
Negative temperature
Encyclopedia
In physics
, certain systems can achieve negative temperatures; that is, their thermodynamic temperature
can be a negative quantity. Negative temperatures can be expressed as negative numbers on the kelvin
scale.
Temperatures that are expressed as negative numbers on the familiar Celsius
or Fahrenheit
scales are simply colder than the zero points of those scales. By contrast, a system with a truly negative temperature is not colder than absolute zero
; in fact, temperatures colder than absolute zero are impossible by definition. Rather, a system with a truly negative Kelvin temperature is hotter than any system with a positive temperature (in the sense that if a negative-temperature system and a positive-temperature system come in contact, heat will flow from the negative- to the positive-temperature system).
Most familiar systems cannot achieve negative temperatures, because adding energy always increases their entropy
. Some systems, however (see the examples below), have a maximum amount of energy that they can hold, and as they approach that maximum energy their entropy actually begins to decrease. Because temperature may be formally defined by the relationship between energy and entropy, such a system's temperature becomes negative, even though energy is being added -- implying that the system's heat capacity
is negative.
for systems with limited states.) By injecting energy into these systems in the right fashion, it is possible to create a system in which there are more particles in the higher energy states than in the lower ones. The system can then be characterised as having a negative temperature. A substance with a negative temperature is not colder than absolute zero
, but rather it is hotter than infinite temperature. As Kittel and Kroemer (p. 462) put it, "The temperature scale from cold to hot runs:
Generally, temperature as it is felt is defined by the kinetic energy of atoms. Since there is no upper bound on momentum of an atom there is no upper bound to the number of energy states available if enough energy is added, and no way to get to a negative temperature. However, temperature is more generally defined by statistical mechanics than just kinetic energy (see below). The inverse temperature β = 1/kT (where k is Boltzmann's constant) scale runs continuously from low energy to high as +∞, . . . , −∞.
, vibrational
, rotation
al, electronic
, and nuclear
modes of a system determines the macroscopic temperature. In a "normal" system, thermal energy is constantly being exchanged between the various modes.
However, for some cases it is possible to isolate one or more of the modes. In practice the isolated modes still exchange energy with the other modes, but the time scale
of this exchange is much slower than for the exchanges within the isolated mode. One example is the case of nuclear
spin
s in a strong external magnetic field
. In this case, energy flows fairly rapidly among the spin states of interacting atoms, but energy transfer between the nuclear spins and other modes is relatively slow. Since the energy flow is predominantly within the spin system, it makes sense to think of a spin temperature that is distinct from the temperature due to other modes.
A definition of temperature can be based on the relationship:

The relationship suggests that a positive temperature corresponds to the condition where entropy
, S, increases as thermal energy, qrev, is added to the system. This is the "normal" condition in the macroscopic world, and is always the case for the translational, vibrational, rotational, and non-spin related electronic and nuclear modes. The reason for this is that there are an infinite number of these types of modes, and adding more heat to the system increases the number of modes that are energetically accessible, and thus increases the entropy.
, these spin states are degenerate, meaning that they correspond to the same energy. When an external magnetic field is applied, the energy levels are split, since those spin states that are aligned with the magnetic field will have a different energy from those that are anti-parallel to it.
In the absence of a magnetic field, such a two-spin system would have maximum entropy when half the atoms are in the spin-up state and half are in the spin-down state, and so one would expect to find the system with close to an equal distribution of spins. Upon application of a magnetic field, some of the atoms will tend to align so as to minimize the energy of the system, thus slightly more atoms should be in the lower-energy state (for the purposes of this example we'll assume the spin-down state is the lower-energy state). It is possible to add energy to the spin system using radio frequency
(RF) techniques (Spectroscopy with coherent radiation: selected papers of Norman F. Ramsey with commentary. World Scientific Series in 20th Century Physics Vol. 21, 1998. Page xxxi, (h)). This causes atoms to flip from spin-down to spin-up.
