
Nanomesh
Encyclopedia

Graphene
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon, whose structure is one-atom-thick planar sheets of sp2-bonded carbon atoms that are densely packed in a honeycomb crystal lattice. The term graphene was coined as a combination of graphite and the suffix -ene by Hanns-Peter Boehm, who described single-layer...
. It was discovered in 2003 at the University of Zurich, Switzerland
.
It consists of a single layer of boron
Boron
Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the...
(B) and nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
(N) atoms, which forms by self-assembly
Self-assembly
Self-assembly is a term used to describe processes in which a disordered system of pre-existing components forms an organized structure or pattern as a consequence of specific, local interactions among the components themselves, without external direction...
a highly regular mesh after high-temperature exposure of a clean rhodium
Rhodium
Rhodium is a chemical element that is a rare, silvery-white, hard and chemically inert transition metal and a member of the platinum group. It has the chemical symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is composed of only one isotope, 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is found as the free metal, alloyed...
or ruthenium
Ruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element with symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most chemicals. The Russian scientist Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element...
surface to borazine
Borazine
Borazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula 33. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene...
under ultra-high vacuum
UHV
UHV may refer to:* University of Houston–Victoria* Ultra high vacuum* Ultra high voltage power line...
.
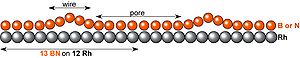
The nanomesh looks like an assembly of hexagonal pores (see right image) at the nanometer (nm) scale. The distance between 2 pore centers is only of 3.2 nm, whereas each pore has a diameter of about 2 nm and is 0.05 nm deep. The lowest regions bind strongly to the underlying metal, while the wires (highest regions) are only bound to the surface through strong cohesive forces within the layer itself.
The boron nitride
Boron nitride
Boron nitride is a chemical compound with chemical formula BN, consisting of equal numbers of boron and nitrogen atoms. BN is isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice and thus exists in various crystalline forms...
nanomesh is not only stable under vacuum, air and some liquids, but also up to temperatures of 796oC (1070 K). In addition it shows the extraordinary ability to trap molecules and metallic clusters
Cluster (physics)
In physics, the term clusters denotes small, multiatom particles. As a rule of thumb, any particle of somewhere between 3 and 3x107 atoms is considered a cluster. Two-atom particles are sometimes considered clusters as well....
, which have similar sizes to the nanomesh pores, forming a well-ordered array. These characteristics promise interesting applications of the nanomesh in areas like nanocatalysis, surface functionalisation, spintronics
Spintronics
Spintronics , also known as magnetoelectronics, is an emerging technology that exploits both the intrinsic spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-state devices.An additional effect occurs when a spin-polarized current is...
, quantum computing and data storage media like hard drives.
Structure
Rhodium
Rhodium is a chemical element that is a rare, silvery-white, hard and chemically inert transition metal and a member of the platinum group. It has the chemical symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is composed of only one isotope, 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is found as the free metal, alloyed...
Rh(111)
Miller index
Miller indices form a notation system in crystallography for planes and directions in crystal lattices.In particular, a family of lattice planes is determined by three integers h, k, and ℓ, the Miller indices. They are written , and each index denotes a plane orthogonal to a direction in the...
or ruthenium
Ruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element with symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most chemicals. The Russian scientist Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element...
Ru(0001)
Miller index
Miller indices form a notation system in crystallography for planes and directions in crystal lattices.In particular, a family of lattice planes is determined by three integers h, k, and ℓ, the Miller indices. They are written , and each index denotes a plane orthogonal to a direction in the...
crystal
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
s by a self-assembly
Self-assembly
Self-assembly is a term used to describe processes in which a disordered system of pre-existing components forms an organized structure or pattern as a consequence of specific, local interactions among the components themselves, without external direction...
process.
