
Network address translation
Encyclopedia
In computer network
ing, network address translation (NAT) is the process of modifying IP address
information in IP packet headers while in transit across a traffic routing device.
The simplest type of NAT provides a one to one translation of IP addresses. RFC 2663 refers to this type of NAT as basic NAT. It is often also referred to as one-to-one NAT. In this type of NAT only the IP addresses, IP header checksum and any higher level checksums that include the IP address need to be changed. The rest of the packet can be left untouched (at least for basic TCP/UDP functionality, some higher level protocols may need further translation). Basic NATs can be used when there is a requirement to interconnect two IP networks with incompatible addressing.
However it is common to hide an entire IP address space, usually consisting of private IP addresses, behind a single IP address (or in some cases a small group of IP addresses) in another (usually public) address space. To avoid ambiguity in the handling of returned packets, a one-to-many NAT must alter higher level information such as TCP/UDP ports in outgoing communications and must maintain a translation table so that return packets can be correctly translated back. RFC 2663 uses the term NAPT (network address and port translation) for this type of NAT. Other names include PAT (port address translation), IP masquerading, NAT Overload and many-to-one NAT. Since this is the most common type of NAT it is often referred to simply as NAT.
As described, the method enables communication through the router only when the conversation originates in the masqueraded network, since this establishes the translation tables. For example, a web browser
in the masqueraded network can browse a website outside, but a web browser outside could not browse a web site in the masqueraded network. However, most NAT devices today allow the network administrator to configure translation table entries for permanent use. This feature is often referred to as "static NAT" or port forwarding
and allows traffic originating in the "outside" network to reach designated hosts in the masqueraded network.
In the mid-1990s NAT became a popular tool for alleviating the consequences of IPv4 address exhaustion. It has become a common, indispensable feature in routers for home and small-office Internet connections. Most systems using NAT do so in order to enable multiple host
s on a private network
to access the Internet
using a single public IP address.
Network address translation has serious drawbacks on the quality of Internet connectivity and requires careful attention to the details of its implementation. In particular all types of NAT break the originally envisioned model of IP end-to-end connectivity across the Internet and NAPT makes it difficult for systems behind a NAT to accept incoming communications. As a result, NAT traversal
methods have been devised to alleviate the issues encountered.
subnets (RFC 1918). A router on that network has a private address in that address space. The router is also connected to the Internet with a "public" address assigned by an Internet service provider
. As traffic passes from the local network to the Internet, the source address in each packet is translated on the fly from a private address to the public address. The router tracks basic data about each active connection (particularly the destination address and port). When a reply returns to the router, it uses the connection tracking data it stored during the outbound phase to determine the private address on the internal network to which to forward the reply.
All Internet packets have a source IP address and a destination IP address. Typically packets passing from the private network to the public network will have their source address modified while packets passing from the public network back to the private network will have their destination address modified. More complex configurations are also possible.
To avoid ambiguity in how to translate returned packets, further modifications to the packets are required. The vast bulk of Internet traffic is TCP and UDP packets and for these protocols the port numbers are changed so that the combination of IP and port information on the returned packet can be unambiguously mapped to the corresponding private address and port information. Protocols not based on TCP or UDP require other translation techniques. ICMP packets typically relate to an existing connection and need to be mapped using the same IP and port mappings as that connection.
This terminology has been the source of much confusion, as it has proven inadequate at describing real-life NAT behavior.
Many NAT implementations combine these types, and it is therefore better to refer to specific individual NAT behaviors instead of using the Cone/Symmetric terminology. Especially, most NAT translators combine symmetric NAT for outgoing connections with static port mapping, where incoming packets to the external address and port are redirected to a specific internal address and port. Some products can redirect packets to several internal hosts, e.g. to divide the load between a few servers. However, this introduces problems with more sophisticated communications that have many interconnected packets, and thus is rarely used.
, another way is to use various NAT traversal techniques. The most popular technique for TCP NAT traversal is TCP hole punching
, which requires the NAT to follow the port preservation design for TCP, as explained below.
Many NAT implementations follow the port preservation design especially for TCP, which is to say that they use the same values as internal and external port numbers. NAT port preservation for outgoing TCP connections is especially important for TCP NAT traversal
, because programs usually bind distinct TCP sockets to ephemeral ports for distinct TCP connections, rendering NAT port prediction impossible for TCP.
On the other hand, for UDP, NATs do not need to have port preservation because applications usually reuse the same UDP socket to send packets to distinct hosts, making port prediction straightforward, as it is the same source port for each packet.
Furthermore, port preservation in NAT for TCP allows P2P protocols to offer less complexity and less latency because there is no need to use a third party to discover the NAT port since the application already knows the NAT port.
However, if two internal hosts attempt to communicate with the same external host using the same port number, the external port number used by the second host will be chosen at random. Such NAT will be sometimes perceived as (address) restricted cone NAT and other times as symmetric NAT.
Recent studies have shown that roughly 70% of clients in P2P
networks employ some form of NAT.
and source port number as well as a destination IP address and destination port number. The port address/IP address pair forms a socket
. In particular, the source port address and source IP address form the source socket.
For publicly accessible services such as web servers and mail servers the port number is important. For example, port 80 connects to the web server
software and port 25 to a mail server's SMTP daemon
. The IP address of a public server is also important, similar in global uniqueness to a postal address or telephone number. Both IP address and port must be correctly known by all hosts wishing to successfully communicate.
Private IP addresses as described in RFC 1918 are significant only on private networks where they are used, which is also true for host ports. Ports are unique endpoints of communication on a host, so a connection through the NAT device is maintained by the combined mapping of port and IP address.
PAT resolves conflicts that would arise through two different hosts using the same source port number to establish unique connections at the same time.
NAT will only translate IP addresses and ports of its internal hosts, hiding the true endpoint of an internal host on a private network.
Typically the internal host is aware of the true IP address and TCP or UDP port of the external host. Typically the NAT device may function as the default gateway for the internal host. However the external host is only aware of the public IP address for the NAT device and the particular port being used to communicate on behalf of a specific internal host.
, depending on whether the payload is interpreted by a host on the "inside" or "outside" of translation. As soon as the protocol stack is traversed, even with such basic protocols as TCP
and UDP
, the protocols will break unless NAT takes action beyond the network layer.
IP packets have a checksum in each packet header, which provides error detection only for the header. IP datagrams may become fragmented and it is necessary for a NAT to reassemble these fragments to allow correct recalculation of higher-level checksums and correct tracking of which packets belong to which connection.