Since we started with over half the atoms in the spin-down state, initially this drives the system towards a 50/50 mixture, so the entropy is increasing, corresponding to a positive temperature. However, at some point more than half of the spins are in the spin-up position. In this case, adding additional energy reduces the entropy, since it moves the system further from a 50/50 mixture. This reduction in entropy with the addition of energy corresponds to a negative temperature.
systems, wherein a large fraction of the system's atom
s (for chemical and gas lasers) or electron
s (in semiconductor
lasers) are in excited states. This is referred to as a population inversion
.
The Hamiltonian
for a single mode of a luminescent radiation field at frequency ν is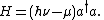
The density operator in the grand canonical ensemble
is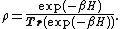
For the system to have a ground state, the trace to converge, and the density operator to be generally meaningful, βH must be positive semidefinite. So if hν < μ, and H is negative semidefinite, then β must itself be negative, implying a negative temperature.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, certain systems can achieve negative temperatures; that is, their thermodynamic temperature
Thermodynamic temperature
Thermodynamic temperature is the absolute measure of temperature and is one of the principal parameters of thermodynamics. Thermodynamic temperature is an "absolute" scale because it is the measure of the fundamental property underlying temperature: its null or zero point, absolute zero, is the...
can be a negative quantity. Negative temperatures can be expressed as negative numbers on the kelvin
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
scale.
Temperatures that are expressed as negative numbers on the familiar Celsius
Celsius
Celsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
or Fahrenheit
Fahrenheit
Fahrenheit is the temperature scale proposed in 1724 by, and named after, the German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit . Within this scale, the freezing of water into ice is defined at 32 degrees, while the boiling point of water is defined to be 212 degrees...
scales are simply colder than the zero points of those scales. By contrast, a system with a truly negative temperature is not colder than absolute zero
Absolute zero
Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. The laws of thermodynamics state that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means....
; in fact, temperatures colder than absolute zero are impossible by definition. Rather, a system with a truly negative Kelvin temperature is hotter than any system with a positive temperature (in the sense that if a negative-temperature system and a positive-temperature system come in contact, heat will flow from the negative- to the positive-temperature system).
Most familiar systems cannot achieve negative temperatures, because adding energy always increases their entropy
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
. Some systems, however (see the examples below), have a maximum amount of energy that they can hold, and as they approach that maximum energy their entropy actually begins to decrease. Because temperature may be formally defined by the relationship between energy and entropy, such a system's temperature becomes negative, even though energy is being added -- implying that the system's heat capacity
Heat capacity
Heat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount...
is negative.
Heat and molecular energy distribution
Negative temperatures can only exist in a system where there are a limited number of energy states (see below). As the temperature is increased on such a system, particles move into higher and higher energy states, and as the temperature increases, the number of particles in the lower energy states and in the higher energy states approaches equality. (This is a consequence of the definition of temperature in statistical mechanicsStatistical mechanics
Statistical mechanics or statistical thermodynamicsThe terms statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics are used interchangeably...
for systems with limited states.) By injecting energy into these systems in the right fashion, it is possible to create a system in which there are more particles in the higher energy states than in the lower ones. The system can then be characterised as having a negative temperature. A substance with a negative temperature is not colder than absolute zero
Absolute zero
Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. The laws of thermodynamics state that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means....
, but rather it is hotter than infinite temperature. As Kittel and Kroemer (p. 462) put it, "The temperature scale from cold to hot runs:
- +0 K, . . . , +300 K, . . . , +∞ K, −∞ K, . . . , −300 K, . . . , −0 K."
Generally, temperature as it is felt is defined by the kinetic energy of atoms. Since there is no upper bound on momentum of an atom there is no upper bound to the number of energy states available if enough energy is added, and no way to get to a negative temperature. However, temperature is more generally defined by statistical mechanics than just kinetic energy (see below). The inverse temperature β = 1/kT (where k is Boltzmann's constant) scale runs continuously from low energy to high as +∞, . . . , −∞.
Temperature and disorder
The distribution of energy among the various translationalTranslation (physics)
In physics, translation is movement that changes the position of an object, as opposed to rotation. For example, according to Whittaker:...
, vibrational
Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. Familiar examples include a swinging pendulum and AC power. The term vibration is sometimes used more narrowly to mean a mechanical oscillation but sometimes...
