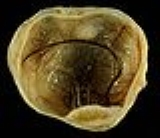
Ovarian cancer
Encyclopedia
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous
growth
arising from the ovary
. Symptoms are frequently very subtle early on and may include: bloating, pelvic pain
, difficulty eating and frequent urination
, and are easily confused with other illnesses.
Most (more than 90%) ovarian cancers are classified as "epithelial" and are believed to arise from the surface (epithelium
) of the ovary. However, some evidence suggests that the fallopian tube
could also be the source of some ovarian cancers. Since the ovaries and tubes are closely related to each other, it is thought that these fallopian cancer cells can mimic ovarian cancer. Other types may arise from the egg cells (germ cell tumor
) or supporting cells. These cancers are grouped into the category of gynecologic cancer. In the United States each year 82,000 women are diagnosed with gynecologic cancer.
or discomfort, an abdominal mass, bloating
, back pain
, urinary urgency
, constipation
, tiredness and a range of other non-specific symptoms, as well as more specific symptoms such as pelvic pain
, abnormal vaginal bleeding
or involuntary weight loss
. There can be a build-up of fluid (ascites
) in the abdominal cavity.
A prospective case-control study of 1,709 women visiting primary care clinics found that the combination of bloating
, increased abdominal size, and urinary symptoms was found in 43% of those with ovarian cancer but in only 8% of those presenting to primary care clinics. Two case-control
studies, (both subject to results being inflated by spectrum bias
), have been reported. The first found that women with ovarian cancer had symptoms of increased abdominal size, bloating, urge to pass urine and pelvic pain. The smaller, second study found that women with ovarian cancer had pelvic/abdominal pain, increased abdominal size/bloating, and difficulty eating/feeling full. The second study produced a list of symptoms that was considered critical if any of the six (6) symptoms "occurred more than 12 times per month but were present for under 1 year".
(most notably BRCA1
and BRCA2
, but also in genes for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
). Infertile
women and those with a condition called endometriosis
, those who have never been pregnant and those who use postmenopausal estrogen replacement therapy
are at increased risk. Use of combined oral contraceptive pills is a protective factor. The more children a woman has, the lower her risk of ovarian cancer. Early age at first pregnancy, older age of final pregnancy and the use of low dose hormonal contraception
have also been shown to have a protective effect. The risk is also lower in women who have had their fallopian tubes blocked surgically (tubal ligation
).
Analysis of 489 high-grade serous ovarian adenocarcinomas found that the p53
gene was mutated in 96% of cases. Other genes commonly mutated were NF1
, BRCA1, BRCA2, RB1 and cyclin-dependent kinase
12 (CDK12).
The ovaries contain eggs and secrete the hormones that control the reproductive cycle. Removing the ovaries and the fallopian tubes greatly reduces the amount of the hormones estrogen and progesterone circulating in your body. This can halt or slow breast and ovarian cancers that need these hormones to grow.
The link to the use of fertility medication
, such as Clomiphene citrate, has been controversial. An analysis in 1991 raised the possibility that use of drugs may increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Several cohort
studies and case-control
studies have been conducted since then without demonstrating conclusive evidence for such a link. It will remain a complex topic to study as the infertile population differs in parity
from the "normal" population.
 There is good evidence that in some women genetic factors are important. Carriers of certain BRCA mutation
There is good evidence that in some women genetic factors are important. Carriers of certain BRCA mutation
s are notably at risk. The BRCA1
and BRCA2
genes account for 5%–13% of ovarian cancers and certain populations (e.g. Ashkenazi Jewish women) are at a higher risk of both breast cancer
and ovarian cancer, often at an earlier age than the general population. Patients with a personal history of breast cancer or a family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer, especially if diagnosed at a young age, may have an elevated risk, and should be tested for the "cancer gene".
In the United States, 10 to 20 percent of patients with breast cancer and patients with ovarian cancer have a first- or second-degree relative with one of these diseases. Mutations in either of two major susceptibility genes, breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1) and breast cancer susceptibility gene 2 (BRCA2), confer a lifetime risk of breast cancer of between 60 and 85 percent and a lifetime risk of ovarian cancer of between 15 and 40 percent. However, mutations in these genes account for only 2 to 3 percent of all breast cancers.
A strong family history of uterine cancer
, colon cancer, or other gastrointestinal cancer
s may indicate the presence of a syndrome known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
(HNPCC, also known as Lynch syndrome
), which confers a higher risk for developing ovarian cancer. Patients with strong genetic risk for ovarian cancer may consider the use of prophylactic, i.e. preventative, oophorectomy
the surgical removal of both ovaries, after completion of childbearing years. Prophylactic oophorectomy significantly reduces the chances of developing both breast cancer and ovarian cancer if you're at high risk. Women with BRCA gene mutations usually also have their fallopian tubes removed at the same time (salpingo-oophorectomy), since they also have an increased risk of fallopian tube cancer.
A study found that Hereditary breast-ovarian cancer syndromes (HBOC) produce higher than normal levels of breast cancer
and ovarian cancer in genetically related families (either one individual suffered from both, or several individuals in the families suffered from one or the other disease). The hereditary factors may be proven or suspected to cause the pattern of breast and ovarian cancer occurrences in the family.
Faults in the RAD51D (either inherited or sporadically occurring) are linked to a significantly increased risk of ovarian cancer, increasing the lifetime risk of the disease roughly 6-fold to around 1 in 11, compared to 1 in 70 for the general population. However, such faults are rare and are thought to contribute to fewer than one in 100 cases of the diseas, accounting for around 40-60 women per year in the UK.
.
Other factors that have been investigated, such as talc
use, asbestos
exposure, high dietary fat content, and childhood mumps
infection, are controversial and have not been definitively proven; moreover, such risk factors may in some cases be more likely to be correlated with cancer in individuals with specific gene
tic makeups.
and hysterectomy
reduce the risk and removal of both tubes and ovaries (bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy) dramatically reduces the risk of not only ovarian cancer but breast cancer also. A hysterectomy that does not include the removal of the ovaries has a one-third reduced risk of developing ovarian cancer, it also has no higher risk of developing other types of cancer, heart disease or hip fractures, researchers from the University of California at San Francisco revealed in the journal Archives of Internal Medicine
.
A study in The Lancet
suggests that tubal ligation can reduce the risk of hereditary ovarian cancer by 72 per cent in women who carry the BRCA1 gene.
The use of oral contraceptives (birth control pills) for five years or more decreases the risk of ovarian cancer in later life by 50%.
), a blood test (for CA-125
and sometimes other markers), and transvaginal ultrasound. The diagnosis must be confirmed with surgery to inspect the abdominal cavity
, take biopsies (tissue samples for microscopic analysis
) and look for cancer cells in the abdominal fluid.
Ovarian cancer at its early stages(I/II) is difficult to diagnose until it spreads and advances to later stages (III/IV). This is because most symptoms are non-specific and thus of little use in diagnosis. The serum BHCG level should be measured in any female in whom pregnancy is a possibility. In addition, serum alpha-fetoprotein
(AFP) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) should be measured in young girls and adolescents with suspected ovarian tumors because the younger the patient, the greater the likelihood of a malignant germ cell tumor.
When an ovarian malignancy is included in the list of diagnostic possibilities, a limited number of laboratory tests are indicated. A complete blood count (CBC) and serum electrolyte test should be obtained in all patients. A blood test called CA-125
is useful in differential diagnosis and in follow up of the disease, but it by itself has not been shown to be an effective method to screen for early-stage ovarian cancer due to its unacceptable low sensitivity and specificity.
The new test approved by the FDA in 2011, OVA1 improves ovarian cancer detection over CA125 blood test and clinical assessment. An article published in the June 2011 issue of Obstetrics & Gynecology showed that adding OVA1 to a physician's preoperative assessment of a woman's ovarian mass would identify more ovarian and ovarian related cancers, than a physician's preoperative assessment alone. OVA1 is intended only for women, 18 years and older, who are already selected for surgery because of their pelvic mass. It is not intended for ovarian cancer screening or for a definitive diagnosis of ovarian cancer. OVA1 was developed in conjunction with researchers at the Johns Hopkins University
in Baltimore.
Current research is looking at ways to combine tumor markers proteomics
along with other indicators of disease (i.e. radiology and/or symptoms) to improve accuracy. The challenge in such an approach is that the disparate prevalence of ovarian cancer means that even testing with very high sensitivity and specificity will still lead to a number of false positive results (i.e. performing surgical procedures in which cancer is not found intra-operatively). However, the contributions of proteomics
are still in the early stages and require further refining. Current studies on proteomics mark the beginning of a paradigm shift towards individually tailored therapy.
A pelvic examination and imaging including CT scan and trans-vaginal ultrasound are essential. Physical examination may reveal increased abdominal girth and/or ascites
(fluid within the abdominal cavity). Pelvic examination may reveal an ovarian or abdominal mass. The pelvic examination can include a Rectovaginal component for better palpation of the ovaries. For very young patients, magnetic resonance imaging
may be preferred to rectal and vaginal examination.
