
Orders of magnitude (time)
Encyclopedia
Seconds
| Factor (s Second The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock.... ) |
Multiple | Symbol | Definition | Comparative examples & common units | Orders of magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−44 | 5.4×10-20 ys = 5.4×10-44 s: One Planck time Planck time In physics, the Planck time, , is the unit of time in the system of natural units known as Planck units. It is the time required for light to travel, in a vacuum, a distance of 1 Planck length... tP = 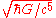 ≈ 5.4×10-44 s, the time required for light to travel one Planck length, is the briefest physically meaningful span of time. It is the unit of time in the natural units ≈ 5.4×10-44 s, the time required for light to travel one Planck length, is the briefest physically meaningful span of time. It is the unit of time in the natural unitsNatural units In physics, natural units are physical units of measurement based only on universal physical constants. For example the elementary charge e is a natural unit of electric charge, or the speed of light c is a natural unit of speed... system known as Planck units Planck units In physics, Planck units are physical units of measurement defined exclusively in terms of five universal physical constants listed below, in such a manner that these five physical constants take on the numerical value of 1 when expressed in terms of these units. Planck units elegantly simplify... . |
10−20 ys, 10−19 ys (10−44 s, 10−43 s) | |||
| 10−24 | 1 yoctosecond | ys | Yoctosecond, (yocto- + second), is one septillionth (short scale Long and short scales The long and short scales are two of several different large-number naming systems used throughout the world for integer powers of ten. Many countries, including most in continental Europe, use the long scale whereas most English-speaking countries use the short scale... ) of a second. |
0.3 ys: mean life of the W and Z bosons. 0.5 ys: time for top quark Top quark The top quark, also known as the t quark or truth quark, is an elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Like all quarks, the top quark is an elementary fermion with spin-, and experiences all four fundamental interactions: gravitation, electromagnetism, weak interactions, and... decay Particle decay Particle decay is the spontaneous process of one elementary particle transforming into other elementary particles. During this process, an elementary particle becomes a different particle with less mass and an intermediate particle such as W boson in muon decay. The intermediate particle then... , according to the Standard Model Standard Model The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, which mediate the dynamics of the known subatomic particles. Developed throughout the mid to late 20th century, the current formulation was finalized in the mid 1970s upon... . 1 ys: time taken for a quark to emit a gluon Gluon Gluons are elementary particles which act as the exchange particles for the color force between quarks, analogous to the exchange of photons in the electromagnetic force between two charged particles.... . 23 ys: half-life Half-life Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to... of 7H Isotopes of hydrogen Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes, sometimes denoted 1H, 2H, and 3H. Other, highly unstable nuclei have been synthesized in the laboratory but not observed in nature. The most stable radioisotope is tritium, with a half-life of 12.32 years... . |
1 ys and less, 10 ys, 100 ys |
| 10−21 | 1 zeptosecond | zs | Zeptosecond, (zepto- + second), is one sextillionth (short scale)of one second. | 7 zs: half-life of helium-9's outer neutron in the second nuclear halo. 17 zs: approximate period of electromagnetic radiation Electromagnetic radiation Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space... at the boundary between gamma rays and X-rays. 300 zs: approximate typical cycle time of X-rays, on the boundary between hard and soft X-rays. 500 zs: current resolution of tools used to measure speed of chemical bonding |
1 zs, 10 zs, 100 zs |
| 10−18 | 1 attosecond | as | One quintillionth of one second | 12 attoseconds: shortest measured period of time. | 1 as 1 E-18 s An attosecond is an SI unit of time equal to 10−18 of a second. . For context, an attosecond is to a second what a second is to about 31.71 billion years, or twice the age of the universe.... , 10 as, 100 as |