, rotation
Rotation
A rotation is a circular movement of an object around a center of rotation. A three-dimensional object rotates always around an imaginary line called a rotation axis. If the axis is within the body, and passes through its center of mass the body is said to rotate upon itself, or spin. A rotation...
al, electronic
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, electron configuration is the arrangement of electrons of an atom, a molecule, or other physical structure...
, and nuclear
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
modes of a system determines the macroscopic temperature. In a "normal" system, thermal energy is constantly being exchanged between the various modes.
However, for some cases it is possible to isolate one or more of the modes. In practice the isolated modes still exchange energy with the other modes, but the time scale
Time scale
A time scale specifies divisions of time.*Time standard, a specification of either the rate at which time passes, or points in time, or both*Duration , a quantity of time...
of this exchange is much slower than for the exchanges within the isolated mode. One example is the case of nuclear
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
s in a strong external magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
. In this case, energy flows fairly rapidly among the spin states of interacting atoms, but energy transfer between the nuclear spins and other modes is relatively slow. Since the energy flow is predominantly within the spin system, it makes sense to think of a spin temperature that is distinct from the temperature due to other modes.
A definition of temperature can be based on the relationship:

The relationship suggests that a positive temperature corresponds to the condition where entropy
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
, S, increases as thermal energy, qrev, is added to the system. This is the "normal" condition in the macroscopic world, and is always the case for the translational, vibrational, rotational, and non-spin related electronic and nuclear modes. The reason for this is that there are an infinite number of these types of modes, and adding more heat to the system increases the number of modes that are energetically accessible, and thus increases the entropy.
Nuclear spins
In the case of electronic and nuclear spin systems there are only a finite number of modes available, often just two, corresponding to spin up and spin down. In the absence of a magnetic fieldMagnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
, these spin states are degenerate, meaning that they correspond to the same energy. When an external magnetic field is applied, the energy levels are split, since those spin states that are aligned with the magnetic field will have a different energy from those that are anti-parallel to it.
In the absence of a magnetic field, such a two-spin system would have maximum entropy when half the atoms are in the spin-up state and half are in the spin-down state, and so one would expect to find the system with close to an equal distribution of spins. Upon application of a magnetic field, some of the atoms will tend to align so as to minimize the energy of the system, thus slightly more atoms should be in the lower-energy state (for the purposes of this example we'll assume the spin-down state is the lower-energy state). It is possible to add energy to the spin system using radio frequency
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
(RF) techniques (Spectroscopy with coherent radiation: selected papers of Norman F. Ramsey with commentary. World Scientific Series in 20th Century Physics Vol. 21, 1998. Page xxxi, (h)). This causes atoms to flip from spin-down to spin-up.
Since we started with over half the atoms in the spin-down state, initially this drives the system towards a 50/50 mixture, so the entropy is increasing, corresponding to a positive temperature. However, at some point more than half of the spins are in the spin-up position. In this case, adding additional energy reduces the entropy, since it moves the system further from a 50/50 mixture. This reduction in entropy with the addition of energy corresponds to a negative temperature.
Lasers
This phenomenon can also be observed in many lasingLaser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
systems, wherein a large fraction of the system's atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s (for chemical and gas lasers) or electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s (in semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
lasers) are in excited states. This is referred to as a population inversion
Population inversion
In physics, specifically statistical mechanics, a population inversion occurs when a system exists in state with more members in an excited state than in lower energy states...
.
The Hamiltonian
Hamiltonian (quantum mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, the Hamiltonian H, also Ȟ or Ĥ, is the operator corresponding to the total energy of the system. Its spectrum is the set of possible outcomes when one measures the total energy of a system...
for a single mode of a luminescent radiation field at frequency ν is
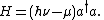
The density operator in the grand canonical ensemble
Grand canonical ensemble
In statistical mechanics, a grand canonical ensemble is a theoretical collection of model systems put together to mirror the calculated probability distribution of microscopic states of a given physical system which is being maintained in a given macroscopic state...
is
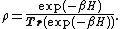
For the system to have a ground state, the trace to converge, and the density operator to be generally meaningful, βH must be positive semidefinite. So if hν < μ, and H is negative semidefinite, then β must itself be negative, implying a negative temperature.

