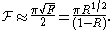Free spectral range
Encyclopedia
Free spectral range is the spacing in optical frequency
or wavelength
between two successive reflected or transmitted optical intensity maxima or minima of an interferometer or diffractive optical element.
is the largest wavelength range for a given order that does not overlap the same range in an adjacent order. If the (m+1)th order of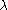 and (m)th order of
and (m)th order of 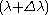 lie at the same angle, then
lie at the same angle, then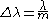
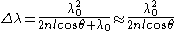
where λ0 is the central wavelength of the nearest transmission peak, n is the index of refraction of the cavity medium,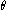 is the angle of incidence, and l is the thickness of the cavity. More often FSR is quoted in frequency, rather than wavelength units:
is the angle of incidence, and l is the thickness of the cavity. More often FSR is quoted in frequency, rather than wavelength units:

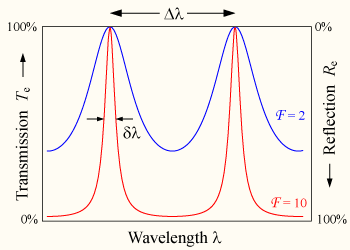 The FSR is related to the full-width half-maximum, δλ, of any one transmission band by a quantity known as the finesse:
The FSR is related to the full-width half-maximum, δλ, of any one transmission band by a quantity known as the finesse:
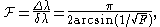
where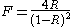 is the coefficient of finesse, and R is the reflectivity of the mirrors.
is the coefficient of finesse, and R is the reflectivity of the mirrors.
This is commonly approximated (for R > 0.5) by
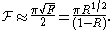
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
or wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
between two successive reflected or transmitted optical intensity maxima or minima of an interferometer or diffractive optical element.
Diffraction gratings
The free spectral range of a diffraction gratingDiffraction grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure, which splits and diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions. The directions of these beams depend on the spacing of the grating and the wavelength of the light so that the grating acts as...
is the largest wavelength range for a given order that does not overlap the same range in an adjacent order. If the (m+1)th order of
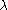 and (m)th order of
and (m)th order of 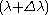 lie at the same angle, then
lie at the same angle, then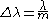
Fabry–Pérot interferometer
In a Fabry–Pérot interferometer or etalon, the wavelength separation between adjacent transmission peaks is called the free spectral range of the etalon, and is given by: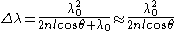
where λ0 is the central wavelength of the nearest transmission peak, n is the index of refraction of the cavity medium,
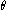 is the angle of incidence, and l is the thickness of the cavity. More often FSR is quoted in frequency, rather than wavelength units:
is the angle of incidence, and l is the thickness of the cavity. More often FSR is quoted in frequency, rather than wavelength units:

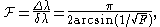
where
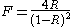 is the coefficient of finesse, and R is the reflectivity of the mirrors.
is the coefficient of finesse, and R is the reflectivity of the mirrors.This is commonly approximated (for R > 0.5) by