
Nor-
Encyclopedia
In chemical nomenclature, nor is a prefix
to name a structural analog that can be derived
from a parent compound by the removal of one carbon atom along with the accompanying hydrogen. The nor-compound can be derived by demethylation
or by removal of a methylene
group, a CH group or a C atom. This includes the elimination of a methylene group in a cyclic
parent compound, followed by ring contraction.
"Nor" is an abbreviation of normal. Originally, the term was used to denote the completely demethylated form of the parent compound.
Later, the meaning was restricted to the removal of one group. If multiple groups are eliminated the prefix dinor, trinor, tetranor, etcetera is used. The prefix is preceded by the position number (locant) of the carbon atoms that disappear. For example 2,3-dinor. The original numbering of the parent compound is retained. According to IUPAC nomenclature, this prefix is not written with italic letters.
Nor is written directly in front of the stem name, without a hyphen between, unless there is another prefix after nor (for example α-).
The alternative use of "nor", in naming the unbranched form of a compound within a series of isomers (also referred to as "normal") is obsolete and not allowed in IUPAC names.
"nor" is that by A. Matthiessen and G.C. Foster in 1867 in a publication about the reaction between a strong acid and opianic acid (see picture).
Opianic acid (C10H10O5) is a compound with two methyl-groups and they called it "dimethyl nor-opianic acid". After reaction with a strong acid a compound was attained with only one methyl (C9H8O5). This partially demethylated opianic acid they called "methyl normal opianic acid". The completely demethylated compound (C8H6O5) was denoted by the term "normal opianic acid", abbreviated as "nor-opianic acid".
Similarly Matthiessen and Foster called narcotine, which has three methoxy
groups, "trimethyl nor-narcotine". The singular demethylated narcotine was called "dimethyl nor-narcotine", the more demethylated narcotine "methyl nor-narcotine" and the completely demethylated form "normal narcotine" or "nor-narcotine".
"Since that time the meaning of the prefix has been generalized to denote the replacement of one or more methyl groups by H, or the disappearance of CH2 from a carbon chain".
At present, the meaning is restricted to denote the removal of only one group from the parent structure, rather than the completely demethylated form of the parent compound.
In literature, "nor" is sometimes called the "next lower homologue", although in this context "homologue"
is an inexact term. "Nor" only refers to the removal of one carbon atom with the accompanying hydrogen, not the removal of other units. "Nor" compares two related compounds; it does not describe the relation to a homologous series
.
but in response to a review of A.M. Woolman,
Gaddum retracted his support for this etymology.
Woolman believed that "N ohne Radikal" was a German mnemonic
and likely a backronym
, rather than the real meaning of the prefix "nor". This can be argued with the fact "that the prefix nor is used for many compounds which contain no nitrogen at all". Moreover, in the German language both Nitrogen and Radikal are written with a capital, whereas the prefix "nor" is written in lower case letters.
Names of unbranched alkanes and alkanols, like "normal butane" and "normal propyl alcohol
", which are obsolete now,
have become the prefix n-,however, not "nor".
Other "normal" compounds got the prefix "nor". Older trivial name
s, like norleucine
and norvaline
are retained, but the use of the prefix for isomeric compounds was already discouraged in 1955 or earlier.
Prefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the root of a word. Particularly in the study of languages,a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed.Examples of prefixes:...
to name a structural analog that can be derived
Derivative (chemistry)
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by some chemical or physical process. In the past it was also used to mean a compound that can be imagined to arise from another compound, if one atom is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern...
from a parent compound by the removal of one carbon atom along with the accompanying hydrogen. The nor-compound can be derived by demethylation
Demethylation
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal a of methyl group from a molecule.A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms....
or by removal of a methylene
Methylene
Methylene is a chemical species in which a carbon atom is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Three different possibilities present themselves:* the -CH2- substituent group: e.g., dichloromethane ....
group, a CH group or a C atom. This includes the elimination of a methylene group in a cyclic
Cyclic compound
In chemistry, a cyclic compound is a compound in which a series of atoms is connected to form a loop or ring.While the vast majority of cyclic compounds are organic, a few inorganic substances form cyclic compounds as well, including sulfur, silanes, phosphanes, phosphoric acid, and triboric acid. ...
parent compound, followed by ring contraction.
"Nor" is an abbreviation of normal. Originally, the term was used to denote the completely demethylated form of the parent compound.
Later, the meaning was restricted to the removal of one group. If multiple groups are eliminated the prefix dinor, trinor, tetranor, etcetera is used. The prefix is preceded by the position number (locant) of the carbon atoms that disappear. For example 2,3-dinor. The original numbering of the parent compound is retained. According to IUPAC nomenclature, this prefix is not written with italic letters.
Nor is written directly in front of the stem name, without a hyphen between, unless there is another prefix after nor (for example α-).
The alternative use of "nor", in naming the unbranched form of a compound within a series of isomers (also referred to as "normal") is obsolete and not allowed in IUPAC names.