To definitively diagnose ovarian cancer, a surgical procedure to take a look into the abdomen is required. This can be an open procedure (laparotomy
, incision through the abdominal wall) or keyhole surgery (laparoscopy
). During this procedure, suspicious areas will be removed and sent for microscopic analysis
. Fluid from the abdominal cavity
can also be analysed for cancerous cells
. If there is cancer, this procedure can also determine its spread (which is a form of tumor staging).
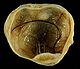 Ovarian cancer is classified according to the histology
Ovarian cancer is classified according to the histology
of the tumor, obtained in a pathology
report. Histology dictates many aspects of clinical treatment, management, and prognosis
.
According to SEER
, types of ovarian cancers in women age 20+ are as follows:
Ovarian cancer can also be a secondary cancer, the result of metastasis
from a primary cancer elsewhere in the body. 7% of ovarian cancers are due to metastases while the rest are primary cancers. Common primary cancers are breast cancer
and gastrointestinal cancer
(a common mistake is to name all peritoneal metastases from any gastrointestinal cancer as Krukenberg cancer, but this is only the case if it originates from primary gastric cancer). Surface epithelial-stromal tumor can originate in the peritoneum
(the lining of the abdominal cavity), in which case the ovarian cancer is secondary to primary peritoneal cancer
, but treatment is basically the same as for primary surface epithelial-stromal tumor involving the peritoneum.
staging system and uses information obtained after surgery, which can include a total abdominal hysterectomy
, removal of (usually) both ovaries and fallopian tubes, (usually) the omentum, and pelvic (peritoneal) washings for cytopathology. The AJCC stage is the same as the FIGO stage.
The AJCC staging system describes the extent of the primary Tumor (T), the absence or presence of metastasis
to nearby lymph Nodes (N), and the absence or presence of distant Metastasis (M).
Para-aortic lymph node metastases are considered regional lymph nodes (Stage IIIC). As there is only one para-aortic lymph node intervening before the thoracic duct on the right side of the body, the ovarian cancer can rapidly spread to distant sites such as the lung.
The AJCC/TNM staging system includes three categories for ovarian cancer, T, N and M. The T category contains three other subcategories, T1, T2 and T3, each of them being classified according to the place where the tumor has developed (in one or both ovaries, inside or outside the ovary). The T1 category of ovarian cancer describes ovarian tumors that are confined to the ovaries, and which may affect one or both of them. The sub-subcategory T1a is used to stage cancer that is found in only one ovary, which has left the capsule intact and which cannot be found in the fluid
taken from the pelvis
. Cancer that has not affected the capsule, is confined to the inside of the ovaries and cannot be found in the fluid taken from the pelvis but has affected both ovaries is staged as T1b. T1c category describes a type of tumor that can affect one or both ovaries, and which has grown through the capsule of an ovary or it is present in the fluid taken from the pelvis. T2 is a more advanced stage of cancer. In this case, the tumor has grown in one or both ovaries and is spread to the uterus
, fallopian tubes or other pelvic tissues. Stage T2a is used to describe a cancerous tumor that has spread to the uterus or the fallopian tubes (or both) but which is not present in the fluid taken from the pelvis. Stages T2b and T2c indicate cancer that metastasized to other pelvic tissues than the uterus and fallopian tubes and which cannot be seen in the fluid taken from the pelvis, respectively tumors that spread to any of the pelvic tissues (including uterus and fallopian tubes) but which can also be found in the fluid taken from the pelvis. T3 is the stage used to describe cancer that has spread to the peritoneum
. This stage provides information on the size of the metastatic tumors (tumors that are located in other areas of the body, but are caused by ovarian cancer). These tumors can be very small, visible only under the microscope
(T3a), visible but not larger than 2 centimeters (T3b) and bigger than 2 centimeters (T3c).
This staging system also uses N categories to describe cancers that have or not spread to nearby lymph nodes. There are only two N categories, N0 which indicates that the cancerous tumors have not affected the lymph nodes, and N1 which indicates the involvement of lymph nodes close to the tumor.
The M categories in the AJCC/TNM staging system provide information on whether the ovarian cancer has metastasized to distant organs such as liver
or lungs. M0 indicates that the cancer did not spread to distant organs and M1 category is used for cancer that has spread to other organs of the body.
The AJCC/TNM staging system also contains a Tx and a Nx sub-category which indicates that the extent of the tumor cannot be described because of insufficient data, respectively the involvement of the lymph nodes cannot be described because of the same reason.
The ovarian cancer stages are made up by combining the TNM categories in the following manner:
Ovarian cancer, as well as any other type of cancer, is also graded, apart from staged. The histologic grade of a tumor measures how abnormal or malignant its cells look under the microscope. There are four grades indicating the likelihood of the cancer to spread and the higher the grade, the more likely for this to occur. Grade 0 is used to describe non-invasive tumors. Grade 0 cancers are also referred to as borderline tumors. Grade 1 tumors have cells
that are well differentiated (look very similar to the normal tissue) and are the ones with the best prognosis. Grade 2 tumors are also called moderately well differentiated and they are made up by cells that resemble the normal tissue. Grade 3 tumors have the worst prognosis and their cells are abnormal, referred to as poorly differentiated.
Researchers are assessing different ways to screen for ovarian cancer. Screening tests that could potentially be used alone or in combination for routine screening include the CA-125
marker and transvaginal ultrasound. Doctors can measure the levels of the CA-125 protein in a woman’s blood - high levels could be a sign of ovarian cancer, but this is not always the case. And not all women with ovarian cancer have high CA-125 levels. Transvaginal ultrasound involves using an ultrasound probe to scan the ovaries from inside the vagina, giving a clearer image than scanning the abdomen. The UK Collaborative Trial of Ovarian Cancer Screening is testing a screening technique that combines CA-125 blood tests with transvaginal ultrasound.
The purpose of screening is to diagnose ovarian cancer at an early stage, when it is more likely to be treated successfully. However, the development of the disease is not fully understood, and it has been argued that early-stage cancers may not always develop into late-stage disease. With any screening technique there are risks and benefits that need to be carefully considered, and health authorities need to assess these before introducing any ovarian cancer screening programmes.
The goal of ovarian cancer screening is to detect the disease at stage I. Several large studies are ongoing, but none have identified an effective technique. In 2009, however, early results from the UK Collaborative Trial of Ovarian Cancer Screening (UKCTOCS) showed that a technique combining annual CA-125 tests with ultrasound imaging did help to detect the disease at an early stage. However, it's not yet clear if this approach could actually help to save lives - the full results of the trial will be published in 2015.
and surgery, and sometimes radiotherapy.
Surgical treatment may be sufficient for malignant tumors that are well-differentiated and confined to the ovary. Addition of chemotherapy may be required for more aggressive tumors that are confined to the ovary. For patients with advanced disease a combination of surgical reduction with a combination chemotherapy regimen is standard. Borderline tumors, even following spread outside of the ovary, are managed well with surgery, and chemotherapy is not seen as useful.
Surgery
is the preferred treatment and is frequently necessary to obtain a tissue specimen for differential diagnosis
via its histology
. Surgery performed by a specialist in gynecologic oncology
usually results in an improved result. Improved survival is attributed to more accurate staging of the disease and a higher rate of aggressive surgical excision of tumor in the abdomen by gynecologic oncologists as opposed to general gynecologists and general surgeons.
The type of surgery depends upon how widespread the cancer is when diagnosed (the cancer stage), as well as the presumed type and grade of cancer. The surgeon may remove one (unilateral oophorectomy) or both ovaries (bilateral oophorectomy), the fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and the uterus (hysterectomy). For some very early tumors (stage 1, low grade or low-risk disease), only the involved ovary and fallopian tube will be removed (called a "unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy," USO), especially in young females who wish to preserve their fertility.
In advanced malignancy, where complete resection is not feasible, as much tumor as possible is removed (debulking surgery). In cases where this type of surgery is successful (i.e. < 1 cm in diameter of tumor is left behind ["optimal debulking"]), the prognosis is improved compared to patients where large tumor masses (> 1 cm in diameter) are left behind. Minimally invasive surgical techniques may facilitate the safe removal of very large (greater than 10 cm) tumors with fewer complications of surgery.
Chemotherapy
has been a general standard of care
for ovarian cancer for decades, although with highly variable protocols.
Chemotherapy is used after surgery to treat any residual disease, if appropriate. This depends on the histology
of the tumor; some kinds of tumor (particularly teratoma
) are not sensitive to chemotherapy. In some cases, there may be reason to perform chemotherapy first, followed by surgery.
For patients with stage IIIC epithelial ovarian adenocarcinomas who have undergone successful optimal debulking, a recent clinical trial demonstrated that median survival time is significantly longer for patient receiving intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy.
Patients in this clinical trial reported less compliance with IP chemotherapy and fewer than half of the patients received all six cycles of IP chemotherapy. Despite this high "drop-out" rate, the group as a whole (including the patients that didn't complete IP chemotherapy treatment) survived longer on average than patients who received intravenous chemotherapy alone.
