.gif)
Monoid (category theory)
Encyclopedia
In category theory
, a monoid (or monoid object)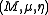 in a monoidal category
in a monoidal category
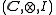 is an object M together with two morphism
is an object M together with two morphism
s
such that the diagrams
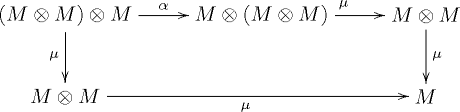 and
and 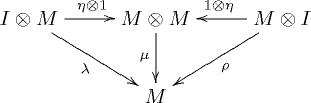
commute. In the above notations, I is the unit element and ,
, 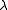 and
and 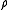 are respectively the associativity, the left identity and the right identity of the monoidal category C.
are respectively the associativity, the left identity and the right identity of the monoidal category C.
Dually, a comonoid in a monoidal category C is a monoid in the dual category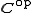 .
.
Suppose that the monoidal category C has a symmetry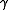 . A monoid
. A monoid 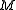 in C is symmetric when
in C is symmetric when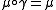 .
.
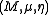 and
and 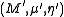 in a monoidal category C, a morphism
in a monoidal category C, a morphism 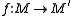 is a morphism of monoids when
is a morphism of monoids when
The category of monoids in C and their monoid morphisms is written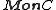 .
.
Category theory
Category theory is an area of study in mathematics that examines in an abstract way the properties of particular mathematical concepts, by formalising them as collections of objects and arrows , where these collections satisfy certain basic conditions...
, a monoid (or monoid object)
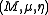 in a monoidal category
in a monoidal categoryMonoidal category
In mathematics, a monoidal category is a category C equipped with a bifunctorwhich is associative, up to a natural isomorphism, and an object I which is both a left and right identity for ⊗, again up to a natural isomorphism...
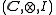 is an object M together with two morphism
is an object M together with two morphismMorphism
In mathematics, a morphism is an abstraction derived from structure-preserving mappings between two mathematical structures. The notion of morphism recurs in much of contemporary mathematics...
s
-
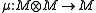 called multiplication,
called multiplication, - and
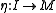 called unit,
called unit,
such that the diagrams
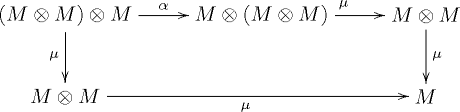 and
and 
commute. In the above notations, I is the unit element and
 ,
, 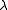 and
and 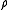 are respectively the associativity, the left identity and the right identity of the monoidal category C.
are respectively the associativity, the left identity and the right identity of the monoidal category C.Dually, a comonoid in a monoidal category C is a monoid in the dual category
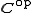 .
.Suppose that the monoidal category C has a symmetry
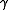 . A monoid
. A monoid 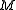 in C is symmetric when
in C is symmetric when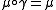 .
.Examples
- A monoid object in SetCategory of setsIn the mathematical field of category theory, the category of sets, denoted as Set, is the category whose objects are sets. The arrows or morphisms between sets A and B are all functions from A to B...
(with the monoidal structure induced by the cartesian product) is a monoidMonoidIn abstract algebra, a branch of mathematics, a monoid is an algebraic structure with a single associative binary operation and an identity element. Monoids are studied in semigroup theory as they are naturally semigroups with identity. Monoids occur in several branches of mathematics; for...
in the usual sense. - A monoid object in TopCategory of topological spacesIn mathematics, the category of topological spaces, often denoted Top, is the category whose objects are topological spaces and whose morphisms are continuous maps. This is a category because the composition of two continuous maps is again continuous...
(with the monoidal structure induced by the product topologyProduct topologyIn topology and related areas of mathematics, a product space is the cartesian product of a family of topological spaces equipped with a natural topology called the product topology...
) is a topological monoid. - A monoid object in the category of monoids (with the direct product of monoids) is just a commutative monoid. This follows easily from the Eckmann–Hilton theorem.
- A monoid object in the category of complete join-semilattices Sup (with the monoidal structure induced by the cartesian product) is a unital quantaleQuantaleIn mathematics, quantales are certain partially ordered algebraic structures that generalize locales as well as various multiplicative lattices of ideals from ring theory and functional analysis...
. - A monoid object in (AbCategory of abelian groupsIn mathematics