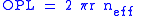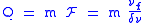Optical ring resonators
Encyclopedia
An optical ring resonator is a set of three or more waveguides in which at least one is a closed loop coupled to one input (or bus) waveguide and one output waveguides. When light of the resonant wavelength
is passed through the loop from input waveguide, it builds up in intensity over multiple round-trips due to constructive interference and is output to the output bus waveguide which serves as a detector waveguide. Because only a select few wavelengths will be at resonance within the loop, the optical ring resonator functions as a filter. Additionally, as implied earlier, two or more ring waveguides can be coupled to each other to form an add/drop optical filter.
and constructive interference.
 The light travelling through the waveguides in an optical ring resonator remain within the waveguides due to total internal reflection
The light travelling through the waveguides in an optical ring resonator remain within the waveguides due to total internal reflection
(TIR). TIR is an optical phenomenon that occurs when a ray of light strikes the boundary of a medium and fails to refract through the boundary. Given that the angle of incidence
is larger than the critical angle (with respect to the normal of the surface) and the refractive index
is lower on the other side of the boundary relative to the incident ray, TIR will occur and no light will be able to pass through.
Interference (wave propagation) is the process by which two waves superimpose to form a resultant wave of greater or lesser amplitude. Interference usually refers to the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other. In constructive interference, the two waves are of the same phase interfere in a way such that the resultant amplitude will be equal to the sum of the individual amplitudes.
where r is the radius of the ring resonator and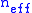 is the effective index of refraction of the waveguide material. Due to the total internal reflection requirement,
is the effective index of refraction of the waveguide material. Due to the total internal reflection requirement, 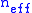 must be greater than the index of refraction of the surrounding fluid in which the resonator is placed (e.g. air). For resonance to take place, the following resonant condition must be satisfied:
must be greater than the index of refraction of the surrounding fluid in which the resonator is placed (e.g. air). For resonance to take place, the following resonant condition must be satisfied:
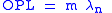
where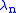 is the resonant wavelength and m is the mode number of the ring resonator. The mode number must be a positive integer for resonance to take place as the circumference of the ring must be an integer multiple of the resonant wavelength. As a result, when the incident light contains multiple wavelengths (such as white light), only the resonant wavelengths will be able to pass through the ring resonator fully.
is the resonant wavelength and m is the mode number of the ring resonator. The mode number must be a positive integer for resonance to take place as the circumference of the ring must be an integer multiple of the resonant wavelength. As a result, when the incident light contains multiple wavelengths (such as white light), only the resonant wavelengths will be able to pass through the ring resonator fully.
The quality factor
of an optical ring resonator can be quantitatively described using the following formula:
where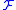 is the finesse
is the finesse
of the ring resonator,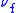 is the free spectral range
is the free spectral range
, and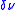 is the full-width half-max
is the full-width half-max
of the transmission spectra. The quality factor is useful in determining the spectral range of the resonance condition for any given ring resonator.
, University of Maryland, College Park
, University of Southern California
, Politecnico di Milano, King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang
and the Hertz Institute (German only).
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
is passed through the loop from input waveguide, it builds up in intensity over multiple round-trips due to constructive interference and is output to the output bus waveguide which serves as a detector waveguide. Because only a select few wavelengths will be at resonance within the loop, the optical ring resonator functions as a filter. Additionally, as implied earlier, two or more ring waveguides can be coupled to each other to form an add/drop optical filter.
Background
Optical ring resonators work on the principles behind total internal reflectionTotal internal reflection
Total internal reflection is an optical phenomenon that happens when a ray of light strikes a medium boundary at an angle larger than a particular critical angle with respect to the normal to the surface. If the refractive index is lower on the other side of the boundary and the incident angle is...
and constructive interference.

Total internal reflection
Total internal reflection is an optical phenomenon that happens when a ray of light strikes a medium boundary at an angle larger than a particular critical angle with respect to the normal to the surface. If the refractive index is lower on the other side of the boundary and the incident angle is...
(TIR). TIR is an optical phenomenon that occurs when a ray of light strikes the boundary of a medium and fails to refract through the boundary. Given that the angle of incidence
Angle of incidence
Angle of incidence is a measure of deviation of something from "straight on", for example:* in the approach of a ray to a surface, or* the angle at which the wing or horizontal tail of an airplane is installed on the fuselage, measured relative to the axis of the fuselage.-Optics:In geometric...
is larger than the critical angle (with respect to the normal of the surface) and the refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
is lower on the other side of the boundary relative to the incident ray, TIR will occur and no light will be able to pass through.
