Niemann-Pick disease, type C
Encyclopedia
Niemann-Pick type C is a lysosomal storage disease
associated with mutations in NPC1
and NPC2
genes. Niemann-Pick Type C strikes an estimated 1:150,000 people. Approximately 50% of cases present before 10 years of age, but manifestations may first be recognized as late as the sixth decade.
. In Types A & B, there is complete or partial deficiency of an enzyme
called acid sphingomyelinase. In Niemann Pick Type C, the protein
product of the major mutated gene NPC1
is not an enzyme but appears to function as a transporter in the endosomal-lysosomal system, which moves large water-insoluble molecules through the cell
. The protein coded by the NPC2
gene more closely resembles an enzyme
structurally but seems to act in cooperation with the NPC1 protein in transporting molecules in the cell. The disruption of this transport system results in the accumulation of cholesterol
and glycolipids in lysosomes.
Cholesterol and glycolipids have varied roles in the cell. Cholesterol is a major component of cell plasma membranes, which define the cell as a whole and its organelles. It is also the basic building block of steroid
hormones, including neurosteroids. In Niemann-Pick Type C, large amounts of free or unesterfied cholesterol accumulates in lysosomes, and leads to relative deficiency of this molecule in multiple membranes and for steroid synthesis. The accumulation of glycosphingolipids
in the nervous system
has been linked to structural changes, namely ectopic dendritogenesis and meganeurite formation, and has been targeted therapeutically.
Several theories have attempted to link the accumulation of cholesterol and glycolipids in the lysosomes with the malfunction of the NPC-1 protein.
Neufeld et al. hypothesized that the accumulation of mannose 6-phosphate receptor
s (MPRs) in the late endosome signals failure of retrograde trafficking of cholesterol via the trans Golgi
Network.
gene, referred to as type C1; 5% are caused by mutations in the NPC2
gene, referred to as type C2. The clinical manifestations of types Niemann Pick Type C1 and C2 are similar because the respective genes are both involved in egress of lipids, particularly cholesterol, from late endosomes or lysosomes. The NPC1 gene is located on chromosome 18 (18q11-q12) and was described by researchers at the National Institutes of Health in July 1997.
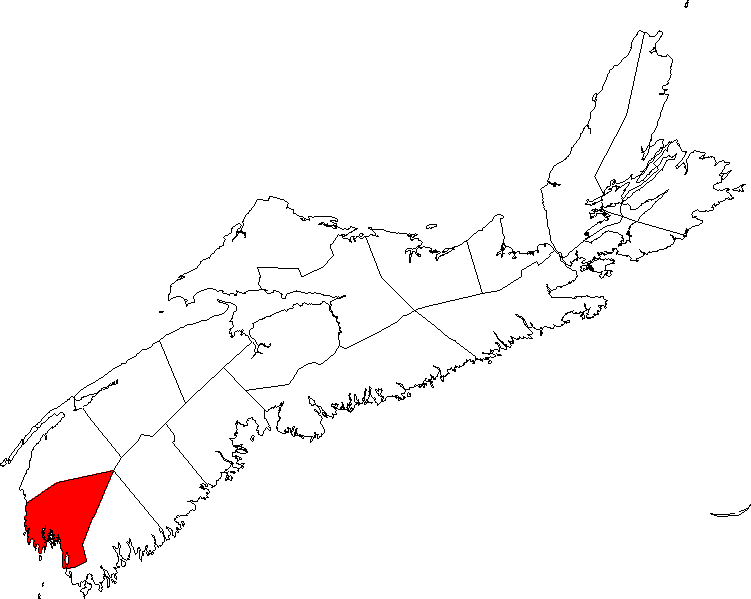 Type D Niemann-Pick has only been found in the French Canadian
Type D Niemann-Pick has only been found in the French Canadian
population of Yarmouth County, Nova Scotia
, and is now known to be allelic with Niemann Pick Type C.
Genelogical research indicates that Joseph Muise (c. 1679 - 1729) and Marie Amirault (1684 - c. 1735) are common ancestors to all people with Type D. This couple is the most likely origin for the type D variant.