The unit cell of the h-BN nanomesh consists of 13x13 BN or 12x12 Rh atoms with a lattice constant
Lattice constant
The lattice constant [or lattice parameter] refers to the constant distance between unit cells in a crystal lattice. Lattices in three dimensions generally have three lattice constants, referred to as a, b, and c. However, in the special case of cubic crystal structures, all of the constants are...
of 3.2 nm. In a cross-section it means that 13 boron or nitrogen atoms are sitting on 12 rhodium atoms. This implies a modification of the relative positions of each BN towards the substrate atoms within a unit cell, where some bonds
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
are more attractive or repulsive than other (site selective bonding), what induces the corrugation of the nanomesh (see right image with pores and wires).
The nanomesh corrugation amplitude of 0.05 nm causes a strong effect on the electronic structure, where two distinct BN regions are observed. They are easily recognized in the lower right image, which is a scanning tunneling microscopy
Scanning tunneling microscope
A scanning tunneling microscope is an instrument for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer , the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. For an STM, good resolution is considered to be 0.1 nm lateral resolution and...
(STM) measurement, as well as in the lower left image representing a theoretical calculation of the same area. A strongly bounded region assigned to the pores is visible in blue in the left image below (center of bright rings in the right image) and a weakly bound region assigned to the wires appears yellow-red in the left image below (area in-between rings in the right image).
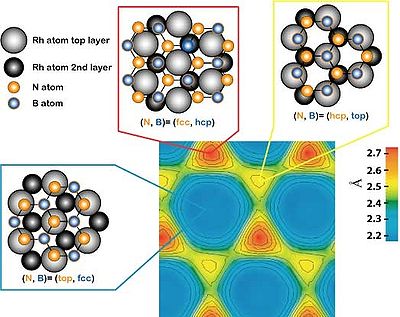 | | 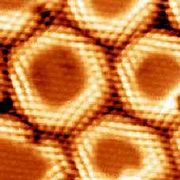 | | The right image shows the boron nitride nanomesh measured by STM at 77K, where each "ball" represents one N atom. The center of each ring corresponds to the center of the pores. The left image is the theoretical calculation of the same area, where the N height relative to the underlying substrate is given. The exact arrangement of Rh, N and B atoms is given for three different areas (blue: pores, yellow-red: wires). |
See for more details.
Properties
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
s among others. It is also temperature resistant since it doesn't decompose up to 1275K under vacuum. In addition to these exceptional stabilities, the nanomesh shows the extraordinary ability to act as a scaffold for metallic nanoclusters
Cluster (physics)
In physics, the term clusters denotes small, multiatom particles. As a rule of thumb, any particle of somewhere between 3 and 3x107 atoms is considered a cluster. Two-atom particles are sometimes considered clusters as well....
and to trap molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s forming a well-ordered array.
In the case of gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
(Au), its evaporation on the nanomesh leads to formation of well-defined round Au nanoparticles, which are centered at the nanomesh pores.
The STM
Scanning tunneling microscope
A scanning tunneling microscope is an instrument for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer , the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. For an STM, good resolution is considered to be 0.1 nm lateral resolution and...
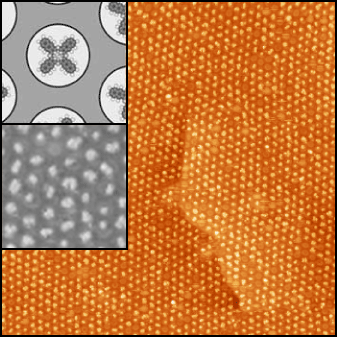
figure on the right shows Naphthalocyanine (Nc) molecules, which were vapor-deposited
Chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition is a chemical process used to produce high-purity, high-performance solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films. In a typical CVD process, the wafer is exposed to one or more volatile precursors, which react and/or...
onto the nanomesh. These planar molecules have a diameter of about 2 nm, whose size is comparable to that of the nanomesh pores (see upper inset). It is spectacularly visible how the molecules form a well-ordered array with the periodicity of the nanomesh (3.22 nm). The lower inset shows a region of this substrate with higher resolution, where individual molecules are trapped inside the pores. In addition, the molecules seem to keep their native conformation
Chemical structure
A chemical structure includes molecular geometry, electronic structure and crystal structure of molecules. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together. Molecular geometry can range from the very simple, such as...