History
Possibly the earliest known use of the prefixPrefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the root of a word. Particularly in the study of languages,a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed.Examples of prefixes:...
"nor" is that by A. Matthiessen and G.C. Foster in 1867 in a publication about the reaction between a strong acid and opianic acid (see picture).
Opianic acid (C10H10O5) is a compound with two methyl-groups and they called it "dimethyl nor-opianic acid". After reaction with a strong acid a compound was attained with only one methyl (C9H8O5). This partially demethylated opianic acid they called "methyl normal opianic acid". The completely demethylated compound (C8H6O5) was denoted by the term "normal opianic acid", abbreviated as "nor-opianic acid".
Similarly Matthiessen and Foster called narcotine, which has three methoxy
Methoxy
In chemistry , methoxy refers to the functional group consisting of a methyl group bound to oxygen. This alkoxy group has the formula O–CH3.The word is used in organic nomenclature usually to describe an ether...
groups, "trimethyl nor-narcotine". The singular demethylated narcotine was called "dimethyl nor-narcotine", the more demethylated narcotine "methyl nor-narcotine" and the completely demethylated form "normal narcotine" or "nor-narcotine".
"Since that time the meaning of the prefix has been generalized to denote the replacement of one or more methyl groups by H, or the disappearance of CH2 from a carbon chain".
At present, the meaning is restricted to denote the removal of only one group from the parent structure, rather than the completely demethylated form of the parent compound.
In literature, "nor" is sometimes called the "next lower homologue", although in this context "homologue"
Homology (chemistry)
In chemistry, homology refers to the appearance of homologues. A homologue is a compound belonging to a series of compounds differing from each other by a repeating unit, such as a methylene group, a peptide residue, etcetera....
is an inexact term. "Nor" only refers to the removal of one carbon atom with the accompanying hydrogen, not the removal of other units. "Nor" compares two related compounds; it does not describe the relation to a homologous series
Homologous series
In chemistry, a homologous series is a series of compounds with a similar general formula, possessing similar chemical properties due to the presence of the same functional group, and showing a gradation in physical properties as a result of increase in molecular size and mass...
.
False etymology
It is suggested that "nor" is an acronym of German "N ohne Radikal". At first, the British pharmacologist John H. Gaddum followed this theory,but in response to a review of A.M. Woolman,
Gaddum retracted his support for this etymology.
Woolman believed that "N ohne Radikal" was a German mnemonic
Mnemonic
A mnemonic , or mnemonic device, is any learning technique that aids memory. To improve long term memory, mnemonic systems are used to make memorization easier. Commonly encountered mnemonics are often verbal, such as a very short poem or a special word used to help a person remember something,...
and likely a backronym
Backronym
A backronym or bacronym is a phrase constructed purposely, such that an acronym can be formed to a specific desired word. Backronyms may be invented with serious or humorous intent, or may be a type of false or folk etymology....
, rather than the real meaning of the prefix "nor". This can be argued with the fact "that the prefix nor is used for many compounds which contain no nitrogen at all". Moreover, in the German language both Nitrogen and Radikal are written with a capital, whereas the prefix "nor" is written in lower case letters.
Obsolete use of the term
Originally, "nor" had an ambiguous meaning, as the term "normal" could also refer to the unbranched form in a series of isomers, for example as with alkanes, alkanols and some amino acids.Names of unbranched alkanes and alkanols, like "normal butane" and "normal propyl alcohol
Propan-1-ol
1-Propanol is a primary alcohol with the molecular formula of C3H8O, and a structural formula of CH3CH2CH2OH. It is also known as propan-1-ol, 1-propyl alcohol, n-propyl alcohol, n-propanol, or simply propanol. It is an isomer of isopropanol . It is used as a solvent in the pharmaceutical...
", which are obsolete now,
have become the prefix n-,however, not "nor".
Other "normal" compounds got the prefix "nor". Older trivial name
Trivial name
In chemistry, a trivial name is a common name or vernacular name; it is a non-systematic name or non-scientific name. That is, the name is not recognised according to the rules of any formal system of nomenclature...
s, like norleucine
Leucines
The leucines are primarily the four isomeric amino acids: leucine, isoleucine, tert-leucine and norleucine. Being compared with the four butanols, they could be classified as butyl-substituted glycines; they represent all four possible variations....
and norvaline
Norvaline
Norvaline is an amino acid with the chemical formula C5H11NO2, isomeric with valine. This amino acid is often made synthetically.-Background:...
are retained, but the use of the prefix for isomeric compounds was already discouraged in 1955 or earlier.
Examples
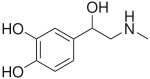 |
||
| epinephrine | norepinephrine | |
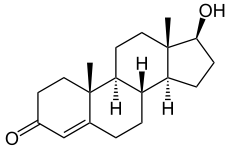 |
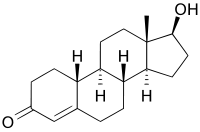 |
|
| testosterone | nortestosterone |