Some specialists believe the toxicities and other complications of IP chemotherapy will be unnecessary with improved IV chemotherapy drugs currently being developed.
Although IP chemotherapy has been recommended as a standard of care
for the first-line treatment of ovarian cancer, the basis for this recommendation has been challenged, and it has not yet become standard treatment for stage III or IV ovarian cancer.
Radiation therapy
is not effective for advanced stages because when vital organs are in the radiation field, a high dose cannot be safely delivered. Radiation therapy is then commonly avoided in such stages as the vital organs may not be able to withstand the problems associated with these ovarian cancer treatments.
. It is disproportionately deadly because it lacks any clear early detection or screening test, meaning that most cases are not diagnosed until they have reached advanced stages. More than 60% of women presenting with this cancer have stage III or stage IV cancer, when it has already spread beyond the ovaries. Ovarian cancers shed cells into the naturally occurring fluid within the abdominal cavity. These cells can then implant on other abdominal (peritoneal) structures, included the uterus
, urinary bladder
, bowel and the lining of the bowel wall omentum
forming new tumor growths before cancer is even suspected.
The five-year survival rate for all stages of ovarian cancer is 47%. For cases where a diagnosis is made early in the disease, when the cancer is still confined to the primary site, the five-year survival rate is 92.7%.
Ovarian cancer is the second most common gynecologic cancer and the deadliest in terms of absolute figure. It caused nearly 14,000 deaths in the United States
alone in 2010. While the overall five-year survival rate for all cancers combined has improved significantly: 68% for the general population diagnosed in 2001 (compared to 50% in the 1970s), ovarian cancer has a poorer outcome with a 47% survival rate (compared to 38% in the late 1970s).
These cells can implant on other abdominal (peritoneal) structures, including the uterus, urinary bladder, bowel, lining of the bowel wall (omentum) and, less frequently, to the lungs.
. In the United States
, females have a 1.4% to 2.5% (1 out of 40-60 women) lifetime chance of developing ovarian cancer. Older women are at highest risk. More than half of the deaths from ovarian cancer occur in women between 55 and 74 years of age and approximately one quarter of ovarian cancer deaths occur in women between 35 and 54 years of age.
In 2010, in the United States, it is estimated that 21,880 new cases were diagnosed and 13,850 women died of ovarian cancer. The risk increases with age and decreases with numbers of pregnancy. Lifetime risk is about 1.6%, but women with affected first-degree relatives have a 5% risk. Women with a mutated BRCA1
or BRCA2
gene carry a risk between 25% and 60% depending on the specific mutation. Ovarian cancer is the second leading cancer in women (affecting about 1/70) and the leading cause of death from gynecological cancer, and the deadliest (1% of all women die of it) It is the 5th leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women, causing an estimated 15,000 deaths in 2008. Incidence is higher in developed countries.
From 2004–2008, the median age at diagnosis for cancer of the ovary was 63 years of age. Approximately 1.2% were diagnosed under age 20; 3.5% between 20 and 34; 7.3% between 35 and 44; 19.1% between 45 and 54; 23.1% between 55 and 64; 19.7% between 65 and 74; 18.2% between 75 and 84; and 8.0% 85+ years of age. 10-year relative survival ranges from 84.1% in stage IA to 10.4% in stage IIIC.
The age-adjusted incidence rate was 12.8 per 100,000 women per year. These rates are based on cases diagnosed in 2004–2008 from 17 SEER geographic areas.
s. Reported tumor types include teratoma, cystadenocarcinoma
, and particularly granulosa cell tumor.
Malignant
Malignancy is the tendency of a medical condition, especially tumors, to become progressively worse and to potentially result in death. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis...
growth
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
arising from the ovary
Ovary
The ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ, often found in pairs as part of the vertebrate female reproductive system. Ovaries in anatomically female individuals are analogous to testes in anatomically male individuals, in that they are both gonads and endocrine glands.-Human anatomy:Ovaries...
. Symptoms are frequently very subtle early on and may include: bloating, pelvic pain
Pelvic pain
Pelvic pain is a symptom that can affect both women and men. The pelvic pain that persists for a period of 3 months or more to be considered chronic while less than this duration is considered acute. The pain may indicate the existence of poorly-understood conditions that likely represent abnormal...
, difficulty eating and frequent urination
Frequent urination
Frequent urination, or urinary frequency, is the need to urinate more often than usual. It is often, though not necessarily, associated with urinary incontinence and polyuria.A frequent need to urinate at night is called nocturia...
, and are easily confused with other illnesses.
Most (more than 90%) ovarian cancers are classified as "epithelial" and are believed to arise from the surface (epithelium
Epithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
) of the ovary. However, some evidence suggests that the fallopian tube
Fallopian tube
The Fallopian tubes, also known as oviducts, uterine tubes, and salpinges are two very fine tubes lined with ciliated epithelia, leading from the ovaries of female mammals into the uterus, via the utero-tubal junction...
could also be the source of some ovarian cancers. Since the ovaries and tubes are closely related to each other, it is thought that these fallopian cancer cells can mimic ovarian cancer. Other types may arise from the egg cells (germ cell tumor
Germ cell tumor
A germ cell tumor is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ cell tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads...
) or supporting cells. These cancers are grouped into the category of gynecologic cancer. In the United States each year 82,000 women are diagnosed with gynecologic cancer.
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer are frequently absent early on and when they exist they may be subtle. In most cases, the symptoms persist for several months before being recognized and diagnosed. Most women with ovarian cancer report one or more symptoms such as abdominal painAbdominal pain
Abdominal pain can be one of the symptoms associated with transient disorders or serious disease. Making a definitive diagnosis of the cause of abdominal pain can be difficult, because many diseases can result in this symptom. Abdominal pain is a common problem...
or discomfort, an abdominal mass, bloating
Bloating
Bloating is any abnormal general swelling, or increase in diameter of the abdominal area. As a symptom, the patient feels a full and tight abdomen, which may cause abdominal pain sometimes accompanied by increased borborygmus or more seriously the total lack of borborygmus.-Symptoms:The most common...
, back pain
Back pain
Back pain is pain felt in the back that usually originates from the muscles, nerves, bones, joints or other structures in the spine.The pain can often be divided into neck pain, upper back pain, lower back pain or tailbone pain...
, urinary urgency
Urinary urgency
Urinary urgency is a sudden, compelling urge to urinate. It is often, though not necessarily, associated with urinary incontinence, polyuria, nocturia, and interstitial cystitis. It tends to increase with age...
, constipation
Constipation
Constipation refers to bowel movements that are infrequent or hard to pass. Constipation is a common cause of painful defecation...
, tiredness and a range of other non-specific symptoms, as well as more specific symptoms such as pelvic pain
Pelvic pain
Pelvic pain is a symptom that can affect both women and men. The pelvic pain that persists for a period of 3 months or more to be considered chronic while less than this duration is considered acute. The pain may indicate the existence of poorly-understood conditions that likely represent abnormal...
, abnormal vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding refers to bleeding in females that is either a physiologic response during the non-conceptional menstrual cycle or caused by hormonal or organic problems of the reproductive system. Vaginal bleeding may occur at any age, but always needs investigation when encountered in female...
or involuntary weight loss
Weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health or physical fitness, is a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue and/or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon and other connective tissue...
. There can be a build-up of fluid (ascites
Ascites
Ascites is a gastroenterological term for an accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity.The medical condition is also known as peritoneal cavity fluid, peritoneal fluid excess, hydroperitoneum or more archaically as abdominal dropsy. Although most commonly due to cirrhosis and severe liver...
) in the abdominal cavity.
A prospective case-control study of 1,709 women visiting primary care clinics found that the combination of bloating
Bloating
Bloating is any abnormal general swelling, or increase in diameter of the abdominal area. As a symptom, the patient feels a full and tight abdomen, which may cause abdominal pain sometimes accompanied by increased borborygmus or more seriously the total lack of borborygmus.-Symptoms:The most common...
, increased abdominal size, and urinary symptoms was found in 43% of those with ovarian cancer but in only 8% of those presenting to primary care clinics. Two case-control
Case-control
A case-control study is a type of study design in epidemiology. Case-control studies are used to identify factors that may contribute to a medical condition by comparing subjects who have that condition with patients who do not have the condition but are otherwise similar .Case-control studies are...
studies, (both subject to results being inflated by spectrum bias
Spectrum bias
Initially identified in 1978, spectrum bias refers to the phenomenon that the performance of a diagnostic test may change between different clinical settings owing to changes in the patient case-mix thereby affecting the transferability of study results in clinical practice...
), have been reported. The first found that women with ovarian cancer had symptoms of increased abdominal size, bloating, urge to pass urine and pelvic pain. The smaller, second study found that women with ovarian cancer had pelvic/abdominal pain, increased abdominal size/bloating, and difficulty eating/feeling full. The second study produced a list of symptoms that was considered critical if any of the six (6) symptoms "occurred more than 12 times per month but were present for under 1 year".