The major transport layer protocols, TCP and UDP, have a checksum that covers all the data they carry, as well as the TCP/UDP header, plus a "pseudo-header" that contains the source and destination IP addresses of the packet carrying the TCP/UDP header. For an originating NAT to pass TCP or UDP successfully, it must recompute the TCP/UDP header checksum based on the translated IP addresses, not the original ones, and put that checksum into the TCP/UDP header of the first packet of the fragmented set of packets. The receiving NAT must recompute the IP checksum on every packet it passes to the destination host, and also recognize and recompute the TCP/UDP header using the retranslated addresses and pseudo-header. This is not a completely solved problem. One solution is for the receiving NAT to reassemble the entire segment and then recompute a checksum calculated across all packets.
The originating host may perform Maximum transmission unit
(MTU) path discovery
to determine the packet size that can be transmitted without fragmentation, and then set the don't fragment (DF) bit in the appropriate packet header field.
of an en-route packet and performing the inverse function for any replies. Any router situated between two endpoints can perform this transformation of the packet.
DNAT is commonly used to publish a service located in a private network on a publicly accessible IP address
. This use of DNAT is also called port forwarding
, or DMZ when used on an entire server, which becomes exposed to the WAN, becoming analogous to an undefended military demilitarised zone (DMZ).
ing, the process of network address translation done in a secure way involves rewriting the source and/or destination address
es of IP
packets as they pass through a router or firewall.
protocols (such as FTP
and SIP
) send explicit network addresses within their application data. FTP
in active mode, for example, uses separate connections for control traffic (commands) and for data traffic (file contents). When requesting a file transfer, the host making the request identifies the corresponding data connection by its network layer and transport layer addresses. If the host making the request lies behind a simple NAT firewall, the translation of the IP address and/or TCP port number makes the information received by the server invalid. The Session Initiation Protocol
(SIP) controls many Voice over IP
(VoIP) calls, and suffers the same problem. SIP and SDP may use multiple ports to set up a connection and transmit voice stream via RTP
. IP addresses and port numbers are encoded in the payload data and must be known prior to the traversal of NATs. Without special techniques, such as STUN
, NAT behavior is unpredictable and communications may fail.
Application layer gateway (ALG) software or hardware may correct these problems. An ALG software module running on a NAT firewall device updates any payload data made invalid by address translation. ALGs obviously need to understand the higher-layer protocol that they need to fix, and so each protocol with this problem requires a separate ALG. For example, on many Linux systems, there are kernel modules called connection trackers which serve to implement ALGs. However, ALG does not work if the control channel is encrypted (e.g. FTPS).
Another possible solution to this problem is to use NAT traversal
techniques using protocols such as STUN
or ICE
, or proprietary approaches in a session border controller
. NAT traversal is possible in both TCP- and UDP-based applications, but the UDP-based technique
is simpler, more widely understood, and more compatible with legacy NATs. In either case, the high level protocol must be designed with NAT traversal in mind, and it does not work reliably across symmetric NATs or other poorly-behaved legacy NATs.
Other possibilities are UPnP
(Universal Plug and Play) or NAT-PMP (NAT Port Mapping Protocol), but these require the cooperation of the NAT device.
Most traditional client-server protocols (FTP being the main exception), however, do not send layer 3 contact information and therefore do not require any special treatment by NATs. In fact, avoiding NAT complications is practically a requirement when designing new higher-layer protocols today (e.g. the use of SFTP
instead of FTP).
NATs can also cause problems where IPsec
encryption is applied and in cases where multiple devices such as SIP
phones are located behind a NAT. Phones which encrypt their signaling with IPsec encapsulate the port information within an encrypted packet, meaning that NA(P)T devices cannot access and translate the port. In these cases the NA(P)T devices revert to simple NAT operation. This means that all traffic returning to the NAT will be mapped onto one client causing service to more than one client "behind" the NAT to fail. There are a couple of solutions to this problem: one is to use TLS
, which operates at level 4 in the OSI Reference Model and therefore does not mask the port number; another is to encapsulate the IPsec within UDP
- the latter being the solution chosen by TISPAN
to achieve secure NAT traversal.
The DNS protocol vulnerability announced by Dan Kaminsky
on July 8, 2008 is indirectly affected by NAT port mapping. To avoid DNS server cache poisoning, it is highly desirable to not translate UDP source port numbers of outgoing DNS requests from a DNS server which is behind a firewall which implements NAT. The recommended work-around for the DNS vulnerability is to make all caching DNS servers use randomized UDP source ports. If the NAT function de-randomizes the UDP source ports, the DNS server will be made vulnerable.
Some have also called this exact feature a major drawback, since it delays the need for the implementation of IPv6
:
Hosts behind NAT-enabled routers do not have end-to-end connectivity and cannot participate in some Internet protocols. Services that require the initiation of TCP
connections from the outside network, or stateless protocols such as those using UDP
, can be disrupted. Unless the NAT router makes a specific effort to support such protocols, incoming packets cannot reach their destination. Some protocols can accommodate one instance of NAT between participating hosts ("passive mode" FTP
, for example), sometimes with the assistance of an application-level gateway
(see below), but fail when both systems are separated from the Internet by NAT. Use of NAT also complicates tunneling protocol
s such as IPsec
because NAT modifies values in the headers which interfere with the integrity checks done by IPsec
and other tunneling protocols.
End-to-end connectivity has been a core principle of the Internet, supported for example by the Internet Architecture Board
. Current Internet architectural documents observe that NAT is a violation of the End-to-End Principle, but that NAT does have a valid role in careful design. There is considerably more concern with the use of IPv6 NAT, and many IPv6 architects believe IPv6 was intended to remove the need for NAT.
Because of the short-lived nature of the stateful translation tables in NAT routers, devices on the internal network lose IP connectivity typically within a very short period of time unless they implement NAT keep-alive
mechanisms by frequently accessing outside hosts. This dramatically shortens the power reserves on battery-operated hand-held devices and has thwarted more widespread deployment of such IP-native Internet-enabled devices.
Some Internet service provider
s (ISPs), especially in India
, Russia
, parts of Asia
and other "developing" regions provide their customers only with "local" IP addresses, due to a limited number of external IP addresses allocated to those entities. Thus, these customers must access services external to the ISP's network through NAT. As a result, the customers cannot achieve true end-to-end connectivity, in violation of the core principles of the Internet as laid out by the Internet Architecture Board
.
IETF RAPT (IP Reachability Using Twice Network Address and Port Translation) The RAT device maps an IP datagram to its associated CN and 0MN by using three additional fields: the IP protocol type number and the transport layer source and destination connection identifiers (e.g. TCP port number or ICMP echo request/reply ID field).
