
Optical path length
Encyclopedia
In optics
, optical path length (OPL) or optical distance is the product of the geometric length of the path light follows through the system, and the index of refraction of the medium
through which it propagates. A difference in optical path length between two paths is often called the optical path difference (OPD). Optical path length is important because it determines the phase
of the light and governs interference and diffraction
of light as it propagates.
of the glass
.
The OPD can be calculated from the following equation:
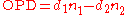
where d1 and d2 are the distances of the ray passing through medium 1 or 2 , n1 is greater refractive index (e.g., glass) and n2 is the smaller refractive index (e.g., air).
where c-speed of light in vacuum ,v -speed of light in medium,γ-wavelength in vacuum,γ°-wavelength in medium
similarly
n=d/d°
d-distance traveled by light in vacuum in time t,d°-distance traveled by light in medium in time t
multiply both side by d°
hence d=n*d°
is the optical path

If the refractive index varies along the path, the OPL is given by
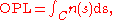
where n(s) is the local refractive index as a function of distance, s, along the path C.
An electromagnetic wave that travels a path of given optical path length arrives with the same phase shift as if it had traveled a path of that physical length in a vacuum
. Thus, if a wave
is traveling through several different media, then the optical path length of each medium can be added to find the total optical path length. The optical path difference between the paths taken by two identical waves can then be used to find the phase change. Finally, using the phase change, the interference between the two waves can be calculated.
Fermat's principle
states that the path light takes between two points is the path that has the minimum optical path length.
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, optical path length (OPL) or optical distance is the product of the geometric length of the path light follows through the system, and the index of refraction of the medium
Medium (optics)
An optical medium is material through which electromagnetic waves propagate. It is a form of transmission medium. The permittivity and permeability of the medium define how electromagnetic waves propagate in it...
through which it propagates. A difference in optical path length between two paths is often called the optical path difference (OPD). Optical path length is important because it determines the phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
of the light and governs interference and diffraction
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
of light as it propagates.
Optical Path Difference (OPD)
Optical path difference is the phase shift which happens between two previously coherent sources when passed through different mediums. For example a wave passed through glass will appear to travel a greater distance than an identical wave in air. This is because the source in the glass will have experienced a greater number of wavelengths due to the higher refractive indexRefractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
of the glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
.
The OPD can be calculated from the following equation:
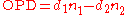
where d1 and d2 are the distances of the ray passing through medium 1 or 2 , n1 is greater refractive index (e.g., glass) and n2 is the smaller refractive index (e.g., air).
Mathematical derivation
n=c/v=γ/γ°where c-speed of light in vacuum ,v -speed of light in medium,γ-wavelength in vacuum,γ°-wavelength in medium
similarly
n=d/d°
d-distance traveled by light in vacuum in time t,d°-distance traveled by light in medium in time t
multiply both side by d°
hence d=n*d°
is the optical path
Details
In a medium of constant refractive index, n, the OPL for a path of physical length d is just
If the refractive index varies along the path, the OPL is given by
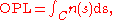
where n(s) is the local refractive index as a function of distance, s, along the path C.
An electromagnetic wave that travels a path of given optical path length arrives with the same phase shift as if it had traveled a path of that physical length in a vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
. Thus, if a wave
Wave
In physics, a wave is a disturbance that travels through space and time, accompanied by the transfer of energy.Waves travel and the wave motion transfers energy from one point to another, often with no permanent displacement of the particles of the medium—that is, with little or no associated mass...
is traveling through several different media, then the optical path length of each medium can be added to find the total optical path length. The optical path difference between the paths taken by two identical waves can then be used to find the phase change. Finally, using the phase change, the interference between the two waves can be calculated.
Fermat's principle
Fermat's principle
In optics, Fermat's principle or the principle of least time is the principle that the path taken between two points by a ray of light is the path that can be traversed in the least time. This principle is sometimes taken as the definition of a ray of light...
states that the path light takes between two points is the path that has the minimum optical path length.