) and liver (hepatomegaly
), or enlarged spleen/liver combined (hepatosplenomegaly
), but this finding may be absent in later onset cases. Prolonged jaundice
or elevated bilirubin
can present at birth. In some cases, however, enlargement of the spleen and/or liver does not occur for months or years - or not at all. Enlargement of the spleen and/or liver frequently becomes less apparent with time, in contrast to the progression of other lysosomal storage diseases such as Niemann-Pick disease, Types A and B or Gaucher disease. Organ enlargement does not usually cause major complications.
Progressive neurological disease is the hallmark of Niemann-Pick Type C disease, and is responsible for disability and premature death in all cases beyond early childhood. Classically, children with NPC may initially present with delays in reaching normal developmental milestones skills before manifesting cognitive decline (dementia
).
Neurological signs and symptoms include cerebellar ataxia
(unsteady walking with uncoordinated limb movements), dysarthria
(slurred speech), dysphagia
(difficulty in swallowing), tremor
, epilepsy
(both partial and generalized), vertical supranuclear palsy (upgaze palsy, downgaze palsy, saccadic palsy or paralysis), sleep inversion, gelastic cataplexy
(sudden loss of muscle tone or drop attacks), dystonia
(abnormal movements or postures caused by contraction of agonist and antagonist muscles across joints), most commonly begins with in turning of one foot when walking (action dystonia) and may spread to become generalized, spasticity
(velocity dependent increase in muscle tone), hypotonia
, ptosis
(drooping of the upper eyelid), microcephaly (abnormally small head), psychosis
, progressive dementia
, progressive hearing loss, bipolar disorder
, major and psychotic depression that can include hallucinations, delusions, mutism, or stupor.
In the terminal stages of Niemann Pick Type C disease, the patient is bedridden, with complete ophthalmoplegia, loss of volitional movement and has severe dementia.
. The fibroblasts are grown from a small skin biopsy taken from a patient with suspected NPC. The diagnosis can be confirmed by identifying mutations in the NPC1
or NPC2
genes in 80-90% of cases. This specialized testing is available at Thomas Jefferson University
Lysosomal Disease Testing Lab and the Mayo Clinic
.
, pulmonology
, gastroenterology
, orthopedics
, nutrition
, physical therapy
and occupational therapy
. Standard medications used to treat symptoms can be used in NPC patients. As patients develop difficulty with swallowing, food may need to be softened or thickened, and eventually, parents will need to consider placement of a gastrostomy tube (g-tube, feeding tube).
An observational study is underway at the National Institutes of Health
to better characterize the natural history of NPC and to attempt to identify markers of disease progression.
(HPBCD) was approved under compassionate use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat Addison and Cassidy Hempel, identical twin girls suffering from Niemann Pick Type C disease. Medi-ports, similar to ports used to administer chemotherapy drugs, were surgically placed into the twins' chest walls and allow doctors to directly infuse HPBCD into their bloodstreams. Treatment with cyclodextrin has been shown to delay clinical disease onset, reduced intraneuronal storage and secondary markers of neurodegeneration, and significantly increased lifespan in both the Niemann Pick Type C mice and feline models. (This is the second time in the United States that cyclodextrin alone has been administered in an attempt treat a fatal pediatric disease. Over 20 years ago, HPBCD was used in a medical case involving a boy suffering from severe hypervitaminosis A
.)
On May 17, 2010, the FDA granted hydroxy-propyl-beta-cyclodextrin orphan drug status and designated hydroxy-propyl-beta-cyclodextrin as a potential treatment for Niemann Pick Type C disease. On July 14, 2010, Dr. Caroline Hastings of Children's Hospital Research Center Oakland filed additional applications with the FDA requesting approval to deliver hydroxy-propyl-beta-cyclodextrin directly into the central nervous system of the twins in an attempt to get HPBCD across the blood-brain barrier. The request was approved by the FDA on September 23, 2010, and bi-monthly intrathecal injections of HPBCD into the spine were started in October 2010. Additional filings have been made to the FDA by Children's Hospital Research Center Oakland requesting approval to surgically install Medtronic SynchroMed pumps into the twins to deliver continuous doses of HPBCD into their brains.
. Miglustat is a glucosylceramide synthase inhibitor, which inhibits the synthesis of glycosphingolipids
in cells. It has been shown to delay the onset of disease in the NPC mouse, and published data from a multi-center clinical trial of Miglustat in the United States and England and from case reports suggests that it may ameliorate the course of human NPC.
