
Monoterpene
Encyclopedia
Monoterpenes are a class of terpene
s that consist of two isoprene
units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings. Biochemical modifications such as oxidation
or rearrangement
produce the related monoterpenoids.
and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
are combined to form geranyl pyrophosphate
.
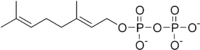
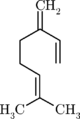 Elimination of the pyrophosphate group leads to the formation of acyclic monoterpenes such as ocimene
Elimination of the pyrophosphate group leads to the formation of acyclic monoterpenes such as ocimene
and the myrcenes. Hydrolysis of the phosphate groups leads to the prototypical acyclic monoterpenoid geraniol
. Additional rearrangements and oxidations provide compounds such as citral
, citronellal
, citronellol
, linalool, and many others. Many monoterpenes found in marine organisms are halogen
ated, such as halomon
.
.
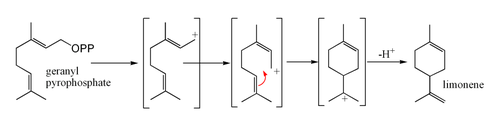
The terpinene
s, phellandrene
s, and terpinolene are formed similarly. Hydroxylation
of any of these compounds followed by dehydration can lead to the aromatic p-cymene. Important terpenoids derived from monocyclic terpenes are menthol
, thymol
, carvacrol
and many others.
which is the primary constituent of pine resin
.
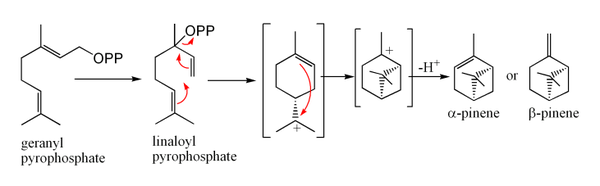
Other bicyclic monoterpenes include carene
, sabinene
, camphene
, and thujene
. Camphor
, borneol
and eucalyptol
are examples of bicyclic monoterpenoids containing ketone, alcohol, and ether functional groups, respectively.
Terpene
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, though also by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies, which emit terpenes from their osmeterium. They are often strong smelling and thus may have had a protective...
s that consist of two isoprene
Isoprene
Isoprene , or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common organic compound with the formula CH2=CCH=CH2. Under standard conditions it is a colorless liquid...
units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings. Biochemical modifications such as oxidation
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
or rearrangement
Rearrangement reaction
A rearrangement reaction is a broad class of organic reactions where the carbon skeleton of a molecule is rearranged to give a structural isomer of the original molecule. Often a substituent moves from one atom to another atom in the same molecule...
produce the related monoterpenoids.
Acyclic
Biosynthetically, isopentenyl pyrophosphateIsopentenyl pyrophosphate
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids. IPP is formed from acetyl-CoA via mevalonic acid...
and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate product of both mevalonic acid pathway and DOXP/MEP pathway. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate and exists in virtually all life forms...
are combined to form geranyl pyrophosphate
Geranyl pyrophosphate
Geranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of farnesyl pyrophosphate, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate, cholesterol, terpenes and terpenoids....
.
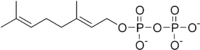

Ocimene
Ocimene refers to several isomeric hydrocarbons. The ocimenes are monoterpenes found within a variety of plants and fruits. α-Ocimene and the two β-ocimenes differ in the position of the isolated double bond: it is terminal in the alpha isomer. α-Ocimene is 3,7-dimethyl-1,3,7-octatriene. ...
and the myrcenes. Hydrolysis of the phosphate groups leads to the prototypical acyclic monoterpenoid geraniol
Geraniol
Geraniol is a monoterpenoid and an alcohol. It is the primary part of rose oil, palmarosa oil, and citronella oil . It also occurs in small quantities in geranium, lemon, and many other essential oils. It appears as a clear to pale-yellow oil that is insoluble in water, but soluble in most common...
. Additional rearrangements and oxidations provide compounds such as citral
Citral
Citral, or 3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienal or lemonal, is either of, or a mixture of, a pair of terpenoids with the molecular formula C10H16O. The two compounds are double bond isomers. The E-isomer is known as geranial or citral A...
, citronellal
Citronellal
Citronellal or rhodinal or 3,7-dimethyloct-6-en-1-al is a monoterpenoid, the main component in the mixture of terpenoid chemical compounds that give citronella oil its distinctive lemon scent....
, citronellol
Citronellol
Citronellol, or dihydrogeraniol, is a natural acyclic monoterpenoid. Both enantiomers occur in nature. -Citronellol, which is found in citronella oils, including Cymbopogon nardus , is the more common isomer. -Citronellol is found in the oils of rose and Pelargonium geraniums.Citronellol is...
, linalool, and many others. Many monoterpenes found in marine organisms are halogen
Halogen
The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine...
ated, such as halomon
Halomon
Halomon is a polyhalogenated monoterpene first isolated from the marine red algae Portieria hornemannii. Halomon has attracted research interest because of its promising profile of selective cytotoxicity that suggests its potential use as an antitumor agent.Halomon is in a class of chemical...
.
Monocyclic
In addition to linear attachments, the isoprene units can make connections to form rings. The most common ring size in monoterpenes is a six-membered ring. A classic example is the cyclization of geranyl pyrophosphate to form limoneneLimonene
Limonene is a colourless liquid hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic terpene. The more common D isomer possesses a strong smell of oranges. It is used in chemical synthesis as a precursor to carvone and as a renewably-based solvent in cleaning products....
.

