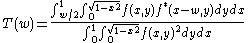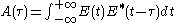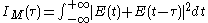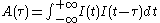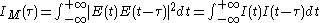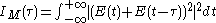
Optical autocorrelation
Encyclopedia
In optics
, various autocorrelation
functions can be experimentally realized. The field autocorrelation may be used to calculate the spectrum of a source of light, while the intensity autocorrelation and the interferometric autocorrelation are commonly used to estimate the duration of ultrashort pulse
s produced by modelocked
laser
s. The laser pulse duration cannot be easily measured by optoelectronic methods, since the response time of photodiode
s and oscilloscope
s are at best of the order of 200 femtoseconds, yet laser pulses can be made as short as a few femtoseconds.
In the following examples, the autocorrelation signal is generated by the nonlinear process of second-harmonic generation (SHG). Other techniques based on two-photon absorption
may also be used in autocorrelation measurements, as well as higher-order nonlinear optical processes such as third-harmonic generation , in which case the mathematical expressions of the signal will be slightly modified, but the basic interpretation of an autocorrelation trace remains the same. A detailed discussion on interferometric autocorrelation is given in several well-known textbooks.
(Note: some practitioners are of the opinion that to accurately and definitively determine the pulse length, one needs to perform a full-intensity-and-phase type of measurement, such as SPIDER
or FROG
. The latter are two competing measuring techniques introduced after optical autocorrelation).
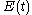 , the field autocorrelation function is defined by
, the field autocorrelation function is defined by
The Wiener-Khinchin theorem states that the Fourier transform
of the field autocorrelation is the spectrum of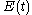 , i.e., the square of the magnitude of the Fourier transform of
, i.e., the square of the magnitude of the Fourier transform of 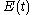 . As a result, the field autocorrelation is not sensitive to the spectral phase.
. As a result, the field autocorrelation is not sensitive to the spectral phase.
The field autocorrelation is readily measured experimentally by placing a slow detector at the output of a Michelson interferometer
. The detector is illuminated by the input electric field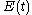 coming from one arm, and by the delayed replica
coming from one arm, and by the delayed replica 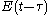 from the other arm. If the time response of the detector is much larger than the time duration of the signal
from the other arm. If the time response of the detector is much larger than the time duration of the signal 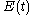 , or if the recorded signal is integrated, the detector measures the intensity
, or if the recorded signal is integrated, the detector measures the intensity 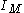 as the delay
as the delay  is scanned:
is scanned:
Expanding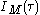 reveals that one of the terms is
reveals that one of the terms is 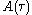 , proving that a Michelson interferometer can be used to measure the field autocorrelation, or the spectrum of
, proving that a Michelson interferometer can be used to measure the field autocorrelation, or the spectrum of 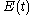 (and only the spectrum). This principle is the basis for Fourier transform spectroscopy
(and only the spectrum). This principle is the basis for Fourier transform spectroscopy
.
 corresponds an intensity
corresponds an intensity  and an intensity autocorrelation function defined by
and an intensity autocorrelation function defined by
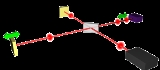
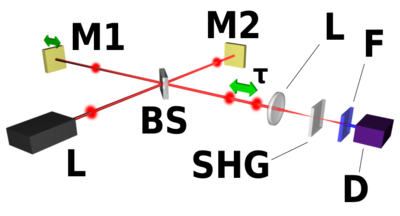
The optical implementation of the intensity autocorrelation is not as straightforward as for the field autocorrelation. Similarly to the previous setup, two parallel beams with a variable delay are generated, then focused into a second-harmonic-generation crystal (see nonlinear optics
) to obtain a signal proportional to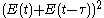 . Only the beam propagating on the optical axis, proportional to the cross-product
. Only the beam propagating on the optical axis, proportional to the cross-product 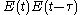 , is retained. This signal is then recorded by a slow detector, which measures
, is retained. This signal is then recorded by a slow detector, which measures
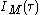 is exactly the intensity autocorrelation
is exactly the intensity autocorrelation 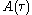 .
.
The generation of the second harmonic in crystals is a nonlinear process that requires high peak power
, unlike the previous setup. However, such high peak power can be obtained from a limited amount of energy
by ultrashort pulse
s, and as a result their intensity autocorrelation is often measured experimentally. Another difficulty with this setup is that both beams must be focused at the same point inside the crystal as the delay is scanned in order for the second harmonic to be generated.