Cisco
RAPT implementation is PAT (Port Address Translation) or overloading , and maps multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address. Multiple addresses can be mapped to a single address because each private address is tracked by a port number.
PAT uses unique source port numbers on the inside global IP address to distinguish between translations. The port number is encoded in 16 bits. The total number of internal addresses that can be translated to one external address could theoretically be as high as 65,536 per IP address. Realistically, the number of ports that can be assigned a single IP address is around 4000. PAT will attempt to preserve the original source port. If this source port is already used, PAT will assign the first available port number starting from the beginning of the appropriate port group 0-511, 512-1023, or 1024-65535. When there are no more ports available and there is more than one external IP address configured, PAT moves to the next IP address to try to allocate the original source port again. This process continues until it runs out of available ports and external IP addresses.
3COM
(Method and system for locating network services with distributed network address translation) Methods and system for locating network services with distributed network address translation. Digital certificates are created that allow an external network device on an external network, such as the Internet, to request a service from an internal network device on an internal distributed network address translation network, such as a stub local area network. The digital certificates include information obtained with a Port Allocation Protocol used for distributed network address translation. The digital certificates are published on the internal network so they are accessible to external network devices. An external network device retrieves a digital certificate, extracts appropriate information, and sends a service request packet to an internal network device on an internal distributed network address translation network. The external network device is able to locate and request a service from an internal network device. An external network device can also request a security service, such as an Internet Protocol security ("IPsec") service from an internal network device. The external network device and the internal network device can establish a security service (e.g., Internet Key Exchange protocol service). The internal network device and external network device can then establish a Security Association using Security Parameter Indexes ("SPI") obtained using a distributed network address translation protocol. External network devices can request services, and security services on internal network devices on an internal distribute network address translation network that were previously unknown and unavailable to the external network devices.
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
ing, network address translation (NAT) is the process of modifying IP address
IP address
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing...
information in IP packet headers while in transit across a traffic routing device.
The simplest type of NAT provides a one to one translation of IP addresses. RFC 2663 refers to this type of NAT as basic NAT. It is often also referred to as one-to-one NAT. In this type of NAT only the IP addresses, IP header checksum and any higher level checksums that include the IP address need to be changed. The rest of the packet can be left untouched (at least for basic TCP/UDP functionality, some higher level protocols may need further translation). Basic NATs can be used when there is a requirement to interconnect two IP networks with incompatible addressing.
However it is common to hide an entire IP address space, usually consisting of private IP addresses, behind a single IP address (or in some cases a small group of IP addresses) in another (usually public) address space. To avoid ambiguity in the handling of returned packets, a one-to-many NAT must alter higher level information such as TCP/UDP ports in outgoing communications and must maintain a translation table so that return packets can be correctly translated back. RFC 2663 uses the term NAPT (network address and port translation) for this type of NAT. Other names include PAT (port address translation), IP masquerading, NAT Overload and many-to-one NAT. Since this is the most common type of NAT it is often referred to simply as NAT.
As described, the method enables communication through the router only when the conversation originates in the masqueraded network, since this establishes the translation tables. For example, a web browser
Web browser
A web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier and may be a web page, image, video, or other piece of content...
in the masqueraded network can browse a website outside, but a web browser outside could not browse a web site in the masqueraded network. However, most NAT devices today allow the network administrator to configure translation table entries for permanent use. This feature is often referred to as "static NAT" or port forwarding
Port forwarding
Port forwarding or port mapping is a name given to the combined technique of# translating the address and/or port number of a packet to a new destination# possibly accepting such packet in a packet filter...
and allows traffic originating in the "outside" network to reach designated hosts in the masqueraded network.
In the mid-1990s NAT became a popular tool for alleviating the consequences of IPv4 address exhaustion. It has become a common, indispensable feature in routers for home and small-office Internet connections. Most systems using NAT do so in order to enable multiple host
Host (network)
A network host is a computer connected to a computer network. A network host may offer information resources, services, and applications to users or other nodes on the network. A network host is a network node that is assigned a network layer host address....
s on a private network
Private network
In the Internet addressing architecture, a private network is a network that uses private IP address space, following the standards set by RFC 1918 and RFC 4193. These addresses are commonly used for home, office, and enterprise local area networks , when globally routable addresses are not...
to access the Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
using a single public IP address.
Network address translation has serious drawbacks on the quality of Internet connectivity and requires careful attention to the details of its implementation. In particular all types of NAT break the originally envisioned model of IP end-to-end connectivity across the Internet and NAPT makes it difficult for systems behind a NAT to accept incoming communications. As a result, NAT traversal
NAT traversal
NAT traversal is a general term for techniques that establish and maintain Internet protocol connections traversing network address translation gateways. Network address translation breaks end-to-end connectivity. Intercepting and modifying traffic can only be performed transparently in the...
methods have been devised to alleviate the issues encountered.
One to many NATs
The majority of NATs map multiple private hosts to one publicly exposed IP address. In a typical configuration, a local network uses one of the designated "private" IP addressPrivate network
In the Internet addressing architecture, a private network is a network that uses private IP address space, following the standards set by RFC 1918 and RFC 4193. These addresses are commonly used for home, office, and enterprise local area networks , when globally routable addresses are not...
subnets (RFC 1918). A router on that network has a private address in that address space. The router is also connected to the Internet with a "public" address assigned by an Internet service provider
Internet service provider
An Internet service provider is a company that provides access to the Internet. Access ISPs directly connect customers to the Internet using copper wires, wireless or fiber-optic connections. Hosting ISPs lease server space for smaller businesses and host other people servers...
. As traffic passes from the local network to the Internet, the source address in each packet is translated on the fly from a private address to the public address. The router tracks basic data about each active connection (particularly the destination address and port). When a reply returns to the router, it uses the connection tracking data it stored during the outbound phase to determine the private address on the internal network to which to forward the reply.
All Internet packets have a source IP address and a destination IP address. Typically packets passing from the private network to the public network will have their source address modified while packets passing from the public network back to the private network will have their destination address modified. More complex configurations are also possible.
To avoid ambiguity in how to translate returned packets, further modifications to the packets are required. The vast bulk of Internet traffic is TCP and UDP packets and for these protocols the port numbers are changed so that the combination of IP and port information on the returned packet can be unambiguously mapped to the corresponding private address and port information. Protocols not based on TCP or UDP require other translation techniques. ICMP packets typically relate to an existing connection and need to be mapped using the same IP and port mappings as that connection.