Cause
In most cases, the exact cause of ovarian cancer remains unknown. The risk of developing ovarian cancer appears to be affected by several factors. Older women, and in those who have a first or second degree relative with the disease, have an increased risk. Hereditary forms of ovarian cancer can be caused by mutations in specific genesGênes
Gênes is the name of a département of the First French Empire in present Italy, named after the city of Genoa. It was formed in 1805, when Napoleon Bonaparte occupied the Republic of Genoa. Its capital was Genoa, and it was divided in the arrondissements of Genoa, Bobbio, Novi Ligure, Tortona and...
(most notably BRCA1
BRCA1
BRCA1 is a human caretaker gene that produces a protein called breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein, responsible for repairing DNA. The first evidence for the existence of the gene was provided by the King laboratory at UC Berkeley in 1990...
and BRCA2
BRCA2
BRCA2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA2 gene.BRCA2 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
, but also in genes for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
Lynch syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic condition which has a high risk of colon cancer as well as other cancers including endometrium, ovary, stomach, small intestine, hepatobiliary tract, upper urinary tract, brain, and skin...
). Infertile
Infertility
Infertility primarily refers to the biological inability of a person to contribute to conception. Infertility may also refer to the state of a woman who is unable to carry a pregnancy to full term...
women and those with a condition called endometriosis
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a gynecological medical condition in which cells from the lining of the uterus appear and flourish outside the uterine cavity, most commonly on the ovaries. The uterine cavity is lined by endometrial cells, which are under the influence of female hormones...
, those who have never been pregnant and those who use postmenopausal estrogen replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause)
Hormone replacement therapy is a system of medical treatment for surgically menopausal, perimenopausal and to a lesser extent postmenopausal women...
are at increased risk. Use of combined oral contraceptive pills is a protective factor. The more children a woman has, the lower her risk of ovarian cancer. Early age at first pregnancy, older age of final pregnancy and the use of low dose hormonal contraception
Hormonal contraception
Hormonal contraception refers to birth control methods that act on the endocrine system. Almost all methods are composed of steroid hormones, although in India one selective estrogen receptor modulator is marketed as a contraceptive. The original hormonal method—the combined oral contraceptive...
have also been shown to have a protective effect. The risk is also lower in women who have had their fallopian tubes blocked surgically (tubal ligation
Tubal ligation
Tubal ligation or tubectomy is a surgical procedure for sterilization in which a woman's fallopian tubes are clamped and blocked, or severed and sealed, either method of which prevents eggs from reaching the uterus for fertilization...
).
Analysis of 489 high-grade serous ovarian adenocarcinomas found that the p53
P53
p53 , is a tumor suppressor protein that in humans is encoded by the TP53 gene. p53 is crucial in multicellular organisms, where it regulates the cell cycle and, thus, functions as a tumor suppressor that is involved in preventing cancer...
gene was mutated in 96% of cases. Other genes commonly mutated were NF1
NF1
NF1 can refer to:* Neurofibromatosis type I, a genetic disorder* Neurofibromin 1, a protein associated with the disorder above* Nuclear factor 1, a transcription factor...
, BRCA1, BRCA2, RB1 and cyclin-dependent kinase
Cyclin-dependent kinase
thumb|350px|Schematic of the cell cycle. outer ring: I=[[Interphase]], M=[[Mitosis]]; inner ring: M=Mitosis; G1=[[G1 phase|Gap phase 1]]; S=[[S phase|Synthesis]]; G2=[[G2 phase|Gap phase 2]]...
12 (CDK12).
Hormones
The relationship between use of oral contraceptives and ovarian cancer was shown in a summary of results of 45 case-control and prospective studies. Cumulatively these studies show a protective effect for ovarian cancers. Women who used oral contraceptives for 10 years had about a 60% reduction in risk of ovarian cancer. (risk ratio .42 with statistical significant confidence intervals given the large study size, not unexpected). This means that if 250 women took oral contraceptives for 10 years, 1 ovarian cancer would be prevented. This is by far the largest epidemiological study to date on this subject (45 studies, over 20,000 women with ovarian cancer and about 80,000 controls).The ovaries contain eggs and secrete the hormones that control the reproductive cycle. Removing the ovaries and the fallopian tubes greatly reduces the amount of the hormones estrogen and progesterone circulating in your body. This can halt or slow breast and ovarian cancers that need these hormones to grow.
The link to the use of fertility medication
Fertility medication
Fertility medication are drugs which enhance reproductive fertility. For women, fertility medication is used to stimulate follicle development of the ovary...
, such as Clomiphene citrate, has been controversial. An analysis in 1991 raised the possibility that use of drugs may increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Several cohort
Cohort study
A cohort study or panel study is a form of longitudinal study used in medicine, social science, actuarial science, and ecology. It is an analysis of risk factors and follows a group of people who do not have the disease, and uses correlations to determine the absolute risk of subject contraction...
studies and case-control
Case-control
A case-control study is a type of study design in epidemiology. Case-control studies are used to identify factors that may contribute to a medical condition by comparing subjects who have that condition with patients who do not have the condition but are otherwise similar .Case-control studies are...
studies have been conducted since then without demonstrating conclusive evidence for such a link. It will remain a complex topic to study as the infertile population differs in parity
Parity (medicine)
In biology, parity is a technical term that refers to the number of times a female has given birth to a fetus.It can lead to some ambiguity for events occurring between 20 and 24 weeks, and for multiple pregnancies.-Enumeration:...
from the "normal" population.
Genetics

BRCA mutation
A BRCA mutation is a mutation in either of the genes BRCA1 and BRCA2. Harmful mutations in these genes produce a hereditary breast-ovarian cancer syndrome in affected families...
s are notably at risk. The BRCA1
BRCA1
BRCA1 is a human caretaker gene that produces a protein called breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein, responsible for repairing DNA. The first evidence for the existence of the gene was provided by the King laboratory at UC Berkeley in 1990...
and BRCA2
BRCA2
BRCA2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA2 gene.BRCA2 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
genes account for 5%–13% of ovarian cancers and certain populations (e.g. Ashkenazi Jewish women) are at a higher risk of both breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
and ovarian cancer, often at an earlier age than the general population. Patients with a personal history of breast cancer or a family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer, especially if diagnosed at a young age, may have an elevated risk, and should be tested for the "cancer gene".
In the United States, 10 to 20 percent of patients with breast cancer and patients with ovarian cancer have a first- or second-degree relative with one of these diseases. Mutations in either of two major susceptibility genes, breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1) and breast cancer susceptibility gene 2 (BRCA2), confer a lifetime risk of breast cancer of between 60 and 85 percent and a lifetime risk of ovarian cancer of between 15 and 40 percent. However, mutations in these genes account for only 2 to 3 percent of all breast cancers.
A strong family history of uterine cancer
Uterine cancer
The term uterine cancer may refer to any of several different types of cancer which occur in the uterus, namely:*Uterine sarcomas: sarcomas of the myometrium, or muscular layer of the uterus, are most commonly leiomyosarcomas.*Endometrial cancer:...
, colon cancer, or other gastrointestinal cancer
Gastrointestinal cancer
Gastrointestinal cancer refers to malignant conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, including the esophagus, stomach, biliary system, pancreas, bowels, and anus. The symptoms relate to the organ affected, and can include obstruction , abnormal bleeding, or other associated problems...
s may indicate the presence of a syndrome known as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
Lynch syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic condition which has a high risk of colon cancer as well as other cancers including endometrium, ovary, stomach, small intestine, hepatobiliary tract, upper urinary tract, brain, and skin...
(HNPCC, also known as Lynch syndrome
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
Lynch syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic condition which has a high risk of colon cancer as well as other cancers including endometrium, ovary, stomach, small intestine, hepatobiliary tract, upper urinary tract, brain, and skin...
), which confers a higher risk for developing ovarian cancer. Patients with strong genetic risk for ovarian cancer may consider the use of prophylactic, i.e. preventative, oophorectomy
Oophorectomy
Oophorectomy is the surgical removal of an ovary or ovaries. The surgery is also called ovariectomy, but this term has been traditionally used in basic science research describing the surgical removal of ovaries in laboratory animals...
the surgical removal of both ovaries, after completion of childbearing years. Prophylactic oophorectomy significantly reduces the chances of developing both breast cancer and ovarian cancer if you're at high risk. Women with BRCA gene mutations usually also have their fallopian tubes removed at the same time (salpingo-oophorectomy), since they also have an increased risk of fallopian tube cancer.
A study found that Hereditary breast-ovarian cancer syndromes (HBOC) produce higher than normal levels of breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
and ovarian cancer in genetically related families (either one individual suffered from both, or several individuals in the families suffered from one or the other disease). The hereditary factors may be proven or suspected to cause the pattern of breast and ovarian cancer occurrences in the family.
