
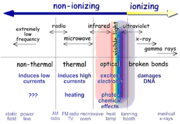
Non-ionizing radiation
Encyclopedia
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
that does not carry enough energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
per quantum
Quantum
In physics, a quantum is the minimum amount of any physical entity involved in an interaction. Behind this, one finds the fundamental notion that a physical property may be "quantized," referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This means that the magnitude can take on only certain discrete...
to ionize atoms or molecules—that is, to completely remove an electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
from an atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
or molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
. Instead of producing charged
ions when passing through matter, the electromagnetic radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
has sufficient energy only for excitation, the movement of an electron to a higher energy state. Nevertheless, different biological effects are observed for different types of non-ionizing radiation.
Near ultraviolet, visible light, infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
, microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
, radio waves
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
, and low-frequency RF (longwave) are all examples of non-ionizing radiation. Visible and near ultraviolet may induce photochemical reactions, ionize some molecules or accelerate radical reactions, such as photochemical aging of varnishes or the breakdown of flavoring compounds in beer to produce the "lightstruck flavor". The light from the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
that reaches the earth is largely composed of non-ionizing radiation, with the notable exception of some ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
rays. However, most ionizing radiation is filtered out by the Earth's atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
. Static fields do not radiate.
Health risks

Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens...
effects such as inciting thermal energy in biological tissue that can lead to burns.
In terms of potential biological effects, the non-ionizing portion of the spectrum can be subdivided into:
- The optical radiation portion, where electron excitation can occur (visible light, infrared light)
- The portion where the wavelength is smaller than the body, and heating via induced currents can occur (MW and higher-frequency RF)
- The portion where the wavelength is much larger than the body, and heating via induced currents seldom occurs (lower-frequency RF, power frequencies, static fields).
| Source | Wavelength | Frequency | Biological effects | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UVA Black light A black light, also referred to as a UV light, ultraviolet light, or Wood's lamp, is a lamp that emits ultraviolet radiation in the long-wave range, and little visible light... |
Black light Black light A black light, also referred to as a UV light, ultraviolet light, or Wood's lamp, is a lamp that emits ultraviolet radiation in the long-wave range, and little visible light... , sunlight |
318–400 nm | 750–950 THz | Eye – photochemical cataract Cataract A cataract is a clouding that develops in the crystalline lens of the eye or in its envelope, varying in degree from slight to complete opacity and obstructing the passage of light... ; skin – erythema, inc. pigmentation |
| Visible light | Lasers, sunlight, fire Fire Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material in the chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products. Slower oxidative processes like rusting or digestion are not included by this definition.... , LEDs, light bulbs |
400–780 nm | 385–750 THz | Skin photoaging Photoaging Photoaging or photoageing is a term used for the characteristic changes induced by chronic UVA and UVB exposure. Tretinoin is the best studied retinoid in the treatment of photoaging... ; eye – photochemical & thermal retinal injury |
| IR-A Infrared Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm... |
Lasers, remote controls | 780 nm – 1.4 µm | 215–385 THz | Eye – thermal retinal injury, thermal cataract; skin burn |
| IR-B Infrared Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm... |
Lasers | 1.4–3 µm | 100–215 THz | Eye – corneal burn, cataract; skin burn |
| IR-C Infrared Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm... |
Far-infrared laser | 3 µm – 1 mm | 300 GHz – 100 THz | Eye – corneal burn, cataract; heating of body surface |
| Microwave Microwave Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries... |
PCS phones, some mobile/cell phones, microwave ovens, cordless phones, motion detectors, long-distance telecommunications, radar, Wi-Fi Wi-Fi Wi-Fi or Wifi, is a mechanism for wirelessly connecting electronic devices. A device enabled with Wi-Fi, such as a personal computer, video game console, smartphone, or digital audio player, can connect to the Internet via a wireless network access point. An access point has a range of about 20... |
1 mm – 33 cm | 1–300 GHz | Heating of body tissue |
| Radio-frequency radiation Radio Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space... |
Mobile/cell phones, television, FM, AM, shortwave, CB, cordless phones | 33 cm – 3 km | 100 kHz – 1 GHz | Heating of body tissue, raised body temperature |
| Low-frequency RF | Power lines | >3 km | <100 kHz | Cumulation of charge on body surface; disturbance of nerve & muscle responses |
| Static field | Strong magnets, MRI | Infinite | 0 Hz | Magnetic – vertigo/nausea; electric – charge on body surface |
Ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet light can cause burnsBurn (injury)
A burn is a type of injury to flesh caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, light, radiation or friction. Most burns affect only the skin . Rarely, deeper tissues, such as muscle, bone, and blood vessels can also be injured...
