
Nuna 3
Encyclopedia

Solar car racing
Solar car racing refers to competitive races of electric vehicles which are powered by solar energy obtained from solar panels on the surface of the car . The first solar car race was the Tour de Sol in 1985 which led to several similar races in Europe, USA and Australia...
developed by Nuon Solar Team form the Delft University of Technology in 2004-2005 for the 2005 World Solar Challenge
World Solar Challenge
The World Solar Challenge is a solar-powered car race which covers through the Australian Outback, from Darwin to Adelaide.The race attracts teams from around the world, most of which are fielded by universities or corporations although some are fielded by high schools...
.
It succeeded the Nuna2
Nuna
Nuna is the name of a series of manned solar powered vehicles that won the World solar challenge in Australia four times in a row, in 2001 , 2003 , 2005 and 2007...
, the solar car that scored a second consecutive win for this solar team by winning the World Solar Challenge
World Solar Challenge
The World Solar Challenge is a solar-powered car race which covers through the Australian Outback, from Darwin to Adelaide.The race attracts teams from around the world, most of which are fielded by universities or corporations although some are fielded by high schools...
for the third time in a row.
Nuna 3 was one of the favourites for the 2005 edition of the World Solar Challenge with a pre-race test-drive recorded top speed of 130 km/h. The final result was that the 3021 kilometers between Darwin and Adelaide were covered in a record 29 hours and 11 minutes, averaging about 103 km/h.
It has very efficient solar cell
Solar cell
A solar cell is a solid state electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect....
s of a type normally used to power orbital satellites (as had the previous Nunas), and it has better aerodynamics
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is a branch of dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a moving object. Aerodynamics is a subfield of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, with much theory shared between them. Aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with...
and is lighter than its predecessors.
It was designed and built by 11 students from different disciplines of the Delft University of Technology, who have partly put their studies on hold for this. They used the hightech labs and workshops of the University and, as with the Nuna 2, they received advice from Wubbo Ockels
Wubbo Ockels
Prof. Dr. Wubbo Johannes Ockels is a Dutch physicist and a former ESA astronaut. In 1985 he participated in a flight on a space shuttle , making him the first Dutch citizen in space. He was not the first Dutch-born astronaut, as he is preceded by the naturalized American Lodewijk van den Berg, who...
, the first Dutch astronaut and professor at the University.
Main specifications
| Dimensions | 5 x 1.8 x 0.8 m | (l x w x h) |
| Weight | < 200 kg | |
| Air friction coefficient | 0.07 | this value is between 0.25 and 0.35 for modern cars |
| Solar cell efficiency | 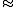 27% 27% |
this is a very high efficiency; for comparison the most efficient solar cells yet created under laboratory conditions were only 14% more efficient than this. The material used to fabricate these cells was a compound containing gallium arsenide Gaas Gaas is a commune in the Landes department in Aquitaine in south-western France.... . The efficiency of most panels is 15% |
| Effective solar cell area | > 8m^2 | including the solar cells attached to the sides of the car |
| Motor efficiency | > 97% | comparison: an average electromotor has an efficiency of 85% |
| Battery capacity | 5 kWh | comparison: an ordinary 24 kg car battery has a capacity of 80 Ah, which equals 1 kWh |
| Battery weight | 30 kg |
Design criteria
To have a good chance to win, the car has to:- collect as much solar energy as possible
- use as little energy as possible to drive at a certain speed. This means special attention to:
- the efficiency of transferring electrical energy to the wheels, and
- minimizing friction, constituted by:
- air friction (air resistance), and
- rolling friction, which in turn is affected by the weight, among other things
Solar cells
The solar cells are made of gallium arsenide (GaAs) and consist of three layers. Sunlight that penetrates the upper layer is used in the lower layers, resulting in an efficiency of over 26%. This type of solar cell is among the best available currently. Apart from efficiency, size also matters, so the entire upper surface of the Nuna 3 is covered with them, except for the cockpit.Efficiency is optimal when the cells are hit by the solar rays perpendicularly. If not, output is reduced by roughly the cosine of the angle with the perpendicular. Because the 2005 race was held in September (as opposed to October or November in previous years) the sun was lower in the sky (it's earlier in spring). To compensate for this, as many cells as possible were placed at the sides, most notably on the wheel caps.
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
depends on the load (more precisely the resistance of the load). The power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
is the product of voltage and current and therefore also depends on the load. Over a certain voltage the current of the solar cell quickly drops to zero, as the graph illustrates.
However, the batteries have a fairly constant voltage, which also has a rather different value than that of the solar cells. So a voltage transformation is needed. A special type of DC-DC converter is used to ensure the load resistance presented to the solar cells is such that the solar cells give maximum power, so also at the top of the green line in the graph. This is called a Maximum power point tracker
Maximum power point tracker
Maximum power point tracking is a technique that grid tie inverters, solar battery chargers and similar devices use to get the maximum possible power from the PV array. Solar cells have a complex relationship between solar irradiation, temperature and total resistance that produces a non-linear...
(MPPT). Here too, the goal is to have this conversion achieve maximum efficiency (>97%).