Interference (wave propagation) is the process by which two waves superimpose to form a resultant wave of greater or lesser amplitude. Interference usually refers to the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other. In constructive interference, the two waves are of the same phase interfere in a way such that the resultant amplitude will be equal to the sum of the individual amplitudes.
Theory
To understand how optical ring resonators work, we must first understand the optical path length (OPL) of a ring resonator. This is given as follows for a single-ring ring resonator:where r is the radius of the ring resonator and
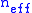 is the effective index of refraction of the waveguide material. Due to the total internal reflection requirement,
is the effective index of refraction of the waveguide material. Due to the total internal reflection requirement, 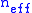 must be greater than the index of refraction of the surrounding fluid in which the resonator is placed (e.g. air). For resonance to take place, the following resonant condition must be satisfied:
must be greater than the index of refraction of the surrounding fluid in which the resonator is placed (e.g. air). For resonance to take place, the following resonant condition must be satisfied:where
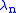 is the resonant wavelength and m is the mode number of the ring resonator. The mode number must be a positive integer for resonance to take place as the circumference of the ring must be an integer multiple of the resonant wavelength. As a result, when the incident light contains multiple wavelengths (such as white light), only the resonant wavelengths will be able to pass through the ring resonator fully.
is the resonant wavelength and m is the mode number of the ring resonator. The mode number must be a positive integer for resonance to take place as the circumference of the ring must be an integer multiple of the resonant wavelength. As a result, when the incident light contains multiple wavelengths (such as white light), only the resonant wavelengths will be able to pass through the ring resonator fully.The quality factor
Q factor
In physics and engineering the quality factor or Q factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how under-damped an oscillator or resonator is, or equivalently, characterizes a resonator's bandwidth relative to its center frequency....
of an optical ring resonator can be quantitatively described using the following formula:
where
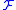 is the finesse
is the finesseFinesse
In contract bridge and similar games, a finesse is a technique which allows one to promote tricks based on a favorable position of one or more cards in the hands of the opponents....
of the ring resonator,
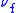 is the free spectral range
is the free spectral rangeFree spectral range
Free spectral range is the spacing in optical frequency or wavelength between two successive reflected or transmitted optical intensity maxima or minima of an interferometer or diffractive optical element.- Diffraction gratings :...
, and
 is the full-width half-max
is the full-width half-maxFull width at half maximum
Full width at half maximum is an expression of the extent of a function, given by the difference between the two extreme values of the independent variable at which the dependent variable is equal to half of its maximum value....
of the transmission spectra. The quality factor is useful in determining the spectral range of the resonance condition for any given ring resonator.
Applications
Research
Numerous groups do related research in optical computing, filters, and photonic logic based on ring resonators, most prominently at Cornell UniversityCornell University
Cornell University is an Ivy League university located in Ithaca, New York, United States. It is a private land-grant university, receiving annual funding from the State of New York for certain educational missions...
, University of Maryland, College Park
University of Maryland, College Park
The University of Maryland, College Park is a top-ranked public research university located in the city of College Park in Prince George's County, Maryland, just outside Washington, D.C...
, University of Southern California
University of Southern California
The University of Southern California is a private, not-for-profit, nonsectarian, research university located in Los Angeles, California, United States. USC was founded in 1880, making it California's oldest private research university...
, Politecnico di Milano, King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang
King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang
King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang is a leading research and educational institution and one of Thailand's leading universities. It is in the city of Bangkok, Thailand...
and the Hertz Institute (German only).
See also
- ResonatorResonatorA resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior, that is, it naturally oscillates at some frequencies, called its resonant frequencies, with greater amplitude than at others. The oscillations in a resonator can be either electromagnetic or mechanical...
- Ring laserRing laserA ring laser is a laser in which the laser cavity has the shape of a ring. Light in ring lasers has two possible directions of propagation: clockwise and counter-clockwise....
- Total Internal ReflectionTotal internal reflectionTotal internal reflection is an optical phenomenon that happens when a ray of light strikes a medium boundary at an angle larger than a particular critical angle with respect to the normal to the surface. If the refractive index is lower on the other side of the boundary and the incident angle is...
- CouplingCouplingA coupling is a device used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power. Couplings do not normally allow disconnection of shafts during operation, however there are torque limiting couplings which can slip or disconnect when some torque limit is exceeded.The...
- Filter (optics)Filter (optics)Optical filters are devices which selectively transmit light of different wavelengths, usually implemented as plane glass or plastic devices in the optical path which are either dyed in the mass or have interference coatings....
- Optical switchOptical switchIn telecommunication, an optical switch is a switch that enables signals in optical fibers or integrated optical circuits to be selectively switched from one circuit to another....