Several other treatment strategies are under investigation in cell culture and animal models of NPC. These include, cholesterol mobilization, neurosteroid (a special type of hormone that effects brain and other nerve cells) replacement using allopregnanolone
, rab overexpression to bypass the trafficking block (Pagano lab) and Curcumin
as an anti-inflammatory
and calcium
modulatory agent. The pregnane X receptor
has been identified as a potential target.
Neural stem cell
s have also been investigated in an animal model, and clear evidence of life extension in the mouse model has been shown.
Low cholesterol diets are often used, but there is no evidence of efficacy. On March 22, 2011, scientists at the University of Notre Dame and Cornell University made a breakthrough in the cure for this disease. No known cure is known yet, but we are much closer to one.
Lysosomal storage disease
Lysosomal storage diseases are a group of approximately 50 rare inherited metabolic disorders that result from defects in lysosomal function...
associated with mutations in NPC1
NPC1
Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 also known as NPC1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NPC1 gene.NPC1 was identified as the gene that when mutated, results in Niemann-Pick disease, type C...
and NPC2
NPC2
NPC2 is a protein associated with Niemann-Pick disease, type C....
genes. Niemann-Pick Type C strikes an estimated 1:150,000 people. Approximately 50% of cases present before 10 years of age, but manifestations may first be recognized as late as the sixth decade.
Pathophysiology
Niemann-Pick Type C is biochemically, genetically and clinically distinct from Niemann Pick Types A or and BNiemann-Pick disease, SMPD1-associated
Niemann-Pick disease, SMPD1-associated refers to two different types of Niemann-Pick disease which are associated with the SMPD1 gene.There are approximately 1,200 cases of NPA and NPB worldwide with the majority of cases being Type B or an intermediate form....
. In Types A & B, there is complete or partial deficiency of an enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
called acid sphingomyelinase. In Niemann Pick Type C, the protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
product of the major mutated gene NPC1
NPC1
Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 also known as NPC1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NPC1 gene.NPC1 was identified as the gene that when mutated, results in Niemann-Pick disease, type C...
is not an enzyme but appears to function as a transporter in the endosomal-lysosomal system, which moves large water-insoluble molecules through the cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
. The protein coded by the NPC2
NPC2
NPC2 is a protein associated with Niemann-Pick disease, type C....
gene more closely resembles an enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
structurally but seems to act in cooperation with the NPC1 protein in transporting molecules in the cell. The disruption of this transport system results in the accumulation of cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
and glycolipids in lysosomes.
Cholesterol and glycolipids have varied roles in the cell. Cholesterol is a major component of cell plasma membranes, which define the cell as a whole and its organelles. It is also the basic building block of steroid
Steroid
A steroid is a type of organic compound that contains a characteristic arrangement of four cycloalkane rings that are joined to each other. Examples of steroids include the dietary fat cholesterol, the sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, and the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone.The core...
hormones, including neurosteroids. In Niemann-Pick Type C, large amounts of free or unesterfied cholesterol accumulates in lysosomes, and leads to relative deficiency of this molecule in multiple membranes and for steroid synthesis. The accumulation of glycosphingolipids
Glycosphingolipids
Glycosphingolipids are a subtype of glycolipids containing the amino alcohol sphingosine. They include:* Cerebrosides* Gangliosides* Globosides...
in the nervous system
Nervous system
The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. In most animals the nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The central nervous...
has been linked to structural changes, namely ectopic dendritogenesis and meganeurite formation, and has been targeted therapeutically.
Several theories have attempted to link the accumulation of cholesterol and glycolipids in the lysosomes with the malfunction of the NPC-1 protein.
Neufeld et al. hypothesized that the accumulation of mannose 6-phosphate receptor
Mannose 6-phosphate receptor
In the fields of biochemistry and cell biology, mannose 6-phosphate receptors are proteins that bind newly synthesized lysosomal hydrolases in the trans-Golgi network and deliver them to pre-lysosomal compartments. There are two different MPRs, one of ~300kDa and a smaller, dimeric receptor of...
s (MPRs) in the late endosome signals failure of retrograde trafficking of cholesterol via the trans Golgi
Golgi
Golgi may refer to:*Camillo Golgi , Italian physician and scientist after which the following terms are named:**Golgi apparatus , an organelle in the eukaryotic cell...