to skin
and cataract
Cataract
A cataract is a clouding that develops in the crystalline lens of the eye or in its envelope, varying in degree from slight to complete opacity and obstructing the passage of light...
s to the eyes. Ultraviolet is classified into near, medium and far UV according to energy, where near ultraviolet is non-ionizing. Ultraviolet light produces free radicals that induce cellular damage, which can be carcinogenic. Ultraviolet light also induces melanin
Melanin
Melanin is a pigment that is ubiquitous in nature, being found in most organisms . In animals melanin pigments are derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine. The most common form of biological melanin is eumelanin, a brown-black polymer of dihydroxyindole carboxylic acids, and their reduced forms...
production from melanocyte
Melanocyte
-External links: - "Eye: fovea, RPE" - "Integument: pigmented skin"...
cells to cause sun tanning
Sun tanning
Sun tanning or simply tanning is the process whereby skin color is darkened or tanned. The process is most often a result of exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or from artificial sources, such as a tanning bed, but can also be a result of windburn or reflected light...
of skin. Vitamin D
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids. In humans, vitamin D is unique both because it functions as a prohormone and because the body can synthesize it when sun exposure is adequate ....
is produced on the skin by a radical reaction initiated by UV radiation.
Plastic (polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
PolycarbonatePhysical PropertiesDensity 1.20–1.22 g/cm3Abbe number 34.0Refractive index 1.584–1.586FlammabilityV0-V2Limiting oxygen index25–27%Water absorption – Equilibrium0.16–0.35%Water absorption – over 24 hours0.1%...
) sunglasses generally absorb UV radiation. UV overexposure to the eyes causes snow blindness
Snow blindness
Photokeratitis or ultraviolet keratitis is a painful eye condition caused by exposure of insufficiently protected eyes to the ultraviolet rays from either natural or artificial sources. Photokeratitis is akin to a sunburn of the cornea and conjunctiva, and is not usually noticed until several...
, which is a risk particularly on the sea or when there is snow on the ground.
Visible and infrared, lasers
Visible light causes few effects to the human body. Bright visible light irritates the eyes. Visible-light lasers have much more powerful effects and may damage the eyes even at small powers. Very strong visible light is used for cauterizing hair follicles.See also
- Ionizing radiationIonizing radiationIonizing radiation is radiation composed of particles that individually have sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. This ionization produces free radicals, which are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons...
- Electromagnetic hypersensitivityElectromagnetic hypersensitivityIdiopathic environmental intolerance attributed to electromagnetic fields is a set of claims of adverse medical symptoms purportedly caused by exposure to electromagnetic fields. Other terms for IEI-EMF include electromagnetic hypersensitivity , electrohypersensitivity, electro-sensitivity, and...
- Mobile phone radiation and healthMobile phone radiation and healthThe effect of mobile phone radiation on human health is the subject of recent interest and study, as a result of the enormous increase in mobile phone usage throughout the world . Mobile phones use electromagnetic radiation in the microwave range...
- Electromagnetic radiation and health
- Wireless electronic devices and healthWireless electronic devices and healthThe World Health Organization has acknowledged that electromagnetic fields are influencing the environment , and that some people are worried about possible effects...
- Electronic harassmentElectronic harassmentElectronic harassment is a term referring to the use of electronic devices to harass, torture, or physically harm a person, not to be confused with cyberstalking.- Michigan :...