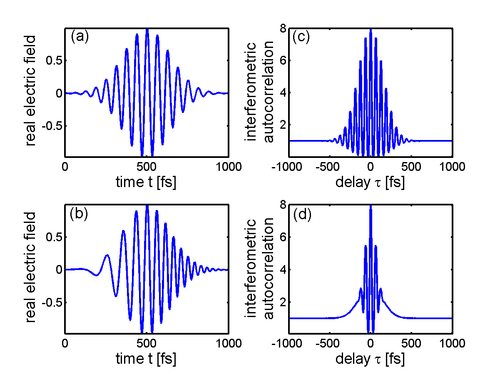
It can be shown that the intensity autocorrelation width of a pulse is related to the intensity width. For a Gaussian time profile, the autocorrelation width is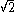 longer than the width of the intensity, and it is 1.54 longer in the case of an hyperbolic secant squared (sech2) pulse. This numerical factor, which depends on the shape of the pulse, is sometimes called the deconvolution factor. If this factor is known, or assumed, the time duration (intensity width) of a pulse can be measured using an intensity autocorrelation. However, the phase cannot be measured.
longer than the width of the intensity, and it is 1.54 longer in the case of an hyperbolic secant squared (sech2) pulse. This numerical factor, which depends on the shape of the pulse, is sometimes called the deconvolution factor. If this factor is known, or assumed, the time duration (intensity width) of a pulse can be measured using an intensity autocorrelation. However, the phase cannot be measured.
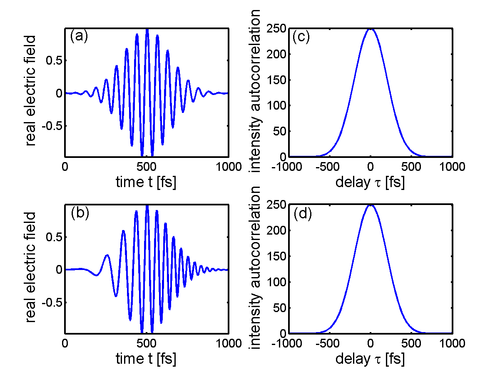
 As a combination of both previous cases, a nonlinear crystal can be used to generate the second harmonic at the output of a Michelson interferometer, in a colinear geometry. In this case, the signal recorded by a slow detector is
As a combination of both previous cases, a nonlinear crystal can be used to generate the second harmonic at the output of a Michelson interferometer, in a colinear geometry. In this case, the signal recorded by a slow detector is
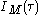 is called the interferometric autocorrelation. It contains some information about the phase of the pulse: the fringes in the autocorrelation trace wash out as the spectral phase becomes more complex.
is called the interferometric autocorrelation. It contains some information about the phase of the pulse: the fringes in the autocorrelation trace wash out as the spectral phase becomes more complex.
T(w) of an optical system is given by the autocorrelation of its pupil
function f(x,y):
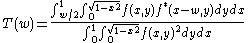
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, various autocorrelation
Autocorrelation
Autocorrelation is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself. Informally, it is the similarity between observations as a function of the time separation between them...
functions can be experimentally realized. The field autocorrelation may be used to calculate the spectrum of a source of light, while the intensity autocorrelation and the interferometric autocorrelation are commonly used to estimate the duration of ultrashort pulse
Ultrashort pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse of light is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a femtosecond . Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators...
s produced by modelocked
Modelocking
Mode-locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds or femtoseconds ....
laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
s. The laser pulse duration cannot be easily measured by optoelectronic methods, since the response time of photodiode
Photodiode
A photodiode is a type of photodetector capable of converting light into either current or voltage, depending upon the mode of operation.The common, traditional solar cell used to generateelectric solar power is a large area photodiode....
s and oscilloscope
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a type of electronic test instrument that allows observation of constantly varying signal voltages, usually as a two-dimensional graph of one or more electrical potential differences using the vertical or 'Y' axis, plotted as a function of time,...
s are at best of the order of 200 femtoseconds, yet laser pulses can be made as short as a few femtoseconds.
In the following examples, the autocorrelation signal is generated by the nonlinear process of second-harmonic generation (SHG). Other techniques based on two-photon absorption
Two-photon absorption
Two-photon absorption is the simultaneous absorption of two photons of identical or different frequencies in order to excite a molecule from one state to a higher energy electronic state. The energy difference between the involved lower and upper states of the molecule is equal to the sum of the...
may also be used in autocorrelation measurements, as well as higher-order nonlinear optical processes such as third-harmonic generation , in which case the mathematical expressions of the signal will be slightly modified, but the basic interpretation of an autocorrelation trace remains the same. A detailed discussion on interferometric autocorrelation is given in several well-known textbooks.
(Note: some practitioners are of the opinion that to accurately and definitively determine the pulse length, one needs to perform a full-intensity-and-phase type of measurement, such as SPIDER
Spectral phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction
In ultrafast optics, spectral phase interferometry for direct electric-field reconstruction is an ultrashort pulse measurement technique.-The basics:...
or FROG
Frequency-resolved optical gating
In optics, frequency-resolved optical gating is a derivative of autocorrelation, but is far superior in its ability to measure ultrafast optical pulse shapes...
. The latter are two competing measuring techniques introduced after optical autocorrelation).