| 10−15 | 1 femtosecond | fs | One quadrillionth of one second | cycle time for 390 nanometre Nanometre A nanometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one billionth of a metre. The name combines the SI prefix nano- with the parent unit name metre .The nanometre is often used to express dimensions on the atomic scale: the diameter... light, transition from visible light to ultraviolet Ultraviolet Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV... |
1 fs 1 E-15 s A femtosecond is the SI unit of time equal to 10-15 of a second. That is one quadrillionth, or one millionth of one billionth of a second. For context, a femtosecond is to a second what a second is to about 31.7 million years.... , 10 fs, 100 fs |
| 10−12 | 1 picosecond Picosecond A picosecond is 10−12 of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000 001 seconds. A picosecond is to one second as one second is to 31,700 years.... |
ps | One trillionth of one second | 1 ps: half-life of a bottom quark Bottom quark The bottom quark, also known as the beauty quark, is a third-generation quark with a charge of − e. Although all quarks are described in a similar way by the quantum chromodynamics, the bottom quark's large bare mass , combined with low values of the CKM matrix elements Vub and Vcb, gives it a... 4 ps: Time to execute one machine cycle by an IBM Silicon-Germanium transistor |
1 ps 1 E-12 s A picosecond is 10−12 of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000 001 seconds. A picosecond is to one second as one second is to 31,700 years.... , 10 ps, 100 ps |
| 10−9 | 1 nanosecond Nanosecond A nanosecond is one billionth of a second . One nanosecond is to one second as one second is to 31.7 years.The word nanosecond is formed by the prefix nano and the unit second. Its symbol is ns.... |
ns | One billionth of one second | 1 ns: Time to execute one machine cycle by a 1 GHz microprocessor 1 ns: Light travels 12 inches (30 cm) |
1 ns 1 E-9 s A nanosecond is one billionth of a second . One nanosecond is to one second as one second is to 31.7 years.The word nanosecond is formed by the prefix nano and the unit second. Its symbol is ns.... , 10 ns, 100 ns |
| 10−6 | 1 microsecond Microsecond A microsecond is an SI unit of time equal to one millionth of a second. Its symbol is µs.A microsecond is equal to 1000 nanoseconds or 1/1000 millisecond... |
µs | One millionth of one second | sometimes also abbreviated µsec 1 µs: Time to execute one machine cycle by an Intel 80186 microprocessor 4–16 µs: Time to execute one machine cycle by a 1960s minicomputer Minicomputer A minicomputer is a class of multi-user computers that lies in the middle range of the computing spectrum, in between the largest multi-user systems and the smallest single-user systems... |
1 µs 1 E-6 s A microsecond is an SI unit of time equal to one millionth of a second. Its symbol is µs.A microsecond is equal to 1000 nanoseconds or 1/1000 millisecond... , 10 µs, 100 µs |
| 10−3 | 1 millisecond Millisecond A millisecond is a thousandth of a second.10 milliseconds are called a centisecond.... |
ms | One thousandth of one second | 4–8 ms: typical seek time for a computer hard disk 100–400 ms: Blink of an eye 150–300 ms: Human reflex Reflex A reflex action, also known as a reflex, is an involuntary and nearly instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus. A true reflex is a behavior which is mediated via the reflex arc; this does not apply to casual uses of the term 'reflex'.-See also:... response to visual stimuli |
1 ms 1 E-3 s A millisecond is a thousandth of a second.10 milliseconds are called a centisecond.... , 10 ms, 100 ms |
| 100 | 1 second | s | 1 s: 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the cesium-133 atom. 60 s: 1 minute |
1 s, 10 s, 100 s | |
| 103 | 1 kilosecond Kilosecond A kilosecond is 1000 seconds , so there are 86.4 kiloseconds in a 24 hour day, and 604.8 kiloseconds in a week. The second is the International System of Units base unit of time, combine with the prefix kilo- which means 1000, results in the definition of a kilosecond... (16.7 minutes) |
ks | 3.6 ks: 3600 s or 1 hour 86.4 ks: 86 400 s or 1 day 604.8 ks: 1 week |
