
Demethylation
Encyclopedia
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal a of methyl group
(CH3) from a molecule.
A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms.
Methyl group
Methyl group is a functional group derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms —CH3. The group is often abbreviated Me. Such hydrocarbon groups occur in many organic compounds. The methyl group can be found in three forms: anion, cation and radical. The anion...
(CH3) from a molecule.
A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms.
In biochemistry
- In biochemical systems, the process of demethylation is often catalyzed by an enzymeEnzymeEnzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
such as one of the Cytochrome P450 (CYP) family of liver enzymes and by fungal aromatic peroxygenases such as Agrocybe aegerita peroxygenase.
Examples
| Krapcho decarboxylation Krapcho decarboxylation The Krapcho decarboxylation is the chemical reaction of esters with halide anions. The ester must contain an electron-withdrawing group in the beta position, such as β-ketoesters, malonic esters, α-cyanoesters, or α-sulfonylesters. It works best with methyl esters, since it is basically a... : |
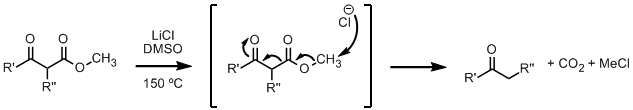 |
| | | |
See also
- MethylationMethylationIn the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a hydrogen atom...
, the addition of a methyl groupMethyl groupMethyl group is a functional group derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms —CH3. The group is often abbreviated Me. Such hydrocarbon groups occur in many organic compounds. The methyl group can be found in three forms: anion, cation and radical. The anion...
to a substrateSubstrate (chemistry)In chemistry, a substrate is the chemical species being observed, which reacts with a reagent. This term is highly context-dependent. In particular, in biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts....

