
Periodic annual increment
Encyclopedia
Periodic annual increment (PAI), is a forestry
term that describes the change in the size of a tree between the beginning and ending of a growth period, divided by the number of years that was designated as the growing period (Avery, 339). For sigmoid
growth, the graph of PAI increases rapidly and then quickly declines, approaching zero. PAI may go negative if a tree loses volume due to damage or disease.
Periodic annual increment is commonly used instead of current annual increment as a basis for computing growth per cent. Growth per cent indicates the rate of increase with relation to the wood capital required for its production, this is usually based on a single year's growth (Chapman, 315).

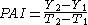
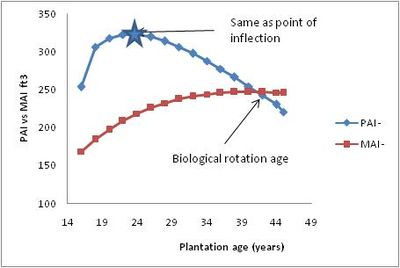
Where: Y is the yield (volume, height, DBH
, etc.) at times 1 and 2 and T1 represents the year starting the growth period, and T2 is the end year.
Example: Say that the growth period is from age 5 to age 10, and the yield
(height of the tree), is 14 feet at the beginning of the period and 34 feet
at the end.
Then:
on a graph of yield versus time. The inflection point is the point corresponding to the fastest change in yield.
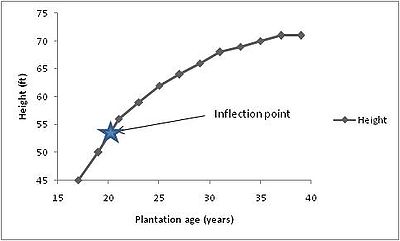
When mean annual increment
(MAI) and periodic annual increment (PAI) are graphed together, the point in which they intersect is called the biological rotation age
. The biological rotation age is the age in which a stand should be harvested to maximize long-term yield.
Forestry
Forestry is the interdisciplinary profession embracing the science, art, and craft of creating, managing, using, and conserving forests and associated resources in a sustainable manner to meet desired goals, needs, and values for human benefit. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands...
term that describes the change in the size of a tree between the beginning and ending of a growth period, divided by the number of years that was designated as the growing period (Avery, 339). For sigmoid
Sigmoid function
Many natural processes, including those of complex system learning curves, exhibit a progression from small beginnings that accelerates and approaches a climax over time. When a detailed description is lacking, a sigmoid function is often used. A sigmoid curve is produced by a mathematical...
growth, the graph of PAI increases rapidly and then quickly declines, approaching zero. PAI may go negative if a tree loses volume due to damage or disease.
Periodic annual increment is commonly used instead of current annual increment as a basis for computing growth per cent. Growth per cent indicates the rate of increase with relation to the wood capital required for its production, this is usually based on a single year's growth (Chapman, 315).

Equation
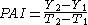
Where: Y is the yield (volume, height, DBH
Diameter at breast height
Diameter at breast height, or DBH, is a standard method of expressing the diameter of the trunk or bole of a standing tree. DBH is one of the most common dendrometric measurements....
, etc.) at times 1 and 2 and T1 represents the year starting the growth period, and T2 is the end year.
Example: Say that the growth period is from age 5 to age 10, and the yield
(height of the tree), is 14 feet at the beginning of the period and 34 feet
at the end.
Then:

Uses
The maximum point on the curve of PAI is the same as the inflection pointInflection point
In differential calculus, an inflection point, point of inflection, or inflection is a point on a curve at which the curvature or concavity changes sign. The curve changes from being concave upwards to concave downwards , or vice versa...
on a graph of yield versus time. The inflection point is the point corresponding to the fastest change in yield.
When mean annual increment
Mean annual increment
The mean annual increment or mean annual growth refers to the average growth per year a tree or stand of trees has exhibited/experienced to a specified age. For example, a 20-year old tree that has a diameter at breast height of 10.0 inches has an MAI of 0.5 inches/year. MAI is...
(MAI) and periodic annual increment (PAI) are graphed together, the point in which they intersect is called the biological rotation age
Maximum sustainable yield
In population ecology and economics, maximum sustainable yield or MSY is, theoretically, the largest yield that can be taken from a species' stock over an indefinite period...
. The biological rotation age is the age in which a stand should be harvested to maximize long-term yield.