103 s, 104 s, 105 s | |
| 106 | 1 megasecond Megasecond A megasecond is 1 million seconds, or roughly 11.6 days. There are roughly 31.5 megaseconds in a year. This page lists times between 1 and 1000 megaseconds , or 11.6 days and 31.7 years.*shorter times-1 year:... (11.6 days) |
Ms | 2.6 Ms: approximately 1 month 31.6 Ms: approximately 1 year ≈ 107.50 s |
106 s, 107 s, 108 s | |
| 109 | 1 gigasecond Gigasecond A gigasecond is 1 billion seconds, or roughly 31.7 years. This table lists times of between 1 and 1000 gigaseconds, or between 31.7 and 31,700 years... (32 years) |
Gs | 2.1 Gs: average human Human Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus... life expectancy Life expectancy Life expectancy is the expected number of years of life remaining at a given age. It is denoted by ex, which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged x, according to a particular mortality experience... at birth (2011 estimate) 3.16 Gs: approximately 1 century 31.6 Gs: approximately 1 millennium |
109 s, 1010 s, 1011 s | |
| 1012 | 1 terasecond (32 000 years) |
Ts | 6 Ts: time since the appearance of Homo Sapiens (approximately) |
1012 s, 1013 s, 1014 s | |
| 1015 | 1 petasecond (32 million years) |
Ps | 7.1–7.9 Ps: 1 galactic year Galactic year The galactic year, also known as a cosmic year, is the duration of time required for the Solar System to orbit once around the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. Estimates of the length of one orbit range from 225 to 250 million "terrestrial" years.... (225-250 million years) 143 Ps: the age of the Earth Age of the Earth The age of the Earth is 4.54 billion years This age is based on evidence from radiometric age dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples... 144 Ps: the approximate age of the Solar system Solar System The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun... and the Sun Sun The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields... . 430 Ps: the approximate age of the Universe |
1015 s, 1016 s, 1017 s | |
| 1018 | 1 exasecond (32 billion years) |
Es | 312 Es: Estimated lifespan of a 0.1 solar mass red dwarf Red dwarf According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, a red dwarf star is a small and relatively cool star, of the main sequence, either late K or M spectral type.... star. |
1018 s, 1019 s, 1020 s | |
| 1021 | 1 zettasecond (32 trillion years) |
Zs | 3 Zs: Estimated duration of Stelliferous Era. 9.8 Zs:the lifetime of Brahma Brahma Brahma is the Hindu god of creation and one of the Trimurti, the others being Vishnu and Shiva. According to the Brahma Purana, he is the father of Mānu, and from Mānu all human beings are descended. In the Ramayana and the... in Hindu Hindu Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion... mythology |
1021 s, 1022 s, 1023 s | |
| 1024 | 1 yottasecond (32 quadrillion years) |
Ys | 6.616×1050 Ys: Time required for a 1 solar mass black hole Black hole A black hole is a region of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will deform spacetime to form a black hole. Around a black hole there is a mathematically defined surface called an event horizon that... to evaporate completely due to Hawking radiation Hawking radiation Hawking radiation is a thermal radiation with a black body spectrum predicted to be emitted by black holes due to quantum effects. It is named after the physicist Stephen Hawking, who provided a theoretical argument for its existence in 1974, and sometimes also after the physicist Jacob Bekenstein... , if nothing more falls in. |
1024 s, 1025 s, 1026 s and more |
See also
- Heat Death
- Second law of thermodynamicsSecond law of thermodynamicsThe second law of thermodynamics is an expression of the tendency that over time, differences in temperature, pressure, and chemical potential equilibrate in an isolated physical system. From the state of thermodynamic equilibrium, the law deduced the principle of the increase of entropy and...
- Big RipBig RipThe Big Rip is a cosmological hypothesis first published in 2003, about the ultimate fate of the universe, in which the matter of the universe, from stars and galaxies to atoms and subatomic particles, is progressively torn apart by the expansion of the universe at a certain time in the future...