Faults in the RAD51D (either inherited or sporadically occurring) are linked to a significantly increased risk of ovarian cancer, increasing the lifetime risk of the disease roughly 6-fold to around 1 in 11, compared to 1 in 70 for the general population. However, such faults are rare and are thought to contribute to fewer than one in 100 cases of the diseas, accounting for around 40-60 women per year in the UK.
Other
A Swedish study, which followed more than 61,000 women for 13 years, has found a significant link between milk consumption and ovarian cancer. According to the BBC, "[Researchers] found that milk had the strongest link with ovarian cancer—those women who drank two or more glasses a day were at double the risk of those who did not consume it at all, or only in small amounts." Recent studies have shown that women in sunnier countries have a lower rate of ovarian cancer, which may have some kind of connection with exposure to Vitamin DVitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids. In humans, vitamin D is unique both because it functions as a prohormone and because the body can synthesize it when sun exposure is adequate ....
.
Other factors that have been investigated, such as talc
Talc
Talc is a mineral composed of hydrated magnesium silicate with the chemical formula H2Mg34 or Mg3Si4O102. In loose form, it is the widely-used substance known as talcum powder. It occurs as foliated to fibrous masses, its crystals being so rare as to be almost unknown...
use, asbestos
Asbestos
Asbestos is a set of six naturally occurring silicate minerals used commercially for their desirable physical properties. They all have in common their eponymous, asbestiform habit: long, thin fibrous crystals...
exposure, high dietary fat content, and childhood mumps
Mumps
Mumps is a viral disease of the human species, caused by the mumps virus. Before the development of vaccination and the introduction of a vaccine, it was a common childhood disease worldwide...
infection, are controversial and have not been definitively proven; moreover, such risk factors may in some cases be more likely to be correlated with cancer in individuals with specific gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
tic makeups.
Risk factors
Women who have had children are less likely to develop ovarian cancer than women who have not, and breastfeeding may also reduce the risk of certain types of ovarian cancer. Tubal ligationTubal ligation
Tubal ligation or tubectomy is a surgical procedure for sterilization in which a woman's fallopian tubes are clamped and blocked, or severed and sealed, either method of which prevents eggs from reaching the uterus for fertilization...
and hysterectomy
Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus, usually performed by a gynecologist. Hysterectomy may be total or partial...
reduce the risk and removal of both tubes and ovaries (bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy) dramatically reduces the risk of not only ovarian cancer but breast cancer also. A hysterectomy that does not include the removal of the ovaries has a one-third reduced risk of developing ovarian cancer, it also has no higher risk of developing other types of cancer, heart disease or hip fractures, researchers from the University of California at San Francisco revealed in the journal Archives of Internal Medicine
Archives of Internal Medicine
The Archives of Internal Medicine is a peer-reviewed medical journal published twice a month by the American Medical Association. The Archives of Internal Medicine was established in 1908 and covers all aspects of internal medicine, including cardiovascular disease, geriatrics, infectious disease,...
.
A study in The Lancet
The Lancet
The Lancet is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal. It is one of the world's best known, oldest, and most respected general medical journals...
suggests that tubal ligation can reduce the risk of hereditary ovarian cancer by 72 per cent in women who carry the BRCA1 gene.
The use of oral contraceptives (birth control pills) for five years or more decreases the risk of ovarian cancer in later life by 50%.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of ovarian cancer starts with a physical examination (including a pelvic examinationPelvic examination
A pelvic examination, also pelvic exam, is a physical examination of the female pelvic organs.Broadly, it can be divided into the external examination and internal examination.It is also called "Bimanual Exam" & "Manual Uterine Palpation"....
), a blood test (for CA-125
CA-125
CA-125 also known as mucin 16 or MUC16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MUC16 gene. MUC16 is a member of the mucin family glycoproteins...
and sometimes other markers), and transvaginal ultrasound. The diagnosis must be confirmed with surgery to inspect the abdominal cavity
Abdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is the body cavity of the human body that holds the bulk of the viscera. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm , and its oblique floor is the pelvic inlet...
, take biopsies (tissue samples for microscopic analysis
Histopathology
Histopathology refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease...
) and look for cancer cells in the abdominal fluid.
Ovarian cancer at its early stages(I/II) is difficult to diagnose until it spreads and advances to later stages (III/IV). This is because most symptoms are non-specific and thus of little use in diagnosis. The serum BHCG level should be measured in any female in whom pregnancy is a possibility. In addition, serum alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AFP gene....
(AFP) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) should be measured in young girls and adolescents with suspected ovarian tumors because the younger the patient, the greater the likelihood of a malignant germ cell tumor.
When an ovarian malignancy is included in the list of diagnostic possibilities, a limited number of laboratory tests are indicated. A complete blood count (CBC) and serum electrolyte test should be obtained in all patients. A blood test called CA-125
CA-125
CA-125 also known as mucin 16 or MUC16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MUC16 gene. MUC16 is a member of the mucin family glycoproteins...
is useful in differential diagnosis and in follow up of the disease, but it by itself has not been shown to be an effective method to screen for early-stage ovarian cancer due to its unacceptable low sensitivity and specificity.
The new test approved by the FDA in 2011, OVA1 improves ovarian cancer detection over CA125 blood test and clinical assessment. An article published in the June 2011 issue of Obstetrics & Gynecology showed that adding OVA1 to a physician's preoperative assessment of a woman's ovarian mass would identify more ovarian and ovarian related cancers, than a physician's preoperative assessment alone. OVA1 is intended only for women, 18 years and older, who are already selected for surgery because of their pelvic mass. It is not intended for ovarian cancer screening or for a definitive diagnosis of ovarian cancer. OVA1 was developed in conjunction with researchers at the Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University
The Johns Hopkins University, commonly referred to as Johns Hopkins, JHU, or simply Hopkins, is a private research university based in Baltimore, Maryland, United States...
in Baltimore.
Current research is looking at ways to combine tumor markers proteomics
Proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins, particularly their structures and functions. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, as they are the main components of the physiological metabolic pathways of cells. The term "proteomics" was first coined in 1997 to make an analogy with...
along with other indicators of disease (i.e. radiology and/or symptoms) to improve accuracy. The challenge in such an approach is that the disparate prevalence of ovarian cancer means that even testing with very high sensitivity and specificity will still lead to a number of false positive results (i.e. performing surgical procedures in which cancer is not found intra-operatively). However, the contributions of proteomics
Proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins, particularly their structures and functions. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, as they are the main components of the physiological metabolic pathways of cells. The term "proteomics" was first coined in 1997 to make an analogy with...
are still in the early stages and require further refining. Current studies on proteomics mark the beginning of a paradigm shift towards individually tailored therapy.
A pelvic examination and imaging including CT scan and trans-vaginal ultrasound are essential. Physical examination may reveal increased abdominal girth and/or ascites
Ascites
Ascites is a gastroenterological term for an accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity.The medical condition is also known as peritoneal cavity fluid, peritoneal fluid excess, hydroperitoneum or more archaically as abdominal dropsy. Although most commonly due to cirrhosis and severe liver...
(fluid within the abdominal cavity). Pelvic examination may reveal an ovarian or abdominal mass. The pelvic examination can include a Rectovaginal component for better palpation of the ovaries. For very young patients, magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
may be preferred to rectal and vaginal examination.
To definitively diagnose ovarian cancer, a surgical procedure to take a look into the abdomen is required. This can be an open procedure (laparotomy
Laparotomy
A laparotomy is a surgical procedure involving a large incision through the abdominal wall to gain access into the abdominal cavity. It is also known as coeliotomy.- Terminology :...
, incision through the abdominal wall) or keyhole surgery (laparoscopy
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis through small incisions with the aid of a camera...
). During this procedure, suspicious areas will be removed and sent for microscopic analysis
Histopathology
Histopathology refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease...
. Fluid from the abdominal cavity
Abdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is the body cavity of the human body that holds the bulk of the viscera. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm , and its oblique floor is the pelvic inlet...
can also be analysed for cancerous cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
. If there is cancer, this procedure can also determine its spread (which is a form of tumor staging).
Classification

Histology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining cells and tissues commonly by sectioning and staining; followed by examination under a light microscope or electron microscope...
of the tumor, obtained in a pathology
Pathology
Pathology is the precise study and diagnosis of disease. The word pathology is from Ancient Greek , pathos, "feeling, suffering"; and , -logia, "the study of". Pathologization, to pathologize, refers to the process of defining a condition or behavior as pathological, e.g. pathological gambling....
report. Histology dictates many aspects of clinical treatment, management, and prognosis
Prognosis
Prognosis is a medical term to describe the likely outcome of an illness.When applied to large statistical populations, prognostic estimates can be very accurate: for example the statement "45% of patients with severe septic shock will die within 28 days" can be made with some confidence, because...
.
- Surface epithelial-stromal tumour, also known as ovarian epithelial carcinoma, is the most common type of ovarian cancer. It includes serous tumourSerous tumourSerous tumours are part of the surface epithelial-stromal tumour group of ovarian neoplasms.They are common neoplasms with a strong tendency to bilaterality, and they account for 50% of all ovarian tumours....
