision is the capacity of an organism or machine to distinguish objects based on the wavelengths of the light they reflect, emit, or transmit...
and shape. This is because receptor cells on the retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
are greater at the center and lowest at the edges (see visual system
Visual system
The visual system is the part of the central nervous system which enables organisms to process visual detail, as well as enabling several non-image forming photoresponse functions. It interprets information from visible light to build a representation of the surrounding world...
for an explanation of these concepts). In addition, there are two types of receptor cells, rod cell
Rod cell
Rod cells, or rods, are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in less intense light than can the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells. Named for their cylindrical shape, rods are concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in peripheral vision. On...
s and cone cell
Cone cell
Cone cells, or cones, are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that are responsible for color vision; they function best in relatively bright light, as opposed to rod cells that work better in dim light. If the retina is exposed to an intense visual stimulus, a negative afterimage will be...
s; rod cells are unable to distinguish color and are predominant at the periphery, while cone cells are concentrated mostly in the center of the retina, the fovea
Fovea
The fovea centralis, also generally known as the fovea , is a part of the eye, located in the center of the macula region of the retina....
.
Flicker fusion threshold
Flicker fusion threshold
The flicker fusion threshold is a concept in the psychophysics of vision. It is defined as the frequency at which an intermittent light stimulus appears to be completely steady to the observer...
is higher for peripheral than fovea
Fovea
The fovea centralis, also generally known as the fovea , is a part of the eye, located in the center of the macula region of the retina....
l vision. Peripheral vision is good at detecting motion (a feature of rod cells).
Peripheral vision is hard to study in an objective manner, because there is no way to separate the visual detection of the eye from the neural processing of the brain. While the eye can be dissected and examined under a microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
, even if the entirety of the retina is capable of detecting light, that capacity may not be fully utilized or may not be consciously aware within the brain. Certain conditions such as lazy eye
Lazy Eye
Lazy eye may refer to:* Amblyopia, a visual disorder* Strabismus, the most common cause of amblyopia* "Lazy Eye" * "Lazy Eye"...
can cause suppression of an otherwise usable visual field, while stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
or damage to the corpus callosum
Corpus callosum
The corpus callosum , also known as the colossal commissure, is a wide, flat bundle of neural fibers beneath the cortex in the eutherian brain at the longitudinal fissure. It connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres and facilitates interhemispheric communication...
can prevent left/right integration.
It is not possible to directly observe what the brain is detecting and comprehending, so research primarily involves perception tests based on reactions of test subjects to simulated stimuli. This testing is commonly carried out by requesting test subjects to focus on an object in front of them and then flashing lights at increasing distances away from the center of the visual field, noting the subject's reactions.
Central vision is relatively weak at night or in the dark, when the lack of color cues and lighting makes cone cells far less useful. Rod cells, which are concentrated further away from the retina, operate better than cone cells in low light. This makes peripheral vision useful for seeing movement at night. In fact, pilots are taught to use peripheral vision to scan for aircraft at night.
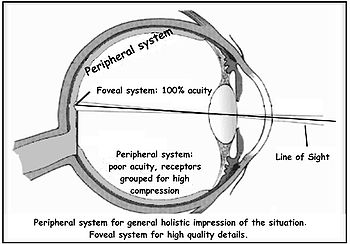
Foveal
The foveal system of the human eye is the only part of the retina that permits 100% visual acuity. The line-of-sight is a virtual line connecting the fovea with a fixation point in the outside world....
(sometimes also called central) and peripheral vision are reflected in subtle physiological and anatomical differences in the visual cortex
Visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the part of the cerebral cortex responsible for processing visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe, in the back of the brain....
. Different visual areas contribute to the processing of visual information coming from different parts of the visual field, and a complex of visual areas located along the banks of the interhemispheric fissure (a deep groove that separates the two brain hemispheres) has been linked to peripheral vision. It has been suggested that these areas are important for fast reactions to visual stimuli in the periphery, and monitoring body position relative to gravity.
Peripheral vision can be practiced, jugglers that regularly locate and catch objects in their peripheral vision do have improved abilities. Jugglers do not follow the paths of individual objects with their eyes, instead they focus on a defined point in mid-air, so almost all of the information necessary for successful catches is perceived in the near-peripheral region. Some juggling patterns and disciplines require extraordinary peripheral vision.
Functions
The main functions of peripheral vision are:- recognition of well-known structures and forms with no need to focus by the foveal line of sight.
- identification of similar forms and movements (Gestalt psychologyGestalt psychologyGestalt psychology or gestaltism is a theory of mind and brain of the Berlin School; the operational principle of gestalt psychology is that the brain is holistic, parallel, and analog, with self-organizing tendencies...
laws) - delivery of sensations which form the background of detailed visual perception.
See also
- Averted visionAverted visionAverted vision is a technique for viewing faint objects which uses peripheral vision. It involves not looking directly at the object, but looking a little off to the side, while continuing to concentrate on the object. This subject is discussed in the popular astronomy literature but only a few...
- Eye movement
- Eye movement in music readingEye movement in music readingEye movement in music reading is the scanning of a musical score by a musician's eyes. This usually occurs as the music is read during performance, although musicians sometimes scan music silently to study it, and sometimes perform from memory without score. The phenomenon has been studied by...
- FoveaFoveaThe fovea centralis, also generally known as the fovea , is a part of the eye, located in the center of the macula region of the retina....
- PerimetryPerimetryPerimetry or campimetry is the systematic measurement of differential light sensitivity in the visual field by the detection of the presence of test targets on a defined background. Visual field testing can be performed clinically with confrontational field testing keeping the subject's gaze fixed...
- Visual fieldVisual fieldThe term visual field is sometimes used as a synonym to field of view, though they do not designate the same thing. The visual field is the "spatial array of visual sensations available to observation in introspectionist psychological experiments", while 'field of view' "refers to the physical...
- Vision spanVision spanVision span or perceptual span is the angular span , within which the human eye has sharp enough vision to read text. The visual field of the human eye spans approximately 120 degrees of arc. However, most of that arc is peripheral vision. The human eye has much greater resolution in the...
- Visual perceptionVisual perceptionVisual perception is the ability to interpret information and surroundings from the effects of visible light reaching the eye. The resulting perception is also known as eyesight, sight, or vision...
- Tunnel visionTunnel visionTunnel vision is the loss of peripheral vision with retention of central vision, resulting in a constricted circular tunnel-like field of vision.- Medical / biological causes :Tunnel vision can be caused by:...