- Big CrunchBig CrunchIn physical cosmology, the Big Crunch is one possible scenario for the ultimate fate of the universe, in which the metric expansion of space eventually reverses and the universe recollapses, ultimately ending as a black hole singularity.- Overview :...
- Big BounceBig BounceThe Big Bounce is a theoretical scientific model of the formation of the known universe. It is implied by the cyclic model or oscillatory universe interpretation of the Big Bang where the first cosmological event was the result of the collapse of a previous universe.- Expansion and contraction...
- Big BangBig BangThe Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
- Cyclic modelCyclic modelA cyclic model is any of several cosmological models in which the universe follows infinite, self-sustaining cycles. For example, the oscillating universe theory briefly considered by Albert Einstein in 1930 theorized a universe following an eternal series of oscillations, each beginning with a...
- Dyson's eternal intelligenceDyson's eternal intelligenceDyson's eternal intelligence is a concept that states an intelligent being would be able to think an infinite number of thoughts in an open universe....
- Final anthropic principle
- Ultimate fate of the UniverseUltimate fate of the universeThe ultimate fate of the universe is a topic in physical cosmology. Many possible fates are predicted by rival scientific theories, including futures of both finite and infinite duration....
- Timeline of the Big BangTimeline of the Big BangThis timeline of the Big Bang describes the history of the universe according to the prevailing scientific theory of how the universe came into being, using the cosmological time parameter of comoving coordinates...
- Graphical timeline of the Big BangGraphical timeline of the Big BangThis timeline of the Big Bang shows the sequence of events as predicted by the Big Bang theory, from the beginning of time to the end of the Dark Ages....
- Graphical timeline from Big Bang to Heat DeathGraphical timeline from Big Bang to Heat DeathThis is the timeline of the Universe from Big Bang to Heat Death scenario. The different Eras of the Universe are shown.Usually the logarithmic scale is used for such timelines but it compresses the most interesting Stelliferous Era too much as this example shows. Therefore a double-logarithmic...
. This timeline uses the loglog scale for comparison with the graphical timeline included in this article. - Graphical timeline of our universeGraphical timeline of our universeThis more than twenty billion years timeline of our universe shows the best estimates of the occurrence of events since its beginning, up until anticipated events in the near future. Zero of the scale is the present day. A large step on the scale is one billion years, a small step one hundred...
. This timeline uses the more intuitive linear time, for comparison with this article. - Graphical timeline of the Stelliferous Era
- The Last QuestionThe Last Question"The Last Question" is a science fiction short story by Isaac Asimov. It first appeared in the November 1956 issue of Science Fiction Quarterly and was reprinted in the collections Nine Tomorrows , The Best of Isaac Asimov , Robot Dreams , the retrospective Opus 100 , and in Isaac Asimov: The...
, a short story by Isaac Asimov which considers the inevitable outcome of heat death in the universe and how it may be reversed. - Orders of magnitude (frequency)Orders of magnitude (frequency)To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following list describes various frequencies, which is measured in Hertz.*262 Hz - The Frequency of Heat that Causes Uranium to Fission*1.85 Hz - Planck frequency, the inverse of the Planck time...
