
Oogenesis
Encyclopedia
Oogenesis, ovogenesis or oögenesis (icon) is the creation of an ovum
(egg cell). It is the female form of gametogenesis
. The male equivalent is spermatogenesis
. It involves the development of the various stages of the immature ovum.
 In mammal
In mammal
s, the first part of oogenesis starts in the germinal epithelium
, which gives rise to the development of ovarian follicles, the functional unit of the ovary
.
Note that this process, important to all animal life cycles yet unlike all other instances of cell division, occurs completely without the aid of oo spindle-coordinating centrosomes.
Oogenesis consists of several sub-processes: oocytogenesis, ootidogenesis, and finally maturation to form an ovum (oogenesis proper). Folliculogenesis
is a separate sub-process that accompanies and supports all three oogenetic sub-processes.
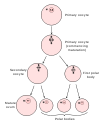
Oogonium --(Oocytogenesis)--> Primary Oocyte --(Meiosis I)-->First Polar Body (Discarded afterward) + Secondary oocyte --(Meiosis II)--> Secondary Polar Body (Discarded afterward) + Ovum
, which in the female human begins with the processes of folliculogenesis
, oocytogenesis, and ootidogenesis.
to form secondary follicles. The primary follicles have formed from primordial follicles, which developed in the ovary at around 10–30 weeks after conception. By around day 9 of the cycle, only one healthy secondary follicle remains, with the rest having undergone cellular atresia
. The remaining follicle is called the dominant follicle and is responsible for producing large amounts of oestradiol during the late follicular phase. Oestradiol production depends upon co-operation between the theca and granulosa cell
s. On day 14 of the cycle, an LH surge occurs, which itself is triggered by the positive feedback of oestradiol. This causes the secondary follicle to develop into a tertiary follicle, which then ovulates some 24–36 hours later. An important event in the development of the tertiary follicle occurs when the primary oocyte completes the first meiotic division, resulting in the formation of a polar body
and a secondary oocyte. The empty follicle then forms a corpus luteum
.
, which occurs via the transformation of primordial follicles
into primary oocyte
s, a process called oocytogenesis. Oocytogenesis is complete either before or shortly after birth.
Recently, however, two publications have challenged the belief that a finite number of oocytes are set around the time of birth. The renewal of ovarian follicles from germline stem cells (originating from bone marrow and peripheral blood) has been reported in the postnatal mouse ovary.
Due to the revolutionary nature of these claims, further experiments are required to determine the true dynamics of small follicle formation.
. In fact, a primary oocyte is, by its biological definition, a cell whose primary function is to divide by the process of meiosis.
However, although this process begins at prenatal age, it stops at prophase I. In late fetal life, all oocytes, still primary oocytes, have halted at this stage of development, called the dictyate
. After menarche
, these cells then continue to develop, although only a few do so every menstrual cycle
.
occurs and tetrad
s form, enabling Chromosomal crossover
to occur. As a result of meiosis I, the primary oocyte has now developed into the secondary oocyte and the first polar body
.
surrounding the ootid has developed from a primordial follicle to a preovulatory one.
The function of forming polar bodies is to discard the extra haploid sets of chromosomes that have resulted as a consequence of meiosis.
s mature in vitro
. It can potentially be performed before an IVF. In such cases, ovarian hyperstimulation isn't essential. Rather, oocytes can mature outside the body prior to IVF. Hence, no (or at least a lower dose of) gonadotropins have to be injected in the body. However, there still isn't enough evidence to prove the effectiveness and security of the technique.
s produce egg cells in structures termed archegonia. Some algae
and the oomycetes produce eggs in oogonia. In the brown alga Fucus
, all four egg cells survive oogenesis, which is an exception to the rule that generally only one product of female meiosis survives to maturity.
In plant
s, oogenesis occurs inside the female gametophyte
via mitosis
. In many plants such as bryophyte
s, fern
s, and gymnosperm
s, egg cells are formed in archegonia. In flowering plant
s, the female gametophyte has been reduced to an eight-celled embryo sac within the ovule
inside the ovary
of the flower. Oogenesis occurs within the embryo sac and leads to the formation of a single egg cell per ovule.
In ascaris
, the oocyte does not even begin meiosis until the sperm
touches it, in contrast to mammals, where meiosis is completed in the estrus cycle.
Ovum
An ovum is a haploid female reproductive cell or gamete. Both animals and embryophytes have ova. The term ovule is used for the young ovum of an animal, as well as the plant structure that carries the female gametophyte and egg cell and develops into a seed after fertilization...