, endometrioid tumorEndometrioid tumorEndometrioid tumors are a class of tumor characterized by a resemblance to endometrium/ endometrial carcinoma, and over a third of cases have focal squamous differentiation.-Ovary:...
and mucinous cystadenocarcinomaCystadenocarcinomaCystadenocarcinoma is a malignant form of a cystadenoma and is a malignant neoplasm derived from glandular epithelium, in which cystic accumulations of retained secretions are formed. The neoplastic cells manifest varying degrees of anaplasia and invasiveness, and local extension and metastases occur...
. - Sex cord-stromal tumorSex cord-stromal tumourSex cord-gonadal stromal tumour is a group of tumours of sex cord-derived tissues of the ovary and testis. In humans, this group accounts for 8% of ovarian cancers and under 5% of testicular cancers. Their diagnosis is histological: only a biopsy of the tumour can make an exact diagnosis...
, including estrogenEstrogenEstrogens , oestrogens , or œstrogens, are a group of compounds named for their importance in the estrous cycle of humans and other animals. They are the primary female sex hormones. Natural estrogens are steroid hormones, while some synthetic ones are non-steroidal...
-producing granulosa cell tumor and virilizing Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor or arrhenoblastoma, accounts for 8% of ovarian cancers. - Germ cell tumorGerm cell tumorA germ cell tumor is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ cell tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads...
accounts for approximately 30% of ovarian tumors but only 5% of ovarian cancers, because most germ cell tumors are teratomaTeratomaA teratoma is an encapsulated tumor with tissue or organ components resembling normal derivatives of all three germ layers. There are rare occasions when not all three germ layers are identifiable...
s and most teratomas are benign (see TeratomaTeratomaA teratoma is an encapsulated tumor with tissue or organ components resembling normal derivatives of all three germ layers. There are rare occasions when not all three germ layers are identifiable...
). Germ cell tumor tends to occur in young women and girls. The prognosis depends on the specific histology of germ cell tumor, but overall is favorable. - Mixed tumors, containing elements of more than one of the above classes of tumor histology.
According to SEER
Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results
The Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program of the National Cancer Institute is a source of information on cancer incidence and survival in the United States.-The Program:...
, types of ovarian cancers in women age 20+ are as follows:
| Percent of ovarian cancers in women age 20+ |
Histology Histology Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining cells and tissues commonly by sectioning and staining; followed by examination under a light microscope or electron microscope... |
5 year RSR |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 89.7 | Surface epithelial-stromal tumor Surface epithelial-stromal tumor Surface epithelial-stromal tumors are a class of ovarian neoplasms that may be benign or malignant. Neoplasms in this group are thought to be derived from the ovarian surface epithelium or from ectopic endometrial or Fallopian tube tissue. This group of tumors accounts for the majority of all... (Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma is a cancer of an epithelium that originates in glandular tissue. Epithelial tissue includes, but is not limited to, the surface layer of skin, glands and a variety of other tissue that lines the cavities and organs of the body. Epithelium can be derived embryologically from... ) |
54.4 | |
| 26.4 | Papillary serous cystadenocarcinoma Papillary serous cystadenocarcinoma Papillary serous cystadenocarcinomas are the most common form of malignant ovarian cancer making up 26 percent of ovarian tumours in women aged over 20 in the United States.... |
21.0 | |
| 15.9 | "Borderline" adenocarcinoma (underestimated b/c short data collection interval) |
98.2 | |
| 12.6 | Adenocarcinoma, not otherwise specified | 18.3 | |
| 9.8 | Endometrioid tumor Endometrioid tumor Endometrioid tumors are a class of tumor characterized by a resemblance to endometrium/ endometrial carcinoma, and over a third of cases have focal squamous differentiation.-Ovary:... |
70.9 | |
| 5.8 | Serous cystadenocarcinoma Serous cystadenocarcinoma Serous cystadenocarcinoma is a type of tumor in the cystadenocarcinoma grouping.Most commonly the primary site of serous cystadenocarcinoma is the ovary. Rare occurrence in the pancreas has been reported, although it is an atypical location with the majority of microcystic pancreatic masses... |
44.2 | |
| 5.5 | Papillary Papilloma Papilloma refers to a benign epithelial tumor growing exophytically in finger-like fronds. In this context papilla refers to the projection created by the tumor, not a tumor on an already existing papilla . When used without context, it frequently refers to infections caused by human... |
21.0 | |
| 4.2 | Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma is a type of tumor in the cystadenocarcinoma grouping.It can occur in the breast.... |
77.7 | |
| 4.0 | Clear-cell ovarian tumor | 61.5 | |
| 3.4 | Mucinous adenocarcinoma | 49.1 | |
| 1.3 | Cystadenocarcinoma Cystadenocarcinoma Cystadenocarcinoma is a malignant form of a cystadenoma and is a malignant neoplasm derived from glandular epithelium, in which cystic accumulations of retained secretions are formed. The neoplastic cells manifest varying degrees of anaplasia and invasiveness, and local extension and metastases occur... |
50.7 | |
| 5.5 | Carcinoma Carcinoma Carcinoma is the medical term for the most common type of cancer occurring in humans. Put simply, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that generally arises from cells originating in the endodermal or ectodermal germ layer during... |
||
| 4.1 | Carcinoma not otherwise specified | 26.8 | |
| 1.1 | Sex cord-stromal tumour Sex cord-stromal tumour Sex cord-gonadal stromal tumour is a group of tumours of sex cord-derived tissues of the ovary and testis. In humans, this group accounts for 8% of ovarian cancers and under 5% of testicular cancers. Their diagnosis is histological: only a biopsy of the tumour can make an exact diagnosis... |
87.8 | |
| 0.3 | Other carcinomas, specified | 37.3 | |
| 1.7 | Mullerian tumor | 29.8 | |
| 1.5 | Germ cell tumor Germ cell tumor A germ cell tumor is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ cell tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads... |
91.0 | |
| 0.8 | Teratoma Teratoma A teratoma is an encapsulated tumor with tissue or organ components resembling normal derivatives of all three germ layers. There are rare occasions when not all three germ layers are identifiable... |
89.1 | |
| 0.5 | Dysgerminoma Dysgerminoma A dysgerminoma is a type of germ cell tumor; it usually is malignant and usually occurs in the ovary.A tumor of the identical histology but not occurring in the ovary may be described by an alternate name: seminoma in the testis or germinoma in the central nervous system or other parts of the... |
96.8 | |
| 0.3 | Other, specified | 85.1 | |
| 0.6 | Not otherwise specified | 23.0 | |
| 0.5 | Epidermoid (Squamous cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma , occasionally rendered as "squamous-cell carcinoma", is a histologically distinct form of cancer. It arises from the uncontrolled multiplication of malignant cells deriving from epithelium, or showing particular cytological or tissue architectural characteristics of... ) |
51.3 | |
| 0.2 | Brenner tumor | 67.9 | |
| 0.2 | Other, specified | 71.7 | |
Ovarian cancer can also be a secondary cancer, the result of metastasis
Metastasis
Metastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
from a primary cancer elsewhere in the body. 7% of ovarian cancers are due to metastases while the rest are primary cancers. Common primary cancers are breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
and gastrointestinal cancer
Gastrointestinal cancer
Gastrointestinal cancer refers to malignant conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, including the esophagus, stomach, biliary system, pancreas, bowels, and anus. The symptoms relate to the organ affected, and can include obstruction , abnormal bleeding, or other associated problems...
(a common mistake is to name all peritoneal metastases from any gastrointestinal cancer as Krukenberg cancer, but this is only the case if it originates from primary gastric cancer). Surface epithelial-stromal tumor can originate in the peritoneum
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom — it covers most of the intra-abdominal organs — in amniotes and some invertebrates...
(the lining of the abdominal cavity), in which case the ovarian cancer is secondary to primary peritoneal cancer
Primary peritoneal cancer
Primary peritoneal cancer or carcinoma is also known as: serous surface papillary carcinoma, primary peritoneal carcinoma, extra-ovarian serous carcinoma, primary serous papillary carcinoma, psammomacarcinoma. It was historically classified under "carcinoma of unknown primary"...
, but treatment is basically the same as for primary surface epithelial-stromal tumor involving the peritoneum.
Staging
Ovarian cancer staging is by the FIGOInternational Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
The International Federation of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, usually just FIGO as the acronym of its French name Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique, is a worldwide NGO organisation representing obstetricians and gynaecologists in over one hundred territories...
staging system and uses information obtained after surgery, which can include a total abdominal hysterectomy
Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus, usually performed by a gynecologist. Hysterectomy may be total or partial...
, removal of (usually) both ovaries and fallopian tubes, (usually) the omentum, and pelvic (peritoneal) washings for cytopathology. The AJCC stage is the same as the FIGO stage.
The AJCC staging system describes the extent of the primary Tumor (T), the absence or presence of metastasis
Metastasis
Metastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
to nearby lymph Nodes (N), and the absence or presence of distant Metastasis (M).
