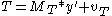Multivariate Cryptography
Encyclopedia
Multivariate cryptography is the generic term for asymmetric cryptographic
primitives based on multivariate polynomials
over finite field
s. In certain cases those polynomials could be defined over both a ground and an extension field
. If the polynomials have the degree
two, we talk about multivariate quadratics
. Solving systems of multivariate polynomial equations is proven to be NP-Hard
or NP-Complete
. That's why those schemes are often considered to be good candidates for post-quantum cryptography
, once quantum computers can break the current schemes. Today multivariate quadratics could be used only to build signatures
. All attempts to build a secure encryption scheme have so far failed.
conference.
On later work the "Hidden Monomial Cryptosystems" was developed by Jacques Patarin. It is based on a ground and an extension field. On this "Hidden Field Equations" was designed and presented in 1996. In the following years J. Patarin developed other schemes. In 1997 he presented “Balanced Oil & Vinegar” and 1999 “Unbalanced Oil and Vinegar
” in cooperation with Aviad Kipnis and Louis Goubin.
In this triple P' is the private transformation which is specially designed for each scheme. P’ maps elements from
 →
→ 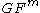 . S transforms from
. S transforms from  →
→ 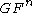 and T from
and T from  →
→ 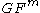 . Each transformation must be invertible. Note that the elements are map in a field not in a group. Sometimes the triple is called a trapdoor. The public key results by linking the private transformation. Public key P can be stated as P=S • P' • T.
. Each transformation must be invertible. Note that the elements are map in a field not in a group. Sometimes the triple is called a trapdoor. The public key results by linking the private transformation. Public key P can be stated as P=S • P' • T.
 as input. During S,
as input. During S,  is multiplied with a matrix
is multiplied with a matrix 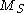 in addition a vector
in addition a vector  with length
with length  is added. The dimension of
is added. The dimension of 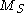 is
is  x
x  . T is a similar transformation to S. Both transformation in a mathematically form are shown below
. T is a similar transformation to S. Both transformation in a mathematically form are shown below
The output of S is the new input for the private transformation P'. Since P' is applied the last transformation T could be performed and the signature is obtained.
A complete signature consists of the elements (x,y) as bit vectors. A potential receiver of this tupel must have the public key in possession. Since he has the key he is able to verify if y is a valid signature of x. Therefore the receiver fill the public equation set with the elements of the bit vectors. A public equations set could look like shown below.




Cryptography
Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties...
primitives based on multivariate polynomials
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
over finite field
Finite field
In abstract algebra, a finite field or Galois field is a field that contains a finite number of elements. Finite fields are important in number theory, algebraic geometry, Galois theory, cryptography, and coding theory...
s. In certain cases those polynomials could be defined over both a ground and an extension field
Field (mathematics)
In abstract algebra, a field is a commutative ring whose nonzero elements form a group under multiplication. As such it is an algebraic structure with notions of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, satisfying certain axioms...
. If the polynomials have the degree
Degree of a polynomial
The degree of a polynomial represents the highest degree of a polynominal's terms , should the polynomial be expressed in canonical form . The degree of an individual term is the sum of the exponents acting on the term's variables...
two, we talk about multivariate quadratics
Quadratic polynomial
In mathematics, a quadratic polynomial or quadratic is a polynomial of degree two, also called second-order polynomial. That means the exponents of the polynomial's variables are no larger than 2...
. Solving systems of multivariate polynomial equations is proven to be NP-Hard
NP-hard
NP-hard , in computational complexity theory, is a class of problems that are, informally, "at least as hard as the hardest problems in NP". A problem H is NP-hard if and only if there is an NP-complete problem L that is polynomial time Turing-reducible to H...
or NP-Complete
NP-complete
In computational complexity theory, the complexity class NP-complete is a class of decision problems. A decision problem L is NP-complete if it is in the set of NP problems so that any given solution to the decision problem can be verified in polynomial time, and also in the set of NP-hard...
. That's why those schemes are often considered to be good candidates for post-quantum cryptography
Post-quantum cryptography
Post-quantum cryptography refers to research on cryptographic primitives that are not breakable using quantum computers...