(egg cell). It is the female form of gametogenesis
Gametogenesis
Gametogenesis is a biological process by which diploid or haploid precursor cells undergo cell division and differentiation to form mature haploid gametes. Depending on the biological life cycle of the organism, gametogenesis occurs by meiotic division of diploid gametocytes into various gametes,...
. The male equivalent is spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which male primary germ cells undergo division, and produce a number of cells termed spermatogonia, from which the primary spermatocytes are derived. Each primary spermatocyte divides into two secondary spermatocytes, and each secondary spermatocyte into two...
. It involves the development of the various stages of the immature ovum.
Oogenesis in mammals

Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s, the first part of oogenesis starts in the germinal epithelium
Germinal epithelium (female)
The surface of the ovary is covered by a layer of simple cuboidal cells which constitutes the germinal epithelium of Waldeyer.These cells are derived from the mesoderm during embryonic development and are closely related to the mesothelium of the peritoneum...
, which gives rise to the development of ovarian follicles, the functional unit of the ovary
Ovary
The ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ, often found in pairs as part of the vertebrate female reproductive system. Ovaries in anatomically female individuals are analogous to testes in anatomically male individuals, in that they are both gonads and endocrine glands.-Human anatomy:Ovaries...
.
Note that this process, important to all animal life cycles yet unlike all other instances of cell division, occurs completely without the aid of oo spindle-coordinating centrosomes.
Oogenesis consists of several sub-processes: oocytogenesis, ootidogenesis, and finally maturation to form an ovum (oogenesis proper). Folliculogenesis
Folliculogenesis
In biology, folliculogenesis is the maturation of the ovarian follicle, a densely-packed shell of somatic cells that contains an immature oocyte...
is a separate sub-process that accompanies and supports all three oogenetic sub-processes.
| Cell type | ploidy Ploidy Ploidy is the number of sets of chromosomes in a biological cell.Human sex cells have one complete set of chromosomes from the male or female parent. Sex cells, also called gametes, combine to produce somatic cells. Somatic cells, therefore, have twice as many chromosomes. The haploid number is... |
Process | Process completion >- | Oogonium Oogonium "Oogonium" may refer to either a primordial oocyte in a female fetus or the female gametangium of certain thallophytes.-in the fetus:Oogonia are formed in large numbers by mitosis early in fetal development from primordial germ cells... |
diploid | Oocytogenesis (mitosis Mitosis Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly... ) |
>- | diploid | Ootidogenesis (meiosis Meiosis Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells.... 1) (Folliculogenesis Folliculogenesis In biology, folliculogenesis is the maturation of the ovarian follicle, a densely-packed shell of somatic cells that contains an immature oocyte... ) |
Dictyate Dictyate The dictyate or dictyotene is a prolonged resting phase in oogenesis. It occurs in the stage of meiotic prophase I in ootidogenesis. It starts late in fetal life and is terminated shortly before ovulation by the LH surge... in prophase I for up to 50 years >- | secondary Oocyte Oocyte An oocyte, ovocyte, or rarely ocyte, is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell which undergoes a mitotic... |
haploid | Ootidogenesis (meiosis Meiosis Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells.... 2) |
>- | haploid |
Oogonium --(Oocytogenesis)--> Primary Oocyte --(Meiosis I)-->First Polar Body (Discarded afterward) + Secondary oocyte --(Meiosis II)--> Secondary Polar Body (Discarded afterward) + Ovum
The Creation of Oogonia
The creation of oogonia traditionally doesn't belong to oogenesis proper but, instead, to the common process of gametogenesisGametogenesis
Gametogenesis is a biological process by which diploid or haploid precursor cells undergo cell division and differentiation to form mature haploid gametes. Depending on the biological life cycle of the organism, gametogenesis occurs by meiotic division of diploid gametocytes into various gametes,...
, which in the female human begins with the processes of folliculogenesis
Folliculogenesis
In biology, folliculogenesis is the maturation of the ovarian follicle, a densely-packed shell of somatic cells that contains an immature oocyte...
, oocytogenesis, and ootidogenesis.
Human Oogenesis
At the start of the menstrual cycle, some 12-20 primary follicles begin to develop under the influence of elevated FSHFollicle-stimulating hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone is a hormone found in humans and other animals. It is synthesized and secreted by gonadotrophs of the anterior pituitary gland. FSH regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, and reproductive processes of the body. FSH and Luteinizing hormone act...
to form secondary follicles. The primary follicles have formed from primordial follicles, which developed in the ovary at around 10–30 weeks after conception. By around day 9 of the cycle, only one healthy secondary follicle remains, with the rest having undergone cellular atresia
Atresia
Atresia is a condition in which a body orifice or passage in the body is abnormally closed or absent.Examples of atresia include:* Imperforate anus - malformation of the opening between the rectum and anus....
