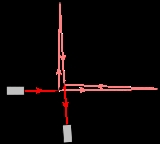
Fourier transform spectroscopy
Overview
Coherence (physics)
In physics, coherence is a property of waves that enables stationary interference. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a wave....
of a radiative
Radiate
Radiate is a verb. See radiation.Radiate may also refer to an antic Roman bronze coin....
source, using time-domain or space-domain measurements of the electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
or other type of radiation.
It can be applied to a variety of types of spectroscopy including optical spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy is the spectroscopy that deals with the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum, that is light with a longer wavelength and lower frequency than visible light. It covers a range of techniques, mostly based on absorption spectroscopy. As with all spectroscopic...
(FTIR
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is a technique which is used to obtain an infrared spectrum of absorption, emission, photoconductivity or Raman scattering of a solid, liquid or gas. An FTIR spectrometer simultaneously collects spectral data in a wide spectral range...
, FT-NIRS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI), mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
and electron spin resonance spectroscopy.
Unanswered Questions