Aerodynamic design

Drag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag refers to forces which act on a solid object in the direction of the relative fluid flow velocity...
is an important part of the total resistance. Important are the frontal surface and the streamline. Any deviation from the ideal streamline will cause turbulence
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
, which costs energy. The ideal streamline is achieved in various stages:
- Through computer simulations of the design
- Through testing of a scale modelScale modelA scale model is a physical model, a representation or copy of an object that is larger or smaller than the actual size of the object, which seeks to maintain the relative proportions of the physical size of the original object. Very often the scale model is used as a guide to making the object in...
in a wind tunnelWind tunnelA wind tunnel is a research tool used in aerodynamic research to study the effects of air moving past solid objects.-Theory of operation:Wind tunnels were first proposed as a means of studying vehicles in free flight...
. For example, liquid paints can be applied to see the flow of air over the surface. The photo shows is taken during one of those tests in the Low Speed Laboratory of the TU Delft. - Through testing of the full scale car in a wind tunnel. For this a German-Dutch wind tunnel in EmmeloordEmmeloordEmmeloord is the administrative center of the municipality of Noordoostpolder, Flevoland, Netherlands.At the heart of the Noordoostpolder, where the three main drainage canals intersect, is the city of Emmeloord . Emmeloord is in a polder: land reclaimed from the IJsselmeer, which earlier was part...
will be used.
From meteorological
Meteorology
Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries...
data from the area where the contest is to take place, it can be concluded that there will likely be a strong side-wind. The wheel caps of the Nuna 3 are designed such that a sidewind will have a propulsory effect.
Motor
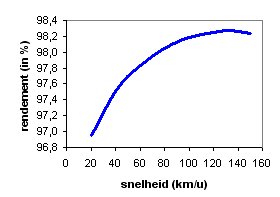
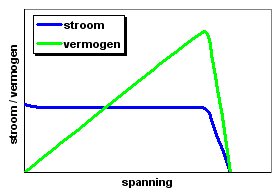
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
compared to the 1993 Spirit of Biel II. The efficiency of the total drive system (including the power electronics losses) is also improved and is now over 98%. But as the graph shows this depends somewhat on the speed and increases with speed. The design was initially made to reach its maximum performance at the normal cruising speed of the solar car at around 100 km/h.
Test drive
During one of the test drives in the Netherlands the Nuna 3 achieved a speed of 130 km/h. On the first day of the race the car achieved a top speed of 140 km/h. For comparison, the SunraycerSunraycer
The Sunraycer was a solar powered race car designed to compete in the world's first race featuring solar-powered cars. This race is now called the World Solar Challenge. The Sunraycer, a joint collaboration between General Motors, AeroVironment, and Hughes Aircraft, won the first race in 1987 by a...
(the first winner of the Solar Challenge race) attained a top speed of 109 km/h in 1987.
Important opponents
The winner of the North American Solar Challenge from the University of MichiganUniversity of Michigan Solar Car Team
The University of Michigan Solar Car Team is a 501 non-profit organization at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. It is the most successful solar car team in North America, having won the North American Solar Challenge six times and is currently the defending three time Champion...
(USA) was considered to be one of the most important opponents. Other important contestants were the MIT (also USA) and the Japanese Ashiya University
Ashiya University
is a private university in Ashiya, Hyōgo, Japan, founded in 1964.- External links :* in Japanese...
team. In 2005 there were also two other European contestants, the Dutch Raedthuys Solar Team from the University of Twente and the Belgian Umicore Solar Team from Leuven
Leuven
Leuven is the capital of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region, Belgium...
.
2005 race monitor
- 5 August 2005: the team arrives in AdelaideAdelaideAdelaide is the capital city of South Australia and the fifth-largest city in Australia. Adelaide has an estimated population of more than 1.2 million...
. - 2 September 2005: The road permit is granted.
- 16 September 2005: During a test drive Nuna 3 strands in the rough next to the road. A defective wheel suspension turned out to be the cause. The damage was limited and repaired after a few days.
- 22 September 2005: The Nuna 3 is approved by the organisation.
- 24 September 2005: The Nuna 3 qualifies for the 8th starting position, which is better than the starting positions the previous two models got.
- 25 September 2005: The Nuna 3 covered 827 km holding first place, leading the next-placed Michigan team by approximately half an hour.
- 26 September 2005: On the second day the Nuna 3 covered 835 km, at an average speed of 105 km/h, which is a new single-day record for the World Solar Challenge. The Michigan team is now 132 km behind.
- 27 September 2005: Nuna 3 covered 858 km, beating yesterdays record. They extended their lead to two hours. 500 km to go.
- 28 September 2005: Nuna 3 arrives as first car in Adelaide, thus scoring a hat-trickHat-trickA hat-trick or hat trick in sport is the achievement of a positive feat three times during a game, or other achievements based on threes. The term was first used in 1858 in cricket to describe HH Stephenson's feat of taking three wickets in three balls. A collection was held for Stephenson, and he...
. The overall average speed of 103 km/h over 3,010 km means an improvement by 6 km/h of the 2003 record.
This average speed, which could lead to maximum speeds of 140 km/h speeds on downhill section, well exceeding speed limits on the Australian highway, has led to rules changes for future races.