. The remaining follicle is called the dominant follicle and is responsible for producing large amounts of oestradiol during the late follicular phase. Oestradiol production depends upon co-operation between the theca and granulosa cell
Granulosa cell
A granulosa cell or follicular cell is a somatic cell of the sex cord that is closely associated with the developing female gamete in the ovary of mammals.-Anatomy and function:...
s. On day 14 of the cycle, an LH surge occurs, which itself is triggered by the positive feedback of oestradiol. This causes the secondary follicle to develop into a tertiary follicle, which then ovulates some 24–36 hours later. An important event in the development of the tertiary follicle occurs when the primary oocyte completes the first meiotic division, resulting in the formation of a polar body
Polar body
A polar body is a cell structure found inside an ovum. Both animal and plant ova possess it. It is also known as a polar cell.Asymmetrical cell division leads to the production of polar bodies during oogenesis. To conserve nutrients, the majority of cytoplasm is segregated into the secondary...
and a secondary oocyte. The empty follicle then forms a corpus luteum
Corpus luteum
The corpus luteum is a temporary endocrine structure in mammals, involved in production of relatively high levels of progesterone and moderate levels of estradiol and inhibin A...
.
Oocytogenesis
Oogenesis starts with the process of developing oogoniaOogonium
"Oogonium" may refer to either a primordial oocyte in a female fetus or the female gametangium of certain thallophytes.-in the fetus:Oogonia are formed in large numbers by mitosis early in fetal development from primordial germ cells...
, which occurs via the transformation of primordial follicles
Ovarian follicle
Ovarian follicles are the basic units of female reproductive biology, each of which is composed of roughly spherical aggregations of cells found in the ovary. They contain a single oocyte . These structures are periodically initiated to grow and develop, culminating in ovulation of usually a single...
into primary oocyte
Oocyte
An oocyte, ovocyte, or rarely ocyte, is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell which undergoes a mitotic...
s, a process called oocytogenesis. Oocytogenesis is complete either before or shortly after birth.
Number of primary oocytes
It is commonly believed that, when oocytogenesis is complete, no additional primary oocytes are created, in contrast to the male process of spermatogenesis, where gametocytes are continuously created. In other words, primary oocytes reach their maximum development at ~20 weeks of gestational age, when approximately seven million primary oocytes have been created; however, at birth, this number has already been reduced to approximately 1-2 million.Recently, however, two publications have challenged the belief that a finite number of oocytes are set around the time of birth. The renewal of ovarian follicles from germline stem cells (originating from bone marrow and peripheral blood) has been reported in the postnatal mouse ovary.
Due to the revolutionary nature of these claims, further experiments are required to determine the true dynamics of small follicle formation.
Ootidogenesis
The succeeding phase of ootidogenesis occurs when the primary oocyte develops into an ootid. This is achieved by the process of meiosisMeiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
. In fact, a primary oocyte is, by its biological definition, a cell whose primary function is to divide by the process of meiosis.
However, although this process begins at prenatal age, it stops at prophase I. In late fetal life, all oocytes, still primary oocytes, have halted at this stage of development, called the dictyate
Dictyate
The dictyate or dictyotene is a prolonged resting phase in oogenesis. It occurs in the stage of meiotic prophase I in ootidogenesis. It starts late in fetal life and is terminated shortly before ovulation by the LH surge...
. After menarche
Menarche
Menarche is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstrual bleeding, in female human beings. From both social and medical perspectives it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility....
, these cells then continue to develop, although only a few do so every menstrual cycle
Menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is the scientific term for the physiological changes that can occur in fertile women for the purpose of sexual reproduction. This article focuses on the human menstrual cycle....
.
Meiosis I
Meiosis I of ootidogenesis begins during embryonic development, but halts in the diplotene stage of prophase I until puberty. For those primary oocytes that continue to develop in each menstrual cycle, however, synapsisSynapsis
Synapsis is the pairing of two homologous chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. It allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation, and possible chromosomal crossover between them. Synapsis takes place during prophase I. When homologous chromosomes synapse, their ends are...
occurs and tetrad
Tetrad
Tetrad may refer to:* Tetrad , Bivalents or Tetrad of homologous chromosomes consisting of four synapsed chromatids that become visible during the Pachytene stage of meiotic prophase...
s form, enabling Chromosomal crossover
Chromosomal crossover
Chromosomal crossover is an exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. It is one of the final phases of genetic recombination, which occurs during prophase I of meiosis in a process called synapsis. Synapsis begins before the synaptonemal complex develops, and is not completed...
to occur. As a result of meiosis I, the primary oocyte has now developed into the secondary oocyte and the first polar body
Polar body
A polar body is a cell structure found inside an ovum. Both animal and plant ova possess it. It is also known as a polar cell.Asymmetrical cell division leads to the production of polar bodies during oogenesis. To conserve nutrients, the majority of cytoplasm is segregated into the secondary...