Network.
- Another theory suggests that the blockage of retrograde cholesterol breakdown in the late endosome is due to decreased membrane elasticity and thus the return vesiclesVesicle (biology)A vesicle is a bubble of liquid within another liquid, a supramolecular assembly made up of many different molecules. More technically, a vesicle is a small membrane-enclosed sack that can store or transport substances. Vesicles can form naturally because of the properties of lipid membranes , or...
of cholesterol to the trans GolgiGolgiGolgi may refer to:*Camillo Golgi , Italian physician and scientist after which the following terms are named:**Golgi apparatus , an organelle in the eukaryotic cell...
Network cannot bud and form.
- Iouannou, et al. have described similarities between the NPC1 protein and members of the resistance-nodulation-division (RND) family of prokaryotic permeases, suggesting a pumping function for NPC1.
- Recent evidence indicates that NPC-1 may play an important role in calciumCalciumCalcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
regulation.
Genetics and classification
Approximately 95% of Niemann-Pick Type C cases are caused by genetic mutations in the NPC1NPC1
Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 also known as NPC1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NPC1 gene.NPC1 was identified as the gene that when mutated, results in Niemann-Pick disease, type C...
gene, referred to as type C1; 5% are caused by mutations in the NPC2
NPC2
NPC2 is a protein associated with Niemann-Pick disease, type C....
gene, referred to as type C2. The clinical manifestations of types Niemann Pick Type C1 and C2 are similar because the respective genes are both involved in egress of lipids, particularly cholesterol, from late endosomes or lysosomes. The NPC1 gene is located on chromosome 18 (18q11-q12) and was described by researchers at the National Institutes of Health in July 1997.
- The NPC1 gene encodes a proteinMembrane proteinA membrane protein is a protein molecule that is attached to, or associated with the membrane of a cell or an organelle. More than half of all proteins interact with membranes.-Function:...
that is located in membranes inside the cell and is involved in the movement of cholesterol and lipids within cells. A deficiency of this protein leads to the abnormal build up of lipids and cholesterol within cell membranes.
- The NPC2 gene encodes a protein that binds and transports cholesterol. It has been shown to closely interact with NPC1.
"Type D" variant

French Canadian
French Canadian or Francophone Canadian, , generally refers to the descendents of French colonists who arrived in New France in the 17th and 18th centuries...
population of Yarmouth County, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The name of the province is Latin for "New Scotland," but "Nova Scotia" is the recognized, English-language name of the province. The provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the...
, and is now known to be allelic with Niemann Pick Type C.
Genelogical research indicates that Joseph Muise (c. 1679 - 1729) and Marie Amirault (1684 - c. 1735) are common ancestors to all people with Type D. This couple is the most likely origin for the type D variant.
Symptoms
Niemann-Pick Type C has a wide clinical spectrum. Affected individuals may have enlargement of the spleen (splenomegalySplenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant of the human abdomen. It is one of the four cardinal signs of hypersplenism, some reduction in the number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any...
) and liver (hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly is the condition of having an enlarged liver. It is a nonspecific medical sign having many causes, which can broadly be broken down into infection, direct toxicity, hepatic tumours, or metabolic disorder. Often, hepatomegaly will present as an abdominal mass...
), or enlarged spleen/liver combined (hepatosplenomegaly
Hepatosplenomegaly
Hepatosplenomegaly is the simultaneous enlargement of both the liver and the spleen . Hepatosplenomegaly can occur as the result of acute viral hepatitis or infectious mononucleosis, or it can be the sign of a serious and life threatening lysosomal storage disease...
), but this finding may be absent in later onset cases. Prolonged jaundice
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellowish pigmentation of the skin, the conjunctival membranes over the sclerae , and other mucous membranes caused by hyperbilirubinemia . This hyperbilirubinemia subsequently causes increased levels of bilirubin in the extracellular fluid...
or elevated bilirubin
Bilirubin
Bilirubin is the yellow breakdown product of normal heme catabolism. Heme is found in hemoglobin, a principal component of red blood cells. Bilirubin is excreted in bile and urine, and elevated levels may indicate certain diseases...
can present at birth. In some cases, however, enlargement of the spleen and/or liver does not occur for months or years - or not at all. Enlargement of the spleen and/or liver frequently becomes less apparent with time, in contrast to the progression of other lysosomal storage diseases such as Niemann-Pick disease, Types A and B or Gaucher disease. Organ enlargement does not usually cause major complications.
