is on the whole more useful, in terms of survival, than diamonds, diamonds command a higher price in the market
. The philosopher Adam Smith
is often considered to be the classic presenter of this paradox. Nicolaus Copernicus
, John Locke
, John Law
and others had previously tried to explain the disparity.
Labor theory of value
In a passage of Adam Smith's An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations, he discusses the concepts of value in use and value in exchange, and notices how they tend to differ:- What are the rules which men naturally observe in exchanging them [goods] for money or for one another, I shall now proceed to examine. These rules determine what may be called the relative or exchangeable value of goods. The word VALUE, it is to be observed, has two different meanings, and sometimes expresses the utility of some particular object, and sometimes the power of purchasing other goods which the possession of that object conveys. The one may be called "value in useUse valueUse value or value in use is the utility of consuming a good; the want-satisfying power of a good or service in classical political economy. In Marx's critique of political economy, any labor-product has a value and a use-value, and if it is traded as a commodity in markets, it additionally has an...
;" the other, "value in exchangeExchange valueIn political economy and especially Marxian economics, exchange value refers to one of four major attributes of a commodity, i.e., an item or service produced for, and sold on the market...
." The things which have the greatest value in use have frequently little or no value in exchange; on the contrary, those which have the greatest value in exchange have frequently little or no value in use. Nothing is more useful than water: but it will purchase scarce anything; scarce anything can be had in exchange for it. A diamond, on the contrary, has scarce any use-value; but a very great quantity of other goods may frequently be had in exchange for it.
Furthermore, he explained the value in exchange as being determined by labor:
- The real price of every thing, what every thing really costs to the man who wants to acquire it, is the toil and trouble of acquiring it.
Hence, Smith denied a necessary relationship between price and utility. Price on this view was related to a factor of production (namely, labor) and not to the point of view of the consumer. Proponents of the labor theory of value saw that as the resolution of the paradox.
The labor theory of value has lost popularity in mainstream economics and has been replaced by the theory of marginal utility
.
Marginalism
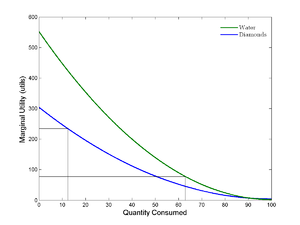
The theory of marginal utility, which is based on the subjective theory of value
, says that the price at which an object trades in the market is determined neither by how much labor was exerted in its production, as in the labor theory of value
, nor on how useful it is on a whole (total utility). Rather, its price is determined by its marginal utility
. The marginal utility
of a good is derived from its most important use to a person. So, if someone possesses a good, he will use it to satisfy some need or want. Which one? Naturally, the one that takes highest-priority. Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk
illustrated this with the example of a farmer having five sacks of grain. With the first, he will make bread to survive. With the second, he will make more bread, in order to be strong enough to work. With the next, he will feed his farm animals. The next is used to make whisky, and the last one he feeds to the pigeons. If one of those bags is stolen, he will not reduce each of those activities by one-fifth; instead he will stop feeding the pigeons. So the value of the fifth bag of grain is equal to the satisfaction he gets from feeding the pigeons. If he sells that bag and neglects the pigeons, his least productive use of the remaining grain is to make whisky, so the value of a fourth bag of grain is the value of his whisky. Only if he loses four bags of grain will he start eating less; that is the most productive use of his grain. The last bag of grain is worth his life.
In explaining the diamond-water paradox, marginalists explain that it is not the total usefulness of diamonds or water that matters, but the usefulness of each unit of water or diamonds. It is true that the total utility of water to people is tremendous, because they need it to survive. However, since water is in such large supply in the world, the marginal utility of water is low. In other words, each additional unit of water that becomes available can be applied to less urgent uses as more urgent uses for water are satisfied. Therefore, any particular unit of water becomes worth less to people as the supply of water increases. On the other hand, diamonds are in much lower supply. They are of such low supply that the usefulness of one diamond is greater than the usefulness of one glass of water, which is in abundant supply. Thus, diamonds are worth more to people. Therefore, those who want diamonds are willing to pay a higher price for one diamond than for one glass of water, and sellers of diamonds ask a price for one diamond that is higher than for one glass of water.
Criticisms
George Stigler has argued that Smith's statement of the paradox is flawed, since it consisted of a comparison between heterogeneous goods, and such comparison would have required using the concept of marginal utility of income. And since this concept was not known in Smith's time, then the value in use and value in exchange judgement may be meaningless:
The paradox—that value in exchange may exceed or fall short of value in use—was, strictly speaking, a meaningless statement, for Smith had no basis (i.e., no concept of marginal utility of income or marginal price of utility) on which he could compare such heterogeneous quantities. On any reasonable interpretation, moreover, Smith's statement that value in use could be less than value in exchange was clearly a moral judgment, not shared by the possessors of diamonds. To avoid the incomparability of money and utility, one may interpret Smith to mean that the ratio of values of two commodities is not equal to the ratio of their total utilities. Or, alternatively, that the ratio of the prices of two commodities is not equal to the ratio of their total utilities; but this also requires an illegitimate selection of units: The price of what quantity of diamonds is to be compared with the price of one gallon of water?
—George Stigler
George StiglerGeorge Joseph Stigler was a U.S. economist. He won the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1982, and was a key leader of the Chicago School of Economics, along with his close friend Milton Friedman....
, The development of Utility Theory. I