.
Meiosis II
Immediately after meiosis I, the haploid secondary oocyte initiates meiosis II. However, this process is also halted at the metaphase II stage until fertilization, if such should ever occur. When meiosis II has completed, an ootid and another polar body have now been created.Folliculogenesis
Synchronously with ootidogenesis, the ovarian follicleOvarian follicle
Ovarian follicles are the basic units of female reproductive biology, each of which is composed of roughly spherical aggregations of cells found in the ovary. They contain a single oocyte . These structures are periodically initiated to grow and develop, culminating in ovulation of usually a single...
surrounding the ootid has developed from a primordial follicle to a preovulatory one.
Maturation into ovum
Both polar bodies disintegrate at the end of Meiosis II, leaving only the ootid, which then eventually undergoes maturation into a mature ovum.The function of forming polar bodies is to discard the extra haploid sets of chromosomes that have resulted as a consequence of meiosis.
In vitro maturation
In vitro maturation (IVM) is the technique of letting ovarian follicleOvarian follicle
Ovarian follicles are the basic units of female reproductive biology, each of which is composed of roughly spherical aggregations of cells found in the ovary. They contain a single oocyte . These structures are periodically initiated to grow and develop, culminating in ovulation of usually a single...
s mature in vitro
In vitro
In vitro refers to studies in experimental biology that are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological context in order to permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms. Colloquially, these experiments...
. It can potentially be performed before an IVF. In such cases, ovarian hyperstimulation isn't essential. Rather, oocytes can mature outside the body prior to IVF. Hence, no (or at least a lower dose of) gonadotropins have to be injected in the body. However, there still isn't enough evidence to prove the effectiveness and security of the technique.
Oogenesis in non-mammals
Many protistProtist
Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms. Historically, protists were treated as the kingdom Protista, which includes mostly unicellular organisms that do not fit into the other kingdoms, but this group is contested in modern taxonomy...
s produce egg cells in structures termed archegonia. Some algae
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
and the oomycetes produce eggs in oogonia. In the brown alga Fucus
Fucus
Fucus is a genus of brown algae found in the intertidal zones of rocky seashores almost throughout the world.-Description and life cycle:...
, all four egg cells survive oogenesis, which is an exception to the rule that generally only one product of female meiosis survives to maturity.
In plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s, oogenesis occurs inside the female gametophyte
Gametophyte
A gametophyte is the haploid, multicellular phase of plants and algae that undergo alternation of generations, with each of its cells containing only a single set of chromosomes....
via mitosis
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
. In many plants such as bryophyte
Bryophyte
Bryophyte is a traditional name used to refer to all embryophytes that do not have true vascular tissue and are therefore called 'non-vascular plants'. Some bryophytes do have specialized tissues for the transport of water; however since these do not contain lignin, they are not considered to be...
s, fern
Fern
A fern is any one of a group of about 12,000 species of plants belonging to the botanical group known as Pteridophyta. Unlike mosses, they have xylem and phloem . They have stems, leaves, and roots like other vascular plants...
s, and gymnosperm
Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms are a group of seed-bearing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales. The term "gymnosperm" comes from the Greek word gymnospermos , meaning "naked seeds", after the unenclosed condition of their seeds...
s, egg cells are formed in archegonia. In flowering plant
Flowering plant
The flowering plants , also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by a series of synapomorphies...
s, the female gametophyte has been reduced to an eight-celled embryo sac within the ovule
Ovule
Ovule means "small egg". In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: The integument forming its outer layer, the nucellus , and the megaspore-derived female gametophyte in its center...
inside the ovary
Ovary (plants)
In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals...
of the flower. Oogenesis occurs within the embryo sac and leads to the formation of a single egg cell per ovule.
In ascaris
Ascaris
Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematode worms known as the "giant intestinal roundworms". One species, A. suum, typically infects pigs, while another, A. lumbricoides, affects human populations, typically in sub-tropical and tropical areas with poor sanitation. A...
, the oocyte does not even begin meiosis until the sperm
Sperm
The term sperm is derived from the Greek word sperma and refers to the male reproductive cells. In the types of sexual reproduction known as anisogamy and oogamy, there is a marked difference in the size of the gametes with the smaller one being termed the "male" or sperm cell...
touches it, in contrast to mammals, where meiosis is completed in the estrus cycle.