Progressive neurological disease is the hallmark of Niemann-Pick Type C disease, and is responsible for disability and premature death in all cases beyond early childhood. Classically, children with NPC may initially present with delays in reaching normal developmental milestones skills before manifesting cognitive decline (dementia
Dementia
Dementia is a serious loss of cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging...
).
Neurological signs and symptoms include cerebellar ataxia
Cerebellar ataxia
Cerebellar ataxia is a form of ataxia originating in the cerebellum.-References:...
(unsteady walking with uncoordinated limb movements), dysarthria
Dysarthria
Dysarthria is a motor speech disorder resulting from neurological injury of the motor component of the motor-speech system and is characterized by poor articulation of phonemes...
(slurred speech), dysphagia
Dysphagia
Dysphagia is the medical term for the symptom of difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, the term is sometimes used as a condition in its own right. Sufferers are sometimes unaware of their dysphagia....
(difficulty in swallowing), tremor
Tremor
A tremor is an involuntary, somewhat rhythmic, muscle contraction and relaxation involving to-and-fro movements of one or more body parts. It is the most common of all involuntary movements and can affect the hands, arms, eyes, face, head, vocal folds, trunk, and legs. Most tremors occur in the...
, epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
(both partial and generalized), vertical supranuclear palsy (upgaze palsy, downgaze palsy, saccadic palsy or paralysis), sleep inversion, gelastic cataplexy
Cataplexy
Cataplexy is a sudden and transient episode of loss of muscle tone, often triggered by emotions. It is a rare disease , but affects roughly 70% of people who have narcolepsy...
(sudden loss of muscle tone or drop attacks), dystonia
Dystonia
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder, in which sustained muscle contractions cause twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures. The disorder may be hereditary or caused by other factors such as birth-related or other physical trauma, infection, poisoning or reaction to...
(abnormal movements or postures caused by contraction of agonist and antagonist muscles across joints), most commonly begins with in turning of one foot when walking (action dystonia) and may spread to become generalized, spasticity
Spasticity
Spasticity is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance in muscle tone involving hypertonia, which is also referred to as an unusual "tightness" of muscles...
(velocity dependent increase in muscle tone), hypotonia
Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone , often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength...
, ptosis
Ptosis
Ptosis refers to droopiness of a body part. Specifically, it can refer to:* Ptosis * Ptosis * Enteroptosis * Gastroptosis...
(drooping of the upper eyelid), microcephaly (abnormally small head), psychosis
Psychosis
Psychosis means abnormal condition of the mind, and is a generic psychiatric term for a mental state often described as involving a "loss of contact with reality"...
, progressive dementia
Dementia
Dementia is a serious loss of cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging...
, progressive hearing loss, bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder or bipolar affective disorder, historically known as manic–depressive disorder, is a psychiatric diagnosis that describes a category of mood disorders defined by the presence of one or more episodes of abnormally elevated energy levels, cognition, and mood with or without one or...
, major and psychotic depression that can include hallucinations, delusions, mutism, or stupor.
In the terminal stages of Niemann Pick Type C disease, the patient is bedridden, with complete ophthalmoplegia, loss of volitional movement and has severe dementia.
Diagnosis
Niemann Pick Type C is diagnosed by assaying cultured fibroblasts for cholesterol esterfication and staining for unesterified cholesterol with filipinFilipin
Filipin is a chemical compound. It was isolated by chemists at the Upjohn company in 1955 from the mycelium and culture filtrates of a previously unknown actinomycete, Streptomyces filipinensis, that was discovered in a soil sample collected in the Philippine Islands. Thus the name Filipin. The...