Methods of Port translation
There are several ways of implementing network address and port translation. In some application protocols that use IP address information, the application running on a node in the masqueraded network needs to determine the external address of the NAT, i.e., the address that its communication peers detect, and, furthermore, often needs to examine and categorize the type of mapping in use. Usually this is done because it is desired to set up a direct communications path (either to save the cost of taking the data via a server or to improve performance) between two clients both of which are behind separate NATs. For this purpose, the Simple traversal of UDP over NATs (STUN) protocol was developed (RFC 3489, March 2003). It classified NAT implementation as full cone NAT, (address) restricted cone NAT, port restricted cone NAT or symmetric NAT and proposed a methodology for testing a device accordingly. However, these procedures have since been deprecated from standards status, as the methods have proven faulty and inadequate to correctly assess many devices. New methods have been standardized in RFC 5389 (October 2008) and the STUN acronym now represents the new title of the specification: Session Traversal Utilities for NAT. Full-cone NAT, also known as one-to-one NAT
|
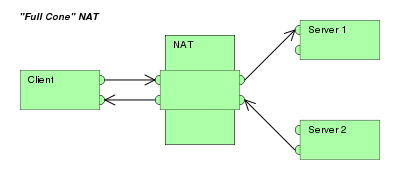 |
(Address) restricted cone NAT
|
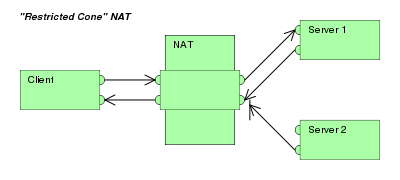 |
| Port-restricted cone NAT
Like an address restricted cone NAT, but the restriction includes port numbers.
|
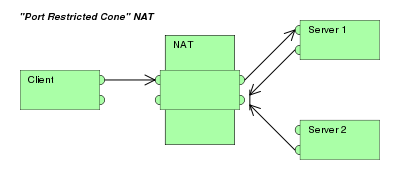 |
Symmetric NAT
|
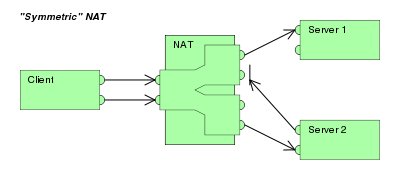 |
This terminology has been the source of much confusion, as it has proven inadequate at describing real-life NAT behavior.
Many NAT implementations combine these types, and it is therefore better to refer to specific individual NAT behaviors instead of using the Cone/Symmetric terminology. Especially, most NAT translators combine symmetric NAT for outgoing connections with static port mapping, where incoming packets to the external address and port are redirected to a specific internal address and port. Some products can redirect packets to several internal hosts, e.g. to divide the load between a few servers. However, this introduces problems with more sophisticated communications that have many interconnected packets, and thus is rarely used.
Type of NAT and NAT Traversal
The NAT traversal problem arises when two peers behind distinct NAT try to communicate. One way to solve this problem is to use port forwardingPort forwarding
Port forwarding or port mapping is a name given to the combined technique of# translating the address and/or port number of a packet to a new destination# possibly accepting such packet in a packet filter...
, another way is to use various NAT traversal techniques. The most popular technique for TCP NAT traversal is TCP hole punching
TCP hole punching
TCP hole punching is a commonly-used NAT traversal technique, for sending 2-way messages between nodes in an Internet computer network. The term "NAT traversal" is a general term for techniques that establish and maintain TCP/IP network and/or TCP connections traversing network-address-translation ...
, which requires the NAT to follow the port preservation design for TCP, as explained below.
Many NAT implementations follow the port preservation design especially for TCP, which is to say that they use the same values as internal and external port numbers. NAT port preservation for outgoing TCP connections is especially important for TCP NAT traversal
NAT traversal
NAT traversal is a general term for techniques that establish and maintain Internet protocol connections traversing network address translation gateways. Network address translation breaks end-to-end connectivity. Intercepting and modifying traffic can only be performed transparently in the...
, because programs usually bind distinct TCP sockets to ephemeral ports for distinct TCP connections, rendering NAT port prediction impossible for TCP.
On the other hand, for UDP, NATs do not need to have port preservation because applications usually reuse the same UDP socket to send packets to distinct hosts, making port prediction straightforward, as it is the same source port for each packet.
Furthermore, port preservation in NAT for TCP allows P2P protocols to offer less complexity and less latency because there is no need to use a third party to discover the NAT port since the application already knows the NAT port.
However, if two internal hosts attempt to communicate with the same external host using the same port number, the external port number used by the second host will be chosen at random. Such NAT will be sometimes perceived as (address) restricted cone NAT and other times as symmetric NAT.
Recent studies have shown that roughly 70% of clients in P2P
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads among peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application...
networks employ some form of NAT.
Establishing Two-Way Communication
Every TCP and UDP packet contains both a source IP addressIP address
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing...
and source port number as well as a destination IP address and destination port number. The port address/IP address pair forms a socket
Internet socket
In computer networking, an Internet socket or network socket is an endpoint of a bidirectional inter-process communication flow across an Internet Protocol-based computer network, such as the Internet....
. In particular, the source port address and source IP address form the source socket.
For publicly accessible services such as web servers and mail servers the port number is important. For example, port 80 connects to the web server
Server (computing)
In the context of client-server architecture, a server is a computer program running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients". Thus, the "server" performs some computational task on behalf of "clients"...
software and port 25 to a mail server's SMTP daemon
Daemon (computer software)
In Unix and other multitasking computer operating systems, a daemon is a computer program that runs as a background process, rather than being under the direct control of an interactive user...
. The IP address of a public server is also important, similar in global uniqueness to a postal address or telephone number. Both IP address and port must be correctly known by all hosts wishing to successfully communicate.
Private IP addresses as described in RFC 1918 are significant only on private networks where they are used, which is also true for host ports. Ports are unique endpoints of communication on a host, so a connection through the NAT device is maintained by the combined mapping of port and IP address.
PAT resolves conflicts that would arise through two different hosts using the same source port number to establish unique connections at the same time.
An Analogy
A NAT device is similar to a phone system at an office that has one public telephone number and multiple extensions. Outbound phone calls made from the office all appear to come from the same telephone number. However, an incoming call that does not specify an extension cannot be transferred to an individual inside the office. In this scenario, the office is a private LAN, the main phone number is the public IP address, and the individual extensions are unique port numbers.Translation of the Endpoint
With NAT, all communication sent to external hosts actually contain the external IP address and port information of the NAT device instead of internal host IPs or port numbers.- When a computer on the private (internal) network sends a packetIPv4Internet Protocol version 4 is the fourth revision in the development of the Internet Protocol and the first version of the protocol to be widely deployed. Together with IPv6, it is at the core of standards-based internetworking methods of the Internet...
to the external network, the NAT device replaces the internal IP address in the source field of the packet header (sender's address) with the external IP address of the NAT device. PAT may then assign the connection a port number from a pool of available ports, inserting this port number in the source port field (much like the post office box number), and forwards the packet to the external network. The NAT device then makes an entry in a translation table containing the internal IP address, original source port, and the translated source port. Subsequent packets from the same connection are translated to the same port number.
- The computer receiving a packet that has undergone NAT establishes a connection to the port and IP address specified in the altered packet, oblivious to the fact that the supplied address is being translated (analogous to using a post office box number).
- A packet coming from the external network is mapped to a corresponding internal IP address and port number from the translation table, replacing the external IP address and port number in the incoming packet header (similar to the translation from post office boxPost Office boxA post-office box or Post Office box is a uniquely addressable lockable box located on the premises of a post office station....
number to street address). The packet is then forwarded over the inside network. Otherwise, if the destination port number of the incoming packet is not found in the translation table, the packet is dropped or rejected because the PAT device doesn't know where to send it.
NAT will only translate IP addresses and ports of its internal hosts, hiding the true endpoint of an internal host on a private network.
Visibility of Operation
NAT operation is typically transparent to both the internal and external hosts.Typically the internal host is aware of the true IP address and TCP or UDP port of the external host. Typically the NAT device may function as the default gateway for the internal host. However the external host is only aware of the public IP address for the NAT device and the particular port being used to communicate on behalf of a specific internal host.
NAT and TCP/UDP
"Pure NAT", operating on IP alone, may or may not correctly parse protocols that are totally concerned with IP information, such as ICMPInternet Control Message Protocol
The Internet Control Message Protocol is one of the core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite. It is chiefly used by the operating systems of networked computers to send error messages indicating, for example, that a requested service is not available or that a host or router could not be...
, depending on whether the payload is interpreted by a host on the "inside" or "outside" of translation. As soon as the protocol stack is traversed, even with such basic protocols as TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
The Transmission Control Protocol is one of the core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite. TCP is one of the two original components of the suite, complementing the Internet Protocol , and therefore the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP...
and UDP
User Datagram Protocol
The User Datagram Protocol is one of the core members of the Internet Protocol Suite, the set of network protocols used for the Internet. With UDP, computer applications can send messages, in this case referred to as datagrams, to other hosts on an Internet Protocol network without requiring...
, the protocols will break unless NAT takes action beyond the network layer.
IP packets have a checksum in each packet header, which provides error detection only for the header. IP datagrams may become fragmented and it is necessary for a NAT to reassemble these fragments to allow correct recalculation of higher-level checksums and correct tracking of which packets belong to which connection.
The major transport layer protocols, TCP and UDP, have a checksum that covers all the data they carry, as well as the TCP/UDP header, plus a "pseudo-header" that contains the source and destination IP addresses of the packet carrying the TCP/UDP header. For an originating NAT to pass TCP or UDP successfully, it must recompute the TCP/UDP header checksum based on the translated IP addresses, not the original ones, and put that checksum into the TCP/UDP header of the first packet of the fragmented set of packets. The receiving NAT must recompute the IP checksum on every packet it passes to the destination host, and also recognize and recompute the TCP/UDP header using the retranslated addresses and pseudo-header. This is not a completely solved problem. One solution is for the receiving NAT to reassemble the entire segment and then recompute a checksum calculated across all packets.
The originating host may perform Maximum transmission unit
Maximum transmission unit
In computer networking, the maximum transmission unit of a communications protocol of a layer is the size of the largest protocol data unit that the layer can pass onwards. MTU parameters usually appear in association with a communications interface...
(MTU) path discovery
Path MTU discovery
Path MTU Discovery is a standardized technique in computer networking for determining the maximum transmission unit size on the network path between two Internet Protocol hosts, usually with the goal of avoiding IP fragmentation...
to determine the packet size that can be transmitted without fragmentation, and then set the don't fragment (DF) bit in the appropriate packet header field.
Destination network address translation (DNAT)
DNAT is a technique for transparently changing the destination IP addressIP address
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing...
of an en-route packet and performing the inverse function for any replies. Any router situated between two endpoints can perform this transformation of the packet.
DNAT is commonly used to publish a service located in a private network on a publicly accessible IP address
IP address
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing...
. This use of DNAT is also called port forwarding
Port forwarding
Port forwarding or port mapping is a name given to the combined technique of# translating the address and/or port number of a packet to a new destination# possibly accepting such packet in a packet filter...
, or DMZ when used on an entire server, which becomes exposed to the WAN, becoming analogous to an undefended military demilitarised zone (DMZ).
SNAT
The meaning of the term SNAT varies by vendor. Many vendors have proprietary definitions for SNAT. A common expansion is source NAT, the counterpart of destination NAT (DNAT). Microsoft uses the acronym for Secure NAT, in regard to the ISA Server. For Cisco Systems, SNAT means stateful NAT.Secure network address translation
In computer networkComputer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
ing, the process of network address translation done in a secure way involves rewriting the source and/or destination address
IP address
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing...
es of IP
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite...
packets as they pass through a router or firewall.
Dynamic network address translation
Dynamic NAT, just like static NAT, is not common in smaller networks but is found within larger corporations with complex networks. The way dynamic NAT differs from static NAT is that where static NAT provides a one-to-one internal to public static IP address mapping, dynamic NAT doesn't make the mapping to the public IP address static and usually uses a group of available public IP addresses.Applications affected by NAT
Some Application LayerApplication layer
The Internet protocol suite and the Open Systems Interconnection model of computer networking each specify a group of protocols and methods identified by the name application layer....
protocols (such as FTP
File Transfer Protocol
File Transfer Protocol is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another host over a TCP-based network, such as the Internet. FTP is built on a client-server architecture and utilizes separate control and data connections between the client and server...
and SIP
Session Initiation Protocol
The Session Initiation Protocol is an IETF-defined signaling protocol widely used for controlling communication sessions such as voice and video calls over Internet Protocol . The protocol can be used for creating, modifying and terminating two-party or multiparty sessions...
) send explicit network addresses within their application data. FTP
File Transfer Protocol
File Transfer Protocol is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another host over a TCP-based network, such as the Internet. FTP is built on a client-server architecture and utilizes separate control and data connections between the client and server...
in active mode, for example, uses separate connections for control traffic (commands) and for data traffic (file contents). When requesting a file transfer, the host making the request identifies the corresponding data connection by its network layer and transport layer addresses. If the host making the request lies behind a simple NAT firewall, the translation of the IP address and/or TCP port number makes the information received by the server invalid. The Session Initiation Protocol
Session Initiation Protocol
The Session Initiation Protocol is an IETF-defined signaling protocol widely used for controlling communication sessions such as voice and video calls over Internet Protocol . The protocol can be used for creating, modifying and terminating two-party or multiparty sessions...
(SIP) controls many Voice over IP
Voice over IP
Voice over Internet Protocol is a family of technologies, methodologies, communication protocols, and transmission techniques for the delivery of voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol networks, such as the Internet...
(VoIP) calls, and suffers the same problem. SIP and SDP may use multiple ports to set up a connection and transmit voice stream via RTP
Real-time Transport Protocol
The Real-time Transport Protocol defines a standardized packet format for delivering audio and video over IP networks. RTP is used extensively in communication and entertainment systems that involve streaming media, such as telephony, video teleconference applications, television services and...
. IP addresses and port numbers are encoded in the payload data and must be known prior to the traversal of NATs. Without special techniques, such as STUN
STUN
STUN is a standardized set of methods, including a network protocol, used in NAT traversal for applications of real-time voice, video, messaging, and other interactive IP communications....
, NAT behavior is unpredictable and communications may fail.
Application layer gateway (ALG) software or hardware may correct these problems. An ALG software module running on a NAT firewall device updates any payload data made invalid by address translation. ALGs obviously need to understand the higher-layer protocol that they need to fix, and so each protocol with this problem requires a separate ALG. For example, on many Linux systems, there are kernel modules called connection trackers which serve to implement ALGs. However, ALG does not work if the control channel is encrypted (e.g. FTPS).
Another possible solution to this problem is to use NAT traversal
NAT traversal
NAT traversal is a general term for techniques that establish and maintain Internet protocol connections traversing network address translation gateways. Network address translation breaks end-to-end connectivity. Intercepting and modifying traffic can only be performed transparently in the...
techniques using protocols such as STUN
STUN
STUN is a standardized set of methods, including a network protocol, used in NAT traversal for applications of real-time voice, video, messaging, and other interactive IP communications....
or ICE
Interactive Connectivity Establishment
Interactive Connectivity Establishment is a technique used in computer networking involving network address translators in Internet applications of Voice over Internet Protocol , peer-to-peer communications, video, instant messaging and other interactive media...
, or proprietary approaches in a session border controller
Session Border Controller
A session border controller is a device regularly deployed in Voice over Internet Protocol networks to exert control over the signaling and usually also the media streams involved in setting up, conducting, and tearing down telephone calls or other interactive media communications.SBC's original...
. NAT traversal is possible in both TCP- and UDP-based applications, but the UDP-based technique
UDP hole punching
UDP hole punching is a commonly used technique employed in network address translator applications for maintaining User Datagram Protocol packet streams that traverse the NAT...
is simpler, more widely understood, and more compatible with legacy NATs. In either case, the high level protocol must be designed with NAT traversal in mind, and it does not work reliably across symmetric NATs or other poorly-behaved legacy NATs.
Other possibilities are UPnP
Universal Plug and Play
Universal Plug and Play is a set of networking protocols for primarily residential networks without enterprise class devices that permits networked devices, such as personal computers, printers, Internet gateways, Wi-Fi access points and mobile devices to seamlessly discover each other's presence...
(Universal Plug and Play) or NAT-PMP (NAT Port Mapping Protocol), but these require the cooperation of the NAT device.
Most traditional client-server protocols (FTP being the main exception), however, do not send layer 3 contact information and therefore do not require any special treatment by NATs. In fact, avoiding NAT complications is practically a requirement when designing new higher-layer protocols today (e.g. the use of SFTP
SSH file transfer protocol
In computing, the SSH File Transfer Protocol is a network protocol that provides file access, file transfer, and file management functionality over any reliable data stream...
instead of FTP).
NATs can also cause problems where IPsec
IPsec
Internet Protocol Security is a protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session...
encryption is applied and in cases where multiple devices such as SIP
Session Initiation Protocol
The Session Initiation Protocol is an IETF-defined signaling protocol widely used for controlling communication sessions such as voice and video calls over Internet Protocol . The protocol can be used for creating, modifying and terminating two-party or multiparty sessions...
phones are located behind a NAT. Phones which encrypt their signaling with IPsec encapsulate the port information within an encrypted packet, meaning that NA(P)T devices cannot access and translate the port. In these cases the NA(P)T devices revert to simple NAT operation. This means that all traffic returning to the NAT will be mapped onto one client causing service to more than one client "behind" the NAT to fail. There are a couple of solutions to this problem: one is to use TLS
Transport Layer Security
Transport Layer Security and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer , are cryptographic protocols that provide communication security over the Internet...
, which operates at level 4 in the OSI Reference Model and therefore does not mask the port number; another is to encapsulate the IPsec within UDP
User Datagram Protocol
The User Datagram Protocol is one of the core members of the Internet Protocol Suite, the set of network protocols used for the Internet. With UDP, computer applications can send messages, in this case referred to as datagrams, to other hosts on an Internet Protocol network without requiring...
- the latter being the solution chosen by TISPAN
TISPAN
The Telecoms & Internet converged Services & Protocols for Advanced Networks is a standardization body of ETSI, specializing in fixed networks and Internet convergence...
to achieve secure NAT traversal.
The DNS protocol vulnerability announced by Dan Kaminsky
Dan Kaminsky
Dan Kaminsky is an American security researcher. He formerly worked for Cisco, Avaya, and IOActive, where he was the Director of Penetration Testing...
on July 8, 2008 is indirectly affected by NAT port mapping. To avoid DNS server cache poisoning, it is highly desirable to not translate UDP source port numbers of outgoing DNS requests from a DNS server which is behind a firewall which implements NAT. The recommended work-around for the DNS vulnerability is to make all caching DNS servers use randomized UDP source ports. If the NAT function de-randomizes the UDP source ports, the DNS server will be made vulnerable.
Advantages of PAT
In addition to the advantages provided by NAT:- PAT (Port Address Translation) allows many internal hosts to share a single external IP address.
- Users who do not require support for inbound connections do not consume public IP addresses.
Drawbacks
The primary purpose of IP-masquerading NAT is that it has been a practical solution to the impending exhaustion of IPv4 address space. Even large networks can be connected to the Internet with as little as a single IP address. The more common arrangement is having machines that require end-to-end connectivity supplied with a routable IP address, while having machines that do not provide services to outside users behind NAT with only a few IP addresses used to enable Internet access, however, this brings some problems, outlined below.Some have also called this exact feature a major drawback, since it delays the need for the implementation of IPv6
IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6 is a version of the Internet Protocol . It is designed to succeed the Internet Protocol version 4...
:
"[...] it is possible that its [NAT's] widespread use will significantly delay the need to deploy IPv6. [...] It is probably safe to say that networks would be better off without NAT [...]"
Hosts behind NAT-enabled routers do not have end-to-end connectivity and cannot participate in some Internet protocols. Services that require the initiation of TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
The Transmission Control Protocol is one of the core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite. TCP is one of the two original components of the suite, complementing the Internet Protocol , and therefore the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP...
connections from the outside network, or stateless protocols such as those using UDP
User Datagram Protocol
The User Datagram Protocol is one of the core members of the Internet Protocol Suite, the set of network protocols used for the Internet. With UDP, computer applications can send messages, in this case referred to as datagrams, to other hosts on an Internet Protocol network without requiring...
, can be disrupted. Unless the NAT router makes a specific effort to support such protocols, incoming packets cannot reach their destination. Some protocols can accommodate one instance of NAT between participating hosts ("passive mode" FTP
File Transfer Protocol
File Transfer Protocol is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another host over a TCP-based network, such as the Internet. FTP is built on a client-server architecture and utilizes separate control and data connections between the client and server...
, for example), sometimes with the assistance of an application-level gateway
Application-level gateway
In the context of computer networking, an application-level gateway consists of a security component that augments a firewall or NAT employed in a computer network...
(see below), but fail when both systems are separated from the Internet by NAT. Use of NAT also complicates tunneling protocol
Tunneling protocol
Computer networks use a tunneling protocol when one network protocol encapsulates a different payload protocol...
s such as IPsec
IPsec
Internet Protocol Security is a protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session...
because NAT modifies values in the headers which interfere with the integrity checks done by IPsec
IPsec
Internet Protocol Security is a protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session...
and other tunneling protocols.
End-to-end connectivity has been a core principle of the Internet, supported for example by the Internet Architecture Board
Internet Architecture Board
The Internet Architecture Board is the committee charged with oversight of the technical and engineering development of the Internet by the Internet Society ....
. Current Internet architectural documents observe that NAT is a violation of the End-to-End Principle, but that NAT does have a valid role in careful design. There is considerably more concern with the use of IPv6 NAT, and many IPv6 architects believe IPv6 was intended to remove the need for NAT.
Because of the short-lived nature of the stateful translation tables in NAT routers, devices on the internal network lose IP connectivity typically within a very short period of time unless they implement NAT keep-alive
Keepalive
A keepalive is a message sent by one device to another to check that the link between the two is operating, or to prevent this link from being broken.-Description:...
mechanisms by frequently accessing outside hosts. This dramatically shortens the power reserves on battery-operated hand-held devices and has thwarted more widespread deployment of such IP-native Internet-enabled devices.
Some Internet service provider
Internet service provider
An Internet service provider is a company that provides access to the Internet. Access ISPs directly connect customers to the Internet using copper wires, wireless or fiber-optic connections. Hosting ISPs lease server space for smaller businesses and host other people servers...
s (ISPs), especially in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, parts of Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
and other "developing" regions provide their customers only with "local" IP addresses, due to a limited number of external IP addresses allocated to those entities. Thus, these customers must access services external to the ISP's network through NAT. As a result, the customers cannot achieve true end-to-end connectivity, in violation of the core principles of the Internet as laid out by the Internet Architecture Board
Internet Architecture Board
The Internet Architecture Board is the committee charged with oversight of the technical and engineering development of the Internet by the Internet Society ....
.
- Scalability - An implementation that only tracks ports can be quickly depleted by internal applications that use multiple simultaneous connections (such as an HTTP request for a web page with many embedded objects). This problem can be mitigated by tracking the destination IP address in addition to the port (thus sharing a single local port with many remote hosts), at the expense of implementation complexity and CPU/memory resources of the translation device.
- Firewall complexity - Because the internal addresses are all disguised behind one publicly-accessible address, it is impossible for external hosts to initiate a connection to a particular internal host without special configuration on the firewall to forward connections to a particular port. Applications such as VOIP, videoconferencingVideoconferencingVideoconferencing is the conduct of a videoconference by a set of telecommunication technologies which allow two or more locations to interact via two-way video and audio transmissions simultaneously...
, and other peer-to-peer applications must use NAT traversalNAT traversalNAT traversal is a general term for techniques that establish and maintain Internet protocol connections traversing network address translation gateways. Network address translation breaks end-to-end connectivity. Intercepting and modifying traffic can only be performed transparently in the...
techniques to function.
Specifications
IEEE Reverse Address and Port Translation (RAPT, or RAT) allows a host whose real IP address is changing from time to time to remain reachable as a server via a fixed home IP address. In principle, this should allow setting up servers on DHCP-run networks. While not a perfect mobility solution, RAPT together with upcoming protocols like DHCP-DDNS, it may end up becoming another useful tool in the network admin's arsenal.IETF RAPT (IP Reachability Using Twice Network Address and Port Translation) The RAT device maps an IP datagram to its associated CN and 0MN by using three additional fields: the IP protocol type number and the transport layer source and destination connection identifiers (e.g. TCP port number or ICMP echo request/reply ID field).
Cisco
Cisco
Cisco may refer to:Companies:*Cisco Systems, a computer networking company* Certis CISCO, corporatised entity of the former Commercial and Industrial Security Corporation in Singapore...
RAPT implementation is PAT (Port Address Translation) or overloading , and maps multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address. Multiple addresses can be mapped to a single address because each private address is tracked by a port number.
PAT uses unique source port numbers on the inside global IP address to distinguish between translations. The port number is encoded in 16 bits. The total number of internal addresses that can be translated to one external address could theoretically be as high as 65,536 per IP address. Realistically, the number of ports that can be assigned a single IP address is around 4000. PAT will attempt to preserve the original source port. If this source port is already used, PAT will assign the first available port number starting from the beginning of the appropriate port group 0-511, 512-1023, or 1024-65535. When there are no more ports available and there is more than one external IP address configured, PAT moves to the next IP address to try to allocate the original source port again. This process continues until it runs out of available ports and external IP addresses.