Years
| Factor (a) | Multiple | common units | orders of magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10−50 | Planck time Planck time In physics, the Planck time, , is the unit of time in the system of natural units known as Planck units. It is the time required for light to travel, in a vacuum, a distance of 1 Planck length... , the shortest physically meaningful interval of time ≈ 1.71 a |
10−50 a | |
| 10−24 | 1 yoctoannum | -- | 1 ya and less, 10 ya, 100 ya |
| 10−21 | 1 zeptoannum | -- | 1 za, 10 za, 100 za |
| 10−18 | 1 attoannum | -- | 1 aa, 10 aa, 100 aa |
| 10−15 | 1 femtoannum | -- | 1 fa, 10 fa, 100 fa |
| 10−12 | 1 picoannum | -- | 1 pa, 10 pa, 100 pa |
| 10−9 | 1 nanoannum | 1 second = 3.17 × 10−8 a ≈ 10-7.50 a | 1 na, 10 na, 100 na |
| 10−6 | 1 microannum | 1 minute = 1.90 × 10−6 a 1 hour = 1.40 × 10−4 a |
1 ua, 10 ua, 100 ua |
| 10−3 | 1 milliannum | 1 day = 2.73 × 10−3 a 1 week = 1.91 × 10−2 a |
1 ma, 10 ma, 100 ma |
| 100 | 1 annum | 1 average year = 1 annum (= 365.24219 SI days) decade = 10 anna century = 100 anna |
1 a, 10 a, 100 a |
| 103 | 1 kiloannum | millennium = 1000 anna | 103 a, 104 a, 105 a |
| 106 | 1 megaannum | epoch = 1,000,000 anna | 106 a, 107 a, 108 a |
| 109 | 1 gigaannum | aeon = 1,000,000,000 anna 13.7 Ga = 1.37×1010 a ≈ 13.7 billion years, the approximate age of the Universe |
109 a, 1010 a, 1011 a |
| 1012 | 1 teraannum | --- | 1012 a, 1013 a, 1014 a |
| 1015 | 1 petaannum | --- | 1015 a, 1016 a, 1017 a |
| 1018 | 1 exaannum | -- | 1018 a, 1019 a, 1020 a |
| 1021 | 1 zettaannum | -- | 1021 a, 1022 a, 1023 a |
| 1024 | 1 yottaannum | -- | 1024 a, 1025 a, 1026 and more |
The pages linked in the right-hand column contain lists of times that are of the same order of magnitude (power of ten). Rows in the table represent increasing powers of a thousand (3 orders of magnitude).
Conversion from year to second is year × 31 557 600 using the Julian year. Conversion from
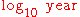 to
to 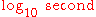 is approximately
is approximately  . Example conversion;
. Example conversion;  .
.See also
- Annum
- Geologic timescale
- Human timescalesHuman timescalesThis is a table of time periods relevant to human beings.0.1 to 0.2 s:*0.1 reaction time, blinking*0.15 seconds—recommended maximum time delay for telephone service0.2 to 1 s*0.2 to 0.67 seconds—a beat of modern dance music...
- Logarithmic timelineLogarithmic timelineA logarithmic timeline is a timeline laid out according to a logarithmic scale. This necessarily implies a zero point and an infinity point, neither of which can be displayed. The most natural zero point is the Big Bang, looking forward, but the most common is the ever-changing present, looking...
- Natural historyNatural historyNatural history is the scientific research of plants or animals, leaning more towards observational rather than experimental methods of study, and encompasses more research published in magazines than in academic journals. Grouped among the natural sciences, natural history is the systematic study...
- Physical unit
- Planck unitsPlanck unitsIn physics, Planck units are physical units of measurement defined exclusively in terms of five universal physical constants listed below, in such a manner that these five physical constants take on the numerical value of 1 when expressed in terms of these units. Planck units elegantly simplify...
- SecondSecondThe second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
- Temporal resolutionTemporal resolutionTemporal resolution refers to the precision of a measurement with respect to time. Often there is a tradeoff between temporal resolution of a measurement and its spatial resolution. This trade-off can be attributed to the finite speed of light and the fact that it takes a certain period of time...
- Timeline of evolutionTimeline of evolutionThis timeline of evolution of life outlines the major events in the development of life on planet Earth since it first originated until the present day. In biology, evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations...
- Timeline of the Big BangTimeline of the Big BangThis timeline of the Big Bang describes the history of the universe according to the prevailing scientific theory of how the universe came into being, using the cosmological time parameter of comoving coordinates...
Footnotes
[a] PDG reports the resonance width (Γ). Here the conversion τ = is given instead.
External links
- Exploring Time from Planck timePlanck timeIn physics, the Planck time, , is the unit of time in the system of natural units known as Planck units. It is the time required for light to travel, in a vacuum, a distance of 1 Planck length...
to the lifespan of the universe