. The fibroblasts are grown from a small skin biopsy taken from a patient with suspected NPC. The diagnosis can be confirmed by identifying mutations in the NPC1
NPC1
Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 also known as NPC1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NPC1 gene.NPC1 was identified as the gene that when mutated, results in Niemann-Pick disease, type C...
or NPC2
NPC2
NPC2 is a protein associated with Niemann-Pick disease, type C....
genes in 80-90% of cases. This specialized testing is available at Thomas Jefferson University
Thomas Jefferson University
Thomas Jefferson University is a private health sciences university in Center City, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in the United States. The university consists of six constituent colleges and schools, Jefferson Medical College, Jefferson College of Graduate Studies, Jefferson School of Health...
Lysosomal Disease Testing Lab and the Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a not-for-profit medical practice and medical research group specializing in treating difficult patients . Patients are referred to Mayo Clinic from across the U.S. and the world, and it is known for innovative and effective treatments. Mayo Clinic is known for being at the top of...
.
Treatment
There is no known cure for Niemann Pick Type C, nor is there any FDA-standard approved disease modifying treatment. Supportive care is essential and substantially improves the quality of life of people affected by NPC. The therapeutic team may include specialists in neurologyNeurology
Neurology is a medical specialty dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Specifically, it deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of disease involving the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems, including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue,...
, pulmonology
Pulmonology
In medicine, pulmonology is the specialty that deals with diseases of the respiratory tract and respiratory disease. It is called chest medicine and respiratory medicine in some countries and areas...
, gastroenterology
Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology is the branch of medicine whereby the digestive system and its disorders are studied. The name is a combination of three Ancient Greek words gaster , enteron , and logos...
, orthopedics
Orthopedics
Orthopedics is the study of the musculoskeletal system. The Greek word 'ortho' means straight or correct and 'pedics' comes from the Greek 'pais' meaning children. For many centuries, orthopedists have been involved in the treatment of crippled children...
, nutrition
Nutrition
Nutrition is the provision, to cells and organisms, of the materials necessary to support life. Many common health problems can be prevented or alleviated with a healthy diet....
, physical therapy
Physical therapy
Physical therapy , often abbreviated PT, is a health care profession. Physical therapy is concerned with identifying and maximizing quality of life and movement potential within the spheres of promotion, prevention, diagnosis, treatment/intervention,and rehabilitation...
and occupational therapy
Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy is a discipline that aims to promote health by enabling people to perform meaningful and purposeful activities. Occupational therapists work with individuals who suffer from a mentally, physically, developmentally, and/or emotionally disabling condition by utilizing treatments...
. Standard medications used to treat symptoms can be used in NPC patients. As patients develop difficulty with swallowing, food may need to be softened or thickened, and eventually, parents will need to consider placement of a gastrostomy tube (g-tube, feeding tube).
An observational study is underway at the National Institutes of Health
National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health are an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and are the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and health-related research. Its science and engineering counterpart is the National Science Foundation...
to better characterize the natural history of NPC and to attempt to identify markers of disease progression.
Hydroxy-propyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HPBCD)
In April 2009, hydroxy-propyl-beta-cyclodextrinCyclodextrin
Cyclodextrins are a family of compounds made up of sugar molecules bound together in a ring ....
(HPBCD) was approved under compassionate use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat Addison and Cassidy Hempel, identical twin girls suffering from Niemann Pick Type C disease. Medi-ports, similar to ports used to administer chemotherapy drugs, were surgically placed into the twins' chest walls and allow doctors to directly infuse HPBCD into their bloodstreams. Treatment with cyclodextrin has been shown to delay clinical disease onset, reduced intraneuronal storage and secondary markers of neurodegeneration, and significantly increased lifespan in both the Niemann Pick Type C mice and feline models. (This is the second time in the United States that cyclodextrin alone has been administered in an attempt treat a fatal pediatric disease. Over 20 years ago, HPBCD was used in a medical case involving a boy suffering from severe hypervitaminosis A
Hypervitaminosis A
Hypervitaminosis A refers to the effects of excessive vitamin A intake.-Presentation:Effects include* Birth defects* Liver problems* Reduced bone mineral density that may result in osteoporosis* Coarse bone growths...
.)