- Stage I - limited to one or both ovaries
- IA - involves one ovary; capsule intact; no tumor on ovarian surface; no malignant cells in ascites or peritoneal washings
- IB - involves both ovaries; capsule intact; no tumor on ovarian surface; negative washings
- IC - tumor limited to ovaries with any of the following: capsule ruptured, tumor on ovarian surface, positive washings
- Stage II - pelvic extension or implants
- IIA - extension or implants onto uterus or fallopian tube; negative washings
- IIB - extension or implants onto other pelvic structures; negative washings
- IIC - pelvic extension or implants with positive peritoneal washings
- Stage III - microscopic peritoneal implants outside of the pelvis; or limited to the pelvis with extension to the small bowel or omentum
- IIIA - microscopic peritoneal metastases beyond pelvis
- IIIB - macroscopic peritoneal metastases beyond pelvis less than 2 cm in size
- IIIC - peritoneal metastases beyond pelvis > 2 cm or lymph node metastases
- Stage IV - distant metastases to the liver or outside the peritoneal cavity
Para-aortic lymph node metastases are considered regional lymph nodes (Stage IIIC). As there is only one para-aortic lymph node intervening before the thoracic duct on the right side of the body, the ovarian cancer can rapidly spread to distant sites such as the lung.
The AJCC/TNM staging system includes three categories for ovarian cancer, T, N and M. The T category contains three other subcategories, T1, T2 and T3, each of them being classified according to the place where the tumor has developed (in one or both ovaries, inside or outside the ovary). The T1 category of ovarian cancer describes ovarian tumors that are confined to the ovaries, and which may affect one or both of them. The sub-subcategory T1a is used to stage cancer that is found in only one ovary, which has left the capsule intact and which cannot be found in the fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
taken from the pelvis
Pelvis
In human anatomy, the pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the lower limbs .The pelvis includes several structures:...
. Cancer that has not affected the capsule, is confined to the inside of the ovaries and cannot be found in the fluid taken from the pelvis but has affected both ovaries is staged as T1b. T1c category describes a type of tumor that can affect one or both ovaries, and which has grown through the capsule of an ovary or it is present in the fluid taken from the pelvis. T2 is a more advanced stage of cancer. In this case, the tumor has grown in one or both ovaries and is spread to the uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
, fallopian tubes or other pelvic tissues. Stage T2a is used to describe a cancerous tumor that has spread to the uterus or the fallopian tubes (or both) but which is not present in the fluid taken from the pelvis. Stages T2b and T2c indicate cancer that metastasized to other pelvic tissues than the uterus and fallopian tubes and which cannot be seen in the fluid taken from the pelvis, respectively tumors that spread to any of the pelvic tissues (including uterus and fallopian tubes) but which can also be found in the fluid taken from the pelvis. T3 is the stage used to describe cancer that has spread to the peritoneum
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or the coelom — it covers most of the intra-abdominal organs — in amniotes and some invertebrates...
. This stage provides information on the size of the metastatic tumors (tumors that are located in other areas of the body, but are caused by ovarian cancer). These tumors can be very small, visible only under the microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
(T3a), visible but not larger than 2 centimeters (T3b) and bigger than 2 centimeters (T3c).
This staging system also uses N categories to describe cancers that have or not spread to nearby lymph nodes. There are only two N categories, N0 which indicates that the cancerous tumors have not affected the lymph nodes, and N1 which indicates the involvement of lymph nodes close to the tumor.
The M categories in the AJCC/TNM staging system provide information on whether the ovarian cancer has metastasized to distant organs such as liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
or lungs. M0 indicates that the cancer did not spread to distant organs and M1 category is used for cancer that has spread to other organs of the body.
The AJCC/TNM staging system also contains a Tx and a Nx sub-category which indicates that the extent of the tumor cannot be described because of insufficient data, respectively the involvement of the lymph nodes cannot be described because of the same reason.
The ovarian cancer stages are made up by combining the TNM categories in the following manner:
- Stage I: T1+N0+M0
- IA: T1a+N0+M0
- IB: T1b+N0+M0
- IC: T1c+N0+M0
- Stage II: T2+N0+M0
- IIa: T2a+N0+M0
- IIB: T2b+N0+M0
- IIC: T2c+N0+M0
- Stage III: T3+ N0+M0
- IIIA: T3a+ N0+M0
- IIIB: T3b+ N0+M0
- IIIC: T3c+ N0+M0 or Any T+N1+M0
- Stage IV: Any T+ Any N+M1
Ovarian cancer, as well as any other type of cancer, is also graded, apart from staged. The histologic grade of a tumor measures how abnormal or malignant its cells look under the microscope. There are four grades indicating the likelihood of the cancer to spread and the higher the grade, the more likely for this to occur. Grade 0 is used to describe non-invasive tumors. Grade 0 cancers are also referred to as borderline tumors. Grade 1 tumors have cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
that are well differentiated (look very similar to the normal tissue) and are the ones with the best prognosis. Grade 2 tumors are also called moderately well differentiated and they are made up by cells that resemble the normal tissue. Grade 3 tumors have the worst prognosis and their cells are abnormal, referred to as poorly differentiated.
Screening
Routine screening of women for ovarian cancer is not recommended by any professional society - this includes the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, the American Cancer Society, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. This is because no trial has shown improved survival for women undergoing screening. Screening for any type of cancer must be accurate and reliable - it needs to accurately detect the disease and it must not give false positive results in people who do not have cancer. As yet there is no technique for ovarian screening that has been shown to fulfil these criteria. However, in some countries such as the UK, women who are likely to have an increased risk of ovarian cancer (for example if they have a family history of the disease) can be offered individual screening through their doctors, although this will not necessarily detect the disease at an early stage.Researchers are assessing different ways to screen for ovarian cancer. Screening tests that could potentially be used alone or in combination for routine screening include the CA-125
CA-125
CA-125 also known as mucin 16 or MUC16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MUC16 gene. MUC16 is a member of the mucin family glycoproteins...
marker and transvaginal ultrasound. Doctors can measure the levels of the CA-125 protein in a woman’s blood - high levels could be a sign of ovarian cancer, but this is not always the case. And not all women with ovarian cancer have high CA-125 levels. Transvaginal ultrasound involves using an ultrasound probe to scan the ovaries from inside the vagina, giving a clearer image than scanning the abdomen. The UK Collaborative Trial of Ovarian Cancer Screening is testing a screening technique that combines CA-125 blood tests with transvaginal ultrasound.
The purpose of screening is to diagnose ovarian cancer at an early stage, when it is more likely to be treated successfully. However, the development of the disease is not fully understood, and it has been argued that early-stage cancers may not always develop into late-stage disease. With any screening technique there are risks and benefits that need to be carefully considered, and health authorities need to assess these before introducing any ovarian cancer screening programmes.
The goal of ovarian cancer screening is to detect the disease at stage I. Several large studies are ongoing, but none have identified an effective technique. In 2009, however, early results from the UK Collaborative Trial of Ovarian Cancer Screening (UKCTOCS) showed that a technique combining annual CA-125 tests with ultrasound imaging did help to detect the disease at an early stage. However, it's not yet clear if this approach could actually help to save lives - the full results of the trial will be published in 2015.
Management
Treatment usually involves chemotherapyChemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
and surgery, and sometimes radiotherapy.
Surgical treatment may be sufficient for malignant tumors that are well-differentiated and confined to the ovary. Addition of chemotherapy may be required for more aggressive tumors that are confined to the ovary. For patients with advanced disease a combination of surgical reduction with a combination chemotherapy regimen is standard. Borderline tumors, even following spread outside of the ovary, are managed well with surgery, and chemotherapy is not seen as useful.
Surgery
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
is the preferred treatment and is frequently necessary to obtain a tissue specimen for differential diagnosis
Medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis refers both to the process of attempting to determine or identify a possible disease or disorder , and to the opinion reached by this process...
via its histology
Histology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining cells and tissues commonly by sectioning and staining; followed by examination under a light microscope or electron microscope...
. Surgery performed by a specialist in gynecologic oncology
Gynecologic oncology
Gynecologic oncology is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on cancers of the female reproductive system, including ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, endometrial cancer, cervical cancer, and vulvar cancer...
usually results in an improved result. Improved survival is attributed to more accurate staging of the disease and a higher rate of aggressive surgical excision of tumor in the abdomen by gynecologic oncologists as opposed to general gynecologists and general surgeons.
The type of surgery depends upon how widespread the cancer is when diagnosed (the cancer stage), as well as the presumed type and grade of cancer. The surgeon may remove one (unilateral oophorectomy) or both ovaries (bilateral oophorectomy), the fallopian tubes (salpingectomy), and the uterus (hysterectomy). For some very early tumors (stage 1, low grade or low-risk disease), only the involved ovary and fallopian tube will be removed (called a "unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy," USO), especially in young females who wish to preserve their fertility.