Field autocorrelation
For a complex electric field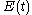 , the field autocorrelation function is defined by
, the field autocorrelation function is defined byThe Wiener-Khinchin theorem states that the Fourier transform
Fourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
of the field autocorrelation is the spectrum of
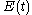 , i.e., the square of the magnitude of the Fourier transform of
, i.e., the square of the magnitude of the Fourier transform of 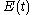 . As a result, the field autocorrelation is not sensitive to the spectral phase.
. As a result, the field autocorrelation is not sensitive to the spectral phase.The field autocorrelation is readily measured experimentally by placing a slow detector at the output of a Michelson interferometer
Michelson interferometer
The Michelson interferometer is the most common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by Albert Abraham Michelson. An interference pattern is produced by splitting a beam of light into two paths, bouncing the beams back and recombining them...
. The detector is illuminated by the input electric field
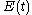 coming from one arm, and by the delayed replica
coming from one arm, and by the delayed replica 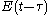 from the other arm. If the time response of the detector is much larger than the time duration of the signal
from the other arm. If the time response of the detector is much larger than the time duration of the signal 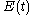 , or if the recorded signal is integrated, the detector measures the intensity
, or if the recorded signal is integrated, the detector measures the intensity 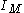 as the delay
as the delay  is scanned:
is scanned:Expanding
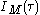 reveals that one of the terms is
reveals that one of the terms is 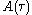 , proving that a Michelson interferometer can be used to measure the field autocorrelation, or the spectrum of
, proving that a Michelson interferometer can be used to measure the field autocorrelation, or the spectrum of 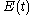 (and only the spectrum). This principle is the basis for Fourier transform spectroscopy
(and only the spectrum). This principle is the basis for Fourier transform spectroscopyFourier transform spectroscopy
Fourier transform spectroscopy is a measurement technique whereby spectra are collected based on measurements of the coherence of a radiative source, using time-domain or space-domain measurements of the electromagnetic radiation or other type of radiation....
.

Intensity autocorrelation
To a complex electric field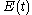 corresponds an intensity
corresponds an intensity 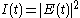 and an intensity autocorrelation function defined by
and an intensity autocorrelation function defined byThe optical implementation of the intensity autocorrelation is not as straightforward as for the field autocorrelation. Similarly to the previous setup, two parallel beams with a variable delay are generated, then focused into a second-harmonic-generation crystal (see nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
) to obtain a signal proportional to
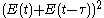 . Only the beam propagating on the optical axis, proportional to the cross-product
. Only the beam propagating on the optical axis, proportional to the cross-product 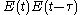 , is retained. This signal is then recorded by a slow detector, which measures
, is retained. This signal is then recorded by a slow detector, which measures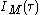 is exactly the intensity autocorrelation
is exactly the intensity autocorrelation 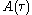 .
.The generation of the second harmonic in crystals is a nonlinear process that requires high peak power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
, unlike the previous setup. However, such high peak power can be obtained from a limited amount of energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
by ultrashort pulse
Ultrashort pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse of light is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a femtosecond . Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators...
s, and as a result their intensity autocorrelation is often measured experimentally. Another difficulty with this setup is that both beams must be focused at the same point inside the crystal as the delay is scanned in order for the second harmonic to be generated.
It can be shown that the intensity autocorrelation width of a pulse is related to the intensity width. For a Gaussian time profile, the autocorrelation width is
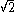 longer than the width of the intensity, and it is 1.54 longer in the case of an hyperbolic secant squared (sech2) pulse. This numerical factor, which depends on the shape of the pulse, is sometimes called the deconvolution factor. If this factor is known, or assumed, the time duration (intensity width) of a pulse can be measured using an intensity autocorrelation. However, the phase cannot be measured.
longer than the width of the intensity, and it is 1.54 longer in the case of an hyperbolic secant squared (sech2) pulse. This numerical factor, which depends on the shape of the pulse, is sometimes called the deconvolution factor. If this factor is known, or assumed, the time duration (intensity width) of a pulse can be measured using an intensity autocorrelation. However, the phase cannot be measured.
Interferometric autocorrelation

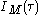 is called the interferometric autocorrelation. It contains some information about the phase of the pulse: the fringes in the autocorrelation trace wash out as the spectral phase becomes more complex.
is called the interferometric autocorrelation. It contains some information about the phase of the pulse: the fringes in the autocorrelation trace wash out as the spectral phase becomes more complex.
Pupil function autocorrelation
The optical transfer functionOptical transfer function
The optical transfer function of an imaging system is the true measure of resolution that the system is capable of...
T(w) of an optical system is given by the autocorrelation of its pupil
Entrance pupil
In an optical system, the entrance pupil is the optical image of the physical aperture stop, as 'seen' through the front of the lens system. The corresponding image of the aperture as seen through the back of the lens system is called the exit pupil...
function f(x,y):