
Leucines
Encyclopedia
The leucines are primarily the four isomer
ic amino acid
s: leucine
, isoleucine
, tert-leucine and norleucine
. Being compared with the four butanol
s, they could be classified as butyl-substituted glycine
s; they represent all four possible variations.
Leucine and isoleucine belong to the proteinogenic amino acid
s; the others are non-natural.
Including the stereoisomers, six further isomers could be added: D-leucine, D-isoleucine, L-allo-isoleucine, D-allo-isoleucine, D-tert-leucine and D-norleucine.,
Cycloleucine
could be classified as a cyclic derivate of norleucine
. With a cyclopentane
-ring, it has two hydrogen atoms less and thus is not an isomer. The α-carbon atom is not a stereocenter.
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
ic amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s: leucine
Leucine
Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins...
, isoleucine
Isoleucine
Isoleucine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCHCH2CH3. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested. Its codons are AUU, AUC and AUA....
, tert-leucine and norleucine
Norleucine
Norleucine is an isomer of leucine, the α-amino acid 2-amino-hexanoic acid. It is not found in natural proteins. Norleucine is used in experimental studies of protein structure and function....
. Being compared with the four butanol
Butanol
Butanol or butyl alcohol can refer to any of the four isomeric alcohols of formula C4H9OH:*n-Butanol, butan-1-ol, 1-butanol, n-butyl alcohol;*Isobutanol, 2-methylpropan-1-ol, isobutyl alcohol;...
s, they could be classified as butyl-substituted glycine
Glycine
Glycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
s; they represent all four possible variations.
Leucine and isoleucine belong to the proteinogenic amino acid
Proteinogenic amino acid
Proteinogenic amino acids are those amino acids that can be found in proteins and require cellular machinery coded for in the genetic code of any organism for their isolated production. There are 22 standard amino acids, but only 21 are found in eukaryotes. Of the 22, 20 are directly encoded by...
s; the others are non-natural.
Including the stereoisomers, six further isomers could be added: D-leucine, D-isoleucine, L-allo-isoleucine, D-allo-isoleucine, D-tert-leucine and D-norleucine.,
Cycloleucine
Cycloleucine
Cycloleucine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid. It could be classified as a cyclic derivate of norleucine, having two hydrogen atoms less. Leading structure is a cyclopentane-ring...
could be classified as a cyclic derivate of norleucine
Norleucine
Norleucine is an isomer of leucine, the α-amino acid 2-amino-hexanoic acid. It is not found in natural proteins. Norleucine is used in experimental studies of protein structure and function....
. With a cyclopentane
Cyclopentane
Cyclopentane is a highly flammable alicyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula 510 and CAS number 287-92-3, consisting of a ring of five carbon atoms each bonded with two hydrogen atoms above and below the plane. It occurs as a colorless liquid with a petrol-like odor. Its melting point is −94 °C...
-ring, it has two hydrogen atoms less and thus is not an isomer. The α-carbon atom is not a stereocenter.
| Leucines | |||||
| Name | L-Leucine Leucine Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins... |
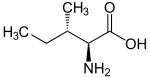
L-Isoleucine Isoleucine Isoleucine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCHCH2CH3. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested. Its codons are AUU, AUC and AUA.... |
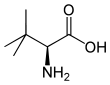
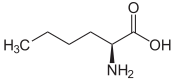
L-tert-Leucine (Terleucine) | L-Norleucine Norleucine Norleucine is an isomer of leucine, the α-amino acid 2-amino-hexanoic acid. It is not found in natural proteins. Norleucine is used in experimental studies of protein structure and function.... |
Cycloleucine Cycloleucine Cycloleucine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid. It could be classified as a cyclic derivate of norleucine, having two hydrogen atoms less. Leading structure is a cyclopentane-ring... |
| Other names | 2-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid, Isobutylglycine |
2-Amino-3-methylpentanoic acid, sec-Butylglycine |
2-Amino-3,3-dimethylbutanoic acid, tert-Butylglycine |
2-Amino-hexanoic acid, n-Butylglycine |
1-Amino-cyclopentane-1-carboxylic acid |
| Structure | 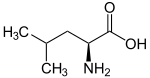 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| CAS-number | 61-90-5 | 73-32-5 | 20859-02-3 | 327-57-1 | 52-52-8 |
| PubChem PubChem PubChem is a database of chemical molecules and their activities against biological assays. The system is maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information , a component of the National Library of Medicine, which is part of the United States National Institutes of Health . PubChem can... |
|||||
| Molecular formula | C6H13NO2 | C6H11NO2 | |||
| Molar mass Molar mass Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol... |
131.18 g/mol Mol -Places:* City Municipality of Ljubljana, known after the acronym MOL in Slovene language * Märkisch-Oderland, a rural district of Brandenburg, Germany* Mol, Belgium, a municipality in Belgium* Mol, Serbia, a town in Serbia... |
129.16 g/mol | |||

