
Nonlinear acoustics
Encyclopedia
Non-linear acoustics is a branch of physics dealing with sound waves being distorted as they travel.
propagates through a material as a localized pressure
change. Increasing the pressure of a gas increases its temperature and the speed of sound
in a compressible material increases with temperature; as a result, the wave travels faster during the high pressure phase of the oscillation than during the lower pressure phase. This affects the wave's frequency structure; for example, in a plane sinusoidal wave of a single frequency, the peaks of the wave travel faster than the troughs, and the signal becomes more like a sawtooth wave. In doing so, other frequency
components are introduced, which can be described by the Fourier Series. This phenomenon is characteristic of a non-linear system, since a linear acoustic system responds only to the driving frequency.
Additionally, waves of different amplitudes will generate different pressure gradients, contributing to the non-linear effect.
The pressure changes within a medium cause the wave energy to transfer to higher harmonics. Since attenuation
generally increases with frequency, a counter effect exists that changes the nature of the nonlinear effect over distance. To describe their level of nonlinearity, materials can be given a nonlinearity parameter, . The values of
. The values of  and
and  are the coefficients of the first and second order terms of the Taylor series
are the coefficients of the first and second order terms of the Taylor series
expansion of the equation relating the material's pressure to its density. Typical values for the nonlinearity parameter in biological mediums are shown in the following table.
If the axis is in the direction of the sound beam path and the
axis is in the direction of the sound beam path and the  plane is perpendicular to that, the KZK equation can be written
plane is perpendicular to that, the KZK equation can be written

where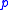 is the sound pressure,
is the sound pressure, 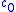 is the small signal sound speed,
is the small signal sound speed, 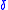 is the sound diffusivity,
is the sound diffusivity, 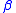 is the non-linearity coefficient,
is the non-linearity coefficient, 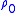 is the ambient density and
is the ambient density and 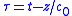 is retarded time.
is retarded time.
The equation can be solved for a particular system using a finite difference
scheme. Such solutions show how the sound beam distorts as it passes through a non-linear medium.
. Generally, this makes the boom more 'sharp' or sudden, as the high-amplitude peak moves to the wavefront.
would not be possible without understanding nonlinear acoustic phenomena. The nonlinear effects are particular evident due to the high-powered acoustic waves involved.
to wavelength
ratio, ultrasonic waves
commonly display nonlinear propagation behavior. For example, nonlinear acoustics is a field of interest for medical ultrasonography
because it can be exploited to produce a better image quality.
Introduction
A sound waveWave
In physics, a wave is a disturbance that travels through space and time, accompanied by the transfer of energy.Waves travel and the wave motion transfers energy from one point to another, often with no permanent displacement of the particles of the medium—that is, with little or no associated mass...
propagates through a material as a localized pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
change. Increasing the pressure of a gas increases its temperature and the speed of sound
Speed of sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled during a unit of time by a sound wave propagating through an elastic medium. In dry air at , the speed of sound is . This is , or about one kilometer in three seconds or approximately one mile in five seconds....
in a compressible material increases with temperature; as a result, the wave travels faster during the high pressure phase of the oscillation than during the lower pressure phase. This affects the wave's frequency structure; for example, in a plane sinusoidal wave of a single frequency, the peaks of the wave travel faster than the troughs, and the signal becomes more like a sawtooth wave. In doing so, other frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
components are introduced, which can be described by the Fourier Series. This phenomenon is characteristic of a non-linear system, since a linear acoustic system responds only to the driving frequency.
Additionally, waves of different amplitudes will generate different pressure gradients, contributing to the non-linear effect.
Physical Analysis
The pressure changes within a medium cause the wave energy to transfer to higher harmonics. Since attenuation
Attenuation
In physics, attenuation is the gradual loss in intensity of any kind of flux through a medium. For instance, sunlight is attenuated by dark glasses, X-rays are attenuated by lead, and light and sound are attenuated by water.In electrical engineering and telecommunications, attenuation affects the...
generally increases with frequency, a counter effect exists that changes the nature of the nonlinear effect over distance. To describe their level of nonlinearity, materials can be given a nonlinearity parameter,
 . The values of
. The values of  and
and  are the coefficients of the first and second order terms of the Taylor series
are the coefficients of the first and second order terms of the Taylor seriesTaylor series
In mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point....
expansion of the equation relating the material's pressure to its density. Typical values for the nonlinearity parameter in biological mediums are shown in the following table.
| Material | 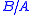 |
|---|---|
| Blood | 6.1 |
| Brain | 6.6 |
| Fat | 10 |
| Liver | 6.8 |
| Muscle | 7.4 |
| Water | 5.2 |
Mathematical model
The propagation of sound beams in a medium that exhibits non-linearity, diffraction and absorption is described by the Khokhlov-Zabolotskaya-Kuznetsov (KZK) equation. Solutions to this equation are generally used to model non-linear acoustics.If the
 axis is in the direction of the sound beam path and the
axis is in the direction of the sound beam path and the  plane is perpendicular to that, the KZK equation can be written
plane is perpendicular to that, the KZK equation can be written
where
 is the sound pressure,
is the sound pressure, 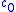 is the small signal sound speed,
is the small signal sound speed, 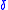 is the sound diffusivity,
is the sound diffusivity, 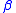 is the non-linearity coefficient,
is the non-linearity coefficient, 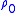 is the ambient density and
is the ambient density and 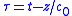 is retarded time.
is retarded time.The equation can be solved for a particular system using a finite difference
Finite difference
A finite difference is a mathematical expression of the form f − f. If a finite difference is divided by b − a, one gets a difference quotient...
scheme. Such solutions show how the sound beam distorts as it passes through a non-linear medium.
Sonic boom
The nonlinear behavior of the atmosphere leads to change of the wave shape in a sonic boomSonic boom
A sonic boom is the sound associated with the shock waves created by an object traveling through the air faster than the speed of sound. Sonic booms generate enormous amounts of sound energy, sounding much like an explosion...
. Generally, this makes the boom more 'sharp' or sudden, as the high-amplitude peak moves to the wavefront.
Acoustic levitation
The practice of acoustic levitationAcoustic levitation
Acoustic levitation is a method for suspending matter in a medium by using acoustic radiation pressure from intense sound waves in the medium. Acoustic levitation is possible because of the non-linear effects of intense sound waves....
would not be possible without understanding nonlinear acoustic phenomena. The nonlinear effects are particular evident due to the high-powered acoustic waves involved.
Ultrasonic waves
Because of their relatively high amplitudeAmplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
to wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
ratio, ultrasonic waves
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
commonly display nonlinear propagation behavior. For example, nonlinear acoustics is a field of interest for medical ultrasonography
Medical ultrasonography
Diagnostic sonography is an ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging technique used for visualizing subcutaneous body structures including tendons, muscles, joints, vessels and internal organs for possible pathology or lesions...
because it can be exploited to produce a better image quality.