In advanced malignancy, where complete resection is not feasible, as much tumor as possible is removed (debulking surgery). In cases where this type of surgery is successful (i.e. < 1 cm in diameter of tumor is left behind ["optimal debulking"]), the prognosis is improved compared to patients where large tumor masses (> 1 cm in diameter) are left behind. Minimally invasive surgical techniques may facilitate the safe removal of very large (greater than 10 cm) tumors with fewer complications of surgery.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
has been a general standard of care
Standard of care
In tort law, the standard of care is the degree of prudence and caution required of an individual who is under a duty of care.The requirements of the standard are closely dependent on circumstances. Whether the standard of care has been breached is determined by the trier of fact, and is usually...
for ovarian cancer for decades, although with highly variable protocols.
Chemotherapy is used after surgery to treat any residual disease, if appropriate. This depends on the histology
Histology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining cells and tissues commonly by sectioning and staining; followed by examination under a light microscope or electron microscope...
of the tumor; some kinds of tumor (particularly teratoma
Teratoma
A teratoma is an encapsulated tumor with tissue or organ components resembling normal derivatives of all three germ layers. There are rare occasions when not all three germ layers are identifiable...
) are not sensitive to chemotherapy. In some cases, there may be reason to perform chemotherapy first, followed by surgery.
For patients with stage IIIC epithelial ovarian adenocarcinomas who have undergone successful optimal debulking, a recent clinical trial demonstrated that median survival time is significantly longer for patient receiving intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy.
Patients in this clinical trial reported less compliance with IP chemotherapy and fewer than half of the patients received all six cycles of IP chemotherapy. Despite this high "drop-out" rate, the group as a whole (including the patients that didn't complete IP chemotherapy treatment) survived longer on average than patients who received intravenous chemotherapy alone.
Some specialists believe the toxicities and other complications of IP chemotherapy will be unnecessary with improved IV chemotherapy drugs currently being developed.
Although IP chemotherapy has been recommended as a standard of care
Standard of care
In tort law, the standard of care is the degree of prudence and caution required of an individual who is under a duty of care.The requirements of the standard are closely dependent on circumstances. Whether the standard of care has been breached is determined by the trier of fact, and is usually...
for the first-line treatment of ovarian cancer, the basis for this recommendation has been challenged, and it has not yet become standard treatment for stage III or IV ovarian cancer.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy , radiation oncology, or radiotherapy , sometimes abbreviated to XRT or DXT, is the medical use of ionizing radiation, generally as part of cancer treatment to control malignant cells.Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control...
is not effective for advanced stages because when vital organs are in the radiation field, a high dose cannot be safely delivered. Radiation therapy is then commonly avoided in such stages as the vital organs may not be able to withstand the problems associated with these ovarian cancer treatments.
Prognosis
Ovarian cancer usually has a poor prognosisPrognosis
Prognosis is a medical term to describe the likely outcome of an illness.When applied to large statistical populations, prognostic estimates can be very accurate: for example the statement "45% of patients with severe septic shock will die within 28 days" can be made with some confidence, because...
. It is disproportionately deadly because it lacks any clear early detection or screening test, meaning that most cases are not diagnosed until they have reached advanced stages. More than 60% of women presenting with this cancer have stage III or stage IV cancer, when it has already spread beyond the ovaries. Ovarian cancers shed cells into the naturally occurring fluid within the abdominal cavity. These cells can then implant on other abdominal (peritoneal) structures, included the uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
, urinary bladder
Urinary bladder
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor...
, bowel and the lining of the bowel wall omentum
Omentum
Omentum may refer to:* greater omentum* lesser omentum...
forming new tumor growths before cancer is even suspected.
The five-year survival rate for all stages of ovarian cancer is 47%. For cases where a diagnosis is made early in the disease, when the cancer is still confined to the primary site, the five-year survival rate is 92.7%.
Ovarian cancer is the second most common gynecologic cancer and the deadliest in terms of absolute figure. It caused nearly 14,000 deaths in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
alone in 2010. While the overall five-year survival rate for all cancers combined has improved significantly: 68% for the general population diagnosed in 2001 (compared to 50% in the 1970s), ovarian cancer has a poorer outcome with a 47% survival rate (compared to 38% in the late 1970s).
Complications
- Spread of the cancer to other organs
- Progressive function loss of various organs
- AscitesAscitesAscites is a gastroenterological term for an accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity.The medical condition is also known as peritoneal cavity fluid, peritoneal fluid excess, hydroperitoneum or more archaically as abdominal dropsy. Although most commonly due to cirrhosis and severe liver...
(fluid in the abdomen) - Intestinal obstructions
These cells can implant on other abdominal (peritoneal) structures, including the uterus, urinary bladder, bowel, lining of the bowel wall (omentum) and, less frequently, to the lungs.
Epidemiology
The disease is more common in industrialized nations, with the exception of JapanJapan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
. In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, females have a 1.4% to 2.5% (1 out of 40-60 women) lifetime chance of developing ovarian cancer. Older women are at highest risk. More than half of the deaths from ovarian cancer occur in women between 55 and 74 years of age and approximately one quarter of ovarian cancer deaths occur in women between 35 and 54 years of age.
In 2010, in the United States, it is estimated that 21,880 new cases were diagnosed and 13,850 women died of ovarian cancer. The risk increases with age and decreases with numbers of pregnancy. Lifetime risk is about 1.6%, but women with affected first-degree relatives have a 5% risk. Women with a mutated BRCA1
BRCA1
BRCA1 is a human caretaker gene that produces a protein called breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein, responsible for repairing DNA. The first evidence for the existence of the gene was provided by the King laboratory at UC Berkeley in 1990...
or BRCA2
BRCA2
BRCA2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA2 gene.BRCA2 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
gene carry a risk between 25% and 60% depending on the specific mutation. Ovarian cancer is the second leading cancer in women (affecting about 1/70) and the leading cause of death from gynecological cancer, and the deadliest (1% of all women die of it) It is the 5th leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women, causing an estimated 15,000 deaths in 2008. Incidence is higher in developed countries.
From 2004–2008, the median age at diagnosis for cancer of the ovary was 63 years of age. Approximately 1.2% were diagnosed under age 20; 3.5% between 20 and 34; 7.3% between 35 and 44; 19.1% between 45 and 54; 23.1% between 55 and 64; 19.7% between 65 and 74; 18.2% between 75 and 84; and 8.0% 85+ years of age. 10-year relative survival ranges from 84.1% in stage IA to 10.4% in stage IIIC.
The age-adjusted incidence rate was 12.8 per 100,000 women per year. These rates are based on cases diagnosed in 2004–2008 from 17 SEER geographic areas.
In other animals
Ovarian tumors have been reported in mareMare
Female horses are called mares.Mare is the Latin word for "sea".The word may also refer to:-People:* Ahmed Marzooq, also known as Mare, a footballer and Secretary General of Maldives Olympic Committee* Mare Winningham, American actress and singer...
s. Reported tumor types include teratoma, cystadenocarcinoma
Cystadenocarcinoma
Cystadenocarcinoma is a malignant form of a cystadenoma and is a malignant neoplasm derived from glandular epithelium, in which cystic accumulations of retained secretions are formed. The neoplastic cells manifest varying degrees of anaplasia and invasiveness, and local extension and metastases occur...
, and particularly granulosa cell tumor.
See also
- List of women with ovarian cancer
- Germ cell tumorGerm cell tumorA germ cell tumor is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ cell tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads...
- Desmoplastic small round cell tumorDesmoplastic small round cell tumorDesmoplastic small-round-cell tumor is classified as a soft tissue sarcoma. It is an aggressive and rare tumor that primarily occurs as masses in the abdomen. Other areas affected may include the lymph nodes, the lining of the abdomen, diaphragm, spleen, liver, chest wall, skull, spinal cord, large...
- Ovarian cystOvarian cystAn ovarian cyst is any collection of fluid, surrounded by a very thin wall, within an ovary. Any ovarian follicle that is larger than about two centimeters is termed an ovarian cyst. An ovarian cyst can be as small as a pea, or larger than an orange....
External links
- Ovarian cancer at the Open Directory ProjectOpen Directory ProjectThe Open Directory Project , also known as Dmoz , is a multilingual open content directory of World Wide Web links. It is owned by Netscape but it is constructed and maintained by a community of volunteer editors.ODP uses a hierarchical ontology scheme for organizing site listings...
- Ovarian Cancer at American Cancer SocietyAmerican Cancer SocietyThe American Cancer Society is the "nationwide community-based voluntary health organization" dedicated, in their own words, "to eliminating cancer as a major health problem by preventing cancer, saving lives, and diminishing suffering from cancer, through research, education, advocacy, and...
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on BRCA1 and BRCA2 Hereditary Breast/Ovarian Cancer
- WebMD: Ovarian Cancer Health Center
- Medical Encyclopedia MayoClinc: Ovarian Cancer
- Interactive Health Tutorials Medline Plus: Ovarian cancer Using animated graphics and you can also listen to the tutorial
- UK statistics for ovarian cancer
- Patient information about ovarian cancer from Cancer Research UK