3COM
3Com
3Com was a pioneering digital electronics manufacturer best known for its computer network infrastructure products. The company was co-founded in 1979 by Robert Metcalfe, Howard Charney, Bruce Borden, and Greg Shaw...
(Method and system for locating network services with distributed network address translation) Methods and system for locating network services with distributed network address translation. Digital certificates are created that allow an external network device on an external network, such as the Internet, to request a service from an internal network device on an internal distributed network address translation network, such as a stub local area network. The digital certificates include information obtained with a Port Allocation Protocol used for distributed network address translation. The digital certificates are published on the internal network so they are accessible to external network devices. An external network device retrieves a digital certificate, extracts appropriate information, and sends a service request packet to an internal network device on an internal distributed network address translation network. The external network device is able to locate and request a service from an internal network device. An external network device can also request a security service, such as an Internet Protocol security ("IPsec") service from an internal network device. The external network device and the internal network device can establish a security service (e.g., Internet Key Exchange protocol service). The internal network device and external network device can then establish a Security Association using Security Parameter Indexes ("SPI") obtained using a distributed network address translation protocol. External network devices can request services, and security services on internal network devices on an internal distribute network address translation network that were previously unknown and unavailable to the external network devices.
Examples of NAT software
- Internet Connection SharingInternet Connection SharingInternet Connection Sharing is the use of a device with Internet access such as 3G cellular service, broadband via Ethernet, or other Internet gateway as an access point for other devices...
(ICS): Windows NAT+DHCP since W98SE - WinGateWinGate (computing)WinGate is an Integrated Gateway Management system for Microsoft Windows, providing firewall and NAT services, along with a number of integrated proxy servers and also email services ....
: like ICS plus lots of control - iptablesIptablesiptables is a user space application program that allows a system administrator to configure the tables provided by the Linux kernel firewall and the chains and rules it stores...
: the Linux packet filter and NAT (interface for NetFilter) - IPFilterIPFilterIPFilter is an open source software package that provides firewall services and network address translation for many UNIX-like operating systems. The author and software maintainer is Darren Reed. IPFilter supports both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols, and is a stateful firewall.IPFilter is delivered...
: Solaris, NetBSD, FreeBSD, xMach. - PF (firewall)PF (firewall)PF is a BSD licensed stateful packet filter, a central piece of software for firewalling. It is comparable to iptables, ipfw and ipfilter...
: The OpenBSD Packet Filter. - Netfilter Linux packet filter framework
See also
- AYIYA (IPv6 over IPv4 UDP thus working IPv6 tunneling over most NATs)
- Carrier Grade NATCarrier Grade NATCarrier-grade NAT , also known as large-scale NAT , is an approach to IPv4 network design in which end sites, in particular residential networks, are configured with private network addresses that are translated to public IPv4 addresses by middlebox network address translator devices embedded in...
- Firewall
- GatewayGateway (telecommunications)In telecommunications, the term gateway has the following meaning:*In a communications network, a network node equipped for interfacing with another network that uses different protocols....
- Internet Gateway Device (IGD) Protocol: UPnP NAT-traversal method
- MiddleboxMiddleboxA middlebox is a device in the Internet thatprovides transport policy enforcement. Examples of these devicesinclude firewalls, network address translators , signature management for intrusion detection...
- Internet Protocol version 4IPv4Internet Protocol version 4 is the fourth revision in the development of the Internet Protocol and the first version of the protocol to be widely deployed. Together with IPv6, it is at the core of standards-based internetworking methods of the Internet...
- NAT-PT
- Port forwardingPort forwardingPort forwarding or port mapping is a name given to the combined technique of# translating the address and/or port number of a packet to a new destination# possibly accepting such packet in a packet filter...
- Port triggeringPort triggeringPort triggering is a configuration option on a NAT-enabled router that allows a host machine to dynamically and automatically forward a specific port back to itself...
- Private IP address
- Proxy serverProxy serverIn computer networks, a proxy server is a server that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or other resource available from a different server...
- RoutingRoutingRouting is the process of selecting paths in a network along which to send network traffic. Routing is performed for many kinds of networks, including the telephone network , electronic data networks , and transportation networks...
- SubnetSubnetworkA subnetwork, or subnet, is a logically visible subdivision of an IP network. The practice of dividing a network into subnetworks is called subnetting....
- portTCP and UDP portIn computer networking, a port is an application-specific or process-specific software construct serving as a communications endpoint in a computer's host operating system. A port is associated with an IP address of the host, as well as the type of protocol used for communication...
- Teredo tunnelingTeredo tunnelingIn computer networking, Teredo is a transition technology that gives full IPv6 connectivity for IPv6-capable hosts which are on the IPv4 Internet but which have no direct native connection to an IPv6 network...
: NAT traversal using IPv6
External links
- NAT-Traversal Test and results
- Characterization of different TCP NATs – Paper discussing the different types of NAT
- Anatomy: A Look Inside Network Address Translators – Volume 7, Issue 3, September 2004
- Jeff Tyson, HowStuffWorks: How Network Address Translation Works
- NAT traversal techniques in multimedia Networks – White Paper from Newport Networks
- Peer-to-Peer Communication Across Network Address Translators (PDF) – NAT traversal techniques for UDP and TCP
- http://www.zdnetasia.com/insight/network/0,39044847,39050002,00.htm
- RFCs
- RFC 1631 (Status: Obsolete) - The IP Network Address Translator (NAT)
- RFC 1918 - Address Allocation for Private Internets
- RFC 3022 (Status: Informational) – Traditional IP Network Address Translator (Traditional NAT)
- RFC 4008 (Status: Standards Track) – Definitions of Managed Objects for Network Address Translators (NAT)
- RFC 5128 (Status: Informational) - State of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Communications across Network Address Translators (NATs)
- RFC 4966 (Status: Informational) - Reasons to Move the Network Address Translator - Protocol Translator (NAT-PT) to Historic Status
- Speak Freely End of Life Announcement – John Walker's discussion of why he stopped developing a famous program for free Internet communication, part of which is directly related to NAT
- natd
- SNAT, DNAT and OCS2007R2 – discussing the SNAT in Microsoft OCS 2007R2
- Alternative Taxonomy (Part of the documentation for the IBM iSeries)
- Network Address Translation - NAT
- Cisco Systems
- Document ID 6450: How NAT Works
- Document ID 26704: Network Address Translation (NAT) FAQ
- White Paper: Cisco IOS Network Address Translation Overview
- Cisco IOS NAT Commands Cisco IOS commands
- Animation Cisco NAT sample