On May 17, 2010, the FDA granted hydroxy-propyl-beta-cyclodextrin orphan drug status and designated hydroxy-propyl-beta-cyclodextrin as a potential treatment for Niemann Pick Type C disease. On July 14, 2010, Dr. Caroline Hastings of Children's Hospital Research Center Oakland filed additional applications with the FDA requesting approval to deliver hydroxy-propyl-beta-cyclodextrin directly into the central nervous system of the twins in an attempt to get HPBCD across the blood-brain barrier. The request was approved by the FDA on September 23, 2010, and bi-monthly intrathecal injections of HPBCD into the spine were started in October 2010. Additional filings have been made to the FDA by Children's Hospital Research Center Oakland requesting approval to surgically install Medtronic SynchroMed pumps into the twins to deliver continuous doses of HPBCD into their brains.
Other treatments under investigation
One drug that has been tried is MiglustatMiglustat
Miglustat is a drug developed by and is used primarily to treat Type 1 Gaucher disease . It is marketed under the trade name Zavesca. Miglustat is an imino sugar , a synthetic analogue of D-glucose and a white to off-white crystalline solid that has a bitter taste...
. Miglustat is a glucosylceramide synthase inhibitor, which inhibits the synthesis of glycosphingolipids
Glycosphingolipids
Glycosphingolipids are a subtype of glycolipids containing the amino alcohol sphingosine. They include:* Cerebrosides* Gangliosides* Globosides...
in cells. It has been shown to delay the onset of disease in the NPC mouse, and published data from a multi-center clinical trial of Miglustat in the United States and England and from case reports suggests that it may ameliorate the course of human NPC.
Several other treatment strategies are under investigation in cell culture and animal models of NPC. These include, cholesterol mobilization, neurosteroid (a special type of hormone that effects brain and other nerve cells) replacement using allopregnanolone
Allopregnanolone
Allopregnanolone is a prototypic neurosteroid present in the blood and also the brain. It is a metabolite of progesterone and potent modulator of GABAA receptors...
, rab overexpression to bypass the trafficking block (Pagano lab) and Curcumin
Curcumin
Curcumin is the principal curcuminoid of the popular Indian spice turmeric, which is a member of the ginger family . The other two curcuminoids are desmethoxycurcumin and bis-desmethoxycurcumin. The curcuminoids are natural phenols and are responsible for the yellow color of turmeric...
as an anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory refers to the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drugs make up about half of analgesics, remedying pain by reducing inflammation as opposed to opioids, which affect the central nervous system....
and calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
modulatory agent. The pregnane X receptor
Pregnane X receptor
In the field of molecular biology, the pregnane X receptor , also known as the steroid and xenobiotic sensing nuclear receptor or nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1I2 gene.PXR is a nuclear receptor whose primary function is to sense...
has been identified as a potential target.
Neural stem cell
Stem cell
This article is about the cell type. For the medical therapy, see Stem Cell TreatmentsStem cells are biological cells found in all multicellular organisms, that can divide and differentiate into diverse specialized cell types and can self-renew to produce more stem cells...
s have also been investigated in an animal model, and clear evidence of life extension in the mouse model has been shown.
Low cholesterol diets are often used, but there is no evidence of efficacy. On March 22, 2011, scientists at the University of Notre Dame and Cornell University made a breakthrough in the cure for this disease. No known cure is known yet, but we are much closer to one.
Prognosis
The lifespan of patients with NPC is usually related to the age of onset. Children with antenatal or infantile onset usually succumb in the first few months or years of life, whereas adolescent and adult onset forms of Niemann Pick Type C have a more insidious onset and slower progression, and affected individuals may survive to the seventh decade. Adult cases of NPC are being recognized with increasing frequency. It is suspected that many patients affected by NPC are undiagnosed, owing to lack of awareness of the disease and the absence of readily available screening or diagnostic tests. For the same reasons the diagnosis is often delayed by many years.External links
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Niemann-Pick Disease Type C
- OMIM entries on Niemann-Pick Type C
- National Institutes of Health Clinical Center Study On Niemann Pick Type C
- Marc C. Patterson, MD, child neurologist, Mayo Clinic
- Coriell Institute: Biobank that stores Niemann Pick Type C cells for research
- Addi and Cassi Hempel: Identical twins living with Niemann Pick Type C disease
- Testing labs for Niemann Pick Type C
- Clinical Description of Niemann Pick Type C
- Hide & Seek Foundation for Lysosomal Disease Research
- Detailed information about Niemann Pick Type C for patients and Healthcare Professionals incl. Glossary
- Portuguese description of Niemann Pick Type C, support and resources