The terpinene
Terpinene
The terpinenes are three isomeric hydrocarbons that are classified as terpenes. They each have the same molecular formula and carbon framework, but they differ in the position of carbon-carbon double bonds. α-Terpinene has been isolated from cardamom and marjoram oils, and from other natural...
s, phellandrene
Phellandrene
Phellandrene is the name for a pair of organic compounds that have a similar molecular structure and similar chemical properties. α-Phellandrene and β-phellandrene are cyclic monoterpenes and are double-bond isomers. In α-phellandrene, both double bonds are endocyclic and in β-phellandrene, one...
s, and terpinolene are formed similarly. Hydroxylation
Hydroxylation
Hydroxylation is a chemical process that introduces a hydroxyl group into an organic compound. In biochemistry, hydroxylation reactions are often facilitated by enzymes called hydroxylases. Hydroxylation is the first step in the oxidative degradation of organic compounds in air...
of any of these compounds followed by dehydration can lead to the aromatic p-cymene. Important terpenoids derived from monocyclic terpenes are menthol
Menthol
Menthol is an organic compound made synthetically or obtained from peppermint or other mint oils. It is a waxy, crystalline substance, clear or white in color, which is solid at room temperature and melts slightly above. The main form of menthol occurring in nature is -menthol, which is assigned...
, thymol
Thymol
Thymol is a natural monoterpene phenol derivative of cymene, C10H14O, isomeric with carvacrol, found in oil of thyme, and extracted from Thymus vulgaris and various other kinds of plants as a white crystalline substance of a pleasant aromatic odor and strong antiseptic properties...
, carvacrol
Carvacrol
Carvacrol, or cymophenol, C6H3CH3, is a monoterpenoid phenol. It has a characteristic pungent, warm odor of oregano and a pizza-like taste.- Natural occurrence :...
and many others.
Bicyclic
Geranyl pyrophosphate can also undergo two sequential cyclization reactions to form bicyclic monoterpenes, such as pinenePinene
Pinene is a bicyclic monoterpene chemical compound. There are two structural isomers of pinene found in nature: α-pinene and β-pinene. As the name suggests, both forms are important constituents of pine resin; they are also found in the resins of many other conifers, as well as in non-coniferous...
which is the primary constituent of pine resin
Pine
Pines are trees in the genus Pinus ,in the family Pinaceae. They make up the monotypic subfamily Pinoideae. There are about 115 species of pine, although different authorities accept between 105 and 125 species.-Etymology:...
.

Other bicyclic monoterpenes include carene
Carene
Carene, or delta-3-carene, is a bicyclic monoterpene which occurs naturally as a constituent of turpentine, with a content as high as 42% depending on the source. Carene has a sweet and pungent odor. It is not soluble in water, but miscible with fats and oils....
, sabinene
Sabinene
Sabinene is a natural bicyclic monoterpene with the molecular formula C10H16. It is isolated from the essential oils of a variety of plants including holm oak and Norway spruce...
, camphene
Camphene
Camphene is bicyclic monoterpene. It is nearly insoluble in water, but very soluble in common organic solvents. It volatilizes readily at room temperature and has a pungent smell. It is a minor constituent of many essential oils such as turpentine, cypress oil, camphor oil, citronella oil,...
, and thujene
Thujene
Thujene is a natural organic compound classified as a monoterpene. It is found in the essential oils of a variety of plants, and contributes pungency to the flavor of some herbs such as Summer savory....
. Camphor
Camphor
Camphor is a waxy, white or transparent solid with a strong, aromatic odor. It is a terpenoid with the chemical formula C10H16O. It is found in wood of the camphor laurel , a large evergreen tree found in Asia and also of Dryobalanops aromatica, a giant of the Bornean forests...
, borneol
Borneol
Borneol is a bicyclic organic compound and a terpene. The hydroxyl group in this compound is placed in an endo position.Borneol is easily oxidized to the ketone yielding camphor. One historical name for borneol is Borneo camphor which explains the name. Borneol can be synthesized by reduction of...
and eucalyptol
Eucalyptol
Eucalyptol is a natural organic compound which is a colorless liquid. It is a cyclic ether and a monoterpenoid.Eucalyptol is also known by a variety of synonyms: 1,8-cineol, 1,8-cineole, limonene oxide, cajeputol, 1,8-epoxy-p-menthane, 1,8-oxido-p-menthane, eucalyptol, eucalyptole,...
are examples of bicyclic monoterpenoids containing ketone, alcohol, and ether functional groups, respectively.