, once quantum computers can break the current schemes. Today multivariate quadratics could be used only to build signatures
Digital signature
A digital signature or digital signature scheme is a mathematical scheme for demonstrating the authenticity of a digital message or document. A valid digital signature gives a recipient reason to believe that the message was created by a known sender, and that it was not altered in transit...
. All attempts to build a secure encryption scheme have so far failed.
History
In 1988 T. Matsumoto and H. Imai presented their scheme "Matsumoto-Imai-Scheme" on the EurocryptEurocrypt
Eurocrypt is a conference for cryptography research. The full name of the conference is currently the Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, but this has not always been its name...
conference.
On later work the "Hidden Monomial Cryptosystems" was developed by Jacques Patarin. It is based on a ground and an extension field. On this "Hidden Field Equations" was designed and presented in 1996. In the following years J. Patarin developed other schemes. In 1997 he presented “Balanced Oil & Vinegar” and 1999 “Unbalanced Oil and Vinegar
Unbalanced Oil and Vinegar
The Unbalanced Oil and Vinegar scheme is a modified version of the Oil and Vinegar scheme designed by J. Patarin. Both are Digital signature schemes, used in Cryptography. They belong to the group of multivariate cryptography. The security of this signature scheme is based on an NP-hard...
” in cooperation with Aviad Kipnis and Louis Goubin.
Construction
Multivariate Quadratics involves a public and a private key. The private key consists of three affine transformations (S,P’,T).In this triple P' is the private transformation which is specially designed for each scheme. P’ maps elements from
 →
→ 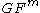 . S transforms from
. S transforms from  →
→ 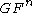 and T from
and T from  →
→ 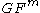 . Each transformation must be invertible. Note that the elements are map in a field not in a group. Sometimes the triple is called a trapdoor. The public key results by linking the private transformation. Public key P can be stated as P=S • P' • T.
. Each transformation must be invertible. Note that the elements are map in a field not in a group. Sometimes the triple is called a trapdoor. The public key results by linking the private transformation. Public key P can be stated as P=S • P' • T.Signature
Signatures are generated using the private key and are verified using the public key. The flow chart below shows how it is done by each party. First the sender takes its message and interpret it as a vector in a small field (for example, if the field has only two elements, then a bit vector). By now S takes as input. During S,
as input. During S,  is multiplied with a matrix
is multiplied with a matrix 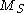 in addition a vector
in addition a vector  with length
with length  is added. The dimension of
is added. The dimension of 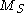 is
is  x
x  . T is a similar transformation to S. Both transformation in a mathematically form are shown below
. T is a similar transformation to S. Both transformation in a mathematically form are shown below
The output of S is the new input for the private transformation P'. Since P' is applied the last transformation T could be performed and the signature is obtained.
A complete signature consists of the elements (x,y) as bit vectors. A potential receiver of this tupel must have the public key in possession. Since he has the key he is able to verify if y is a valid signature of x. Therefore the receiver fill the public equation set with the elements of the bit vectors. A public equations set could look like shown below.




Applications
- Unbalanced Oil and VinegarUnbalanced Oil and VinegarThe Unbalanced Oil and Vinegar scheme is a modified version of the Oil and Vinegar scheme designed by J. Patarin. Both are Digital signature schemes, used in Cryptography. They belong to the group of multivariate cryptography. The security of this signature scheme is based on an NP-hard...
- Hidden Field Equations
- SFLASH by NESSIENESSIENESSIE was a European research project funded from 2000–2003 to identify secure cryptographic primitives. The project was comparable to the NIST AES process and the Japanese Government-sponsored CRYPTREC project, but with notable differences from both...
- Rainbow
- TTS
- QUARTZ
- QUAD (cipher)QUAD (cipher)In cryptography, the QUAD, cipher is a relatively new stream cipher, which was designed with provable security arguments in mind.-Description:...
External links
- http://www.s1on1.com/main/index.cgi/000000A/http://www.minrank.org/hfe/ The HFE public key encryption and signature