, what means that their functionality is kept, which is nowadays a challenge in nanoscience.
Such systems with wide spacing between individual molecules/clusters and negligible intermolecular interactions might be interesting for applications such as molecular electronics
Molecular electronics
Molecular electronics, sometimes called moletronics, involves the study and application of molecular building blocks for the fabrication of electronic components...
and memory elements
Flash memory
Flash memory is a non-volatile computer storage chip that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. It was developed from EEPROM and must be erased in fairly large blocks before these can be rewritten with new data...
, in photochemistry
Photochemistry
Photochemistry, a sub-discipline of chemistry, is the study of chemical reactions that proceed with the absorption of light by atoms or molecules.. Everyday examples include photosynthesis, the degradation of plastics and the formation of vitamin D with sunlight.-Principles:Light is a type of...
or in optical devices.
See for more detailed information.
Preparation and analysis
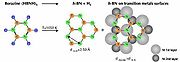
Thermal decomposition
Thermal decomposition, or thermolysis, is a chemical decomposition caused by heat. The decomposition temperature of a substance is the temperature at which the substance chemically decomposes....
of borazine
Borazine
Borazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula 33. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene...
(HBNH)3, a colorless substance that is liquid at room temperature. The nanomesh results after exposing the atomically clean Rh
Rhodium
Rhodium is a chemical element that is a rare, silvery-white, hard and chemically inert transition metal and a member of the platinum group. It has the chemical symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is composed of only one isotope, 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is found as the free metal, alloyed...
(111)
Miller index
Miller indices form a notation system in crystallography for planes and directions in crystal lattices.In particular, a family of lattice planes is determined by three integers h, k, and ℓ, the Miller indices. They are written , and each index denotes a plane orthogonal to a direction in the...
or Ru
Ruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element with symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most chemicals. The Russian scientist Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element...
(0001)
Miller index
Miller indices form a notation system in crystallography for planes and directions in crystal lattices.In particular, a family of lattice planes is determined by three integers h, k, and ℓ, the Miller indices. They are written , and each index denotes a plane orthogonal to a direction in the...
surface to borazine by chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition is a chemical process used to produce high-purity, high-performance solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films. In a typical CVD process, the wafer is exposed to one or more volatile precursors, which react and/or...
(CVD).
The substrate is kept at a temperature of 796°C (1070 K) when borazine is introduced in the vacuum chamber at a dose of about 40 L (1 Langmuir = 10−6 torr sec). A typical borazine vapor pressure inside the ultrahigh vacuum chamber during the exposure is 3x10−7 mbar.
After cooling down to room temperature, the regular mesh structure is observed using different experimental techniques. Scanning tunneling microscopy
Scanning tunneling microscope
A scanning tunneling microscope is an instrument for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer , the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. For an STM, good resolution is considered to be 0.1 nm lateral resolution and...
(STM) gives a direct look on the local real space structure of the nanomesh, while low energy electron diffraction (LEED) gives information about the surface structures ordered over the whole sample. Ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS) gives information about the electronic states in the outermost atomic layers of a sample, i.e. electronic information of the top substrate layers and the nanomesh.
Other forms
CVDChemical vapor deposition
Chemical vapor deposition is a chemical process used to produce high-purity, high-performance solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films. In a typical CVD process, the wafer is exposed to one or more volatile precursors, which react and/or...
of borazine
Borazine
Borazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula 33. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene...
on other substrates didn't led so far to the formation of a corrugated nanomesh. A flat BN layer is observed on nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
and palladium
Palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired...
, whereas stripped structures appear on molybdenum
Molybdenum
Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores...
instead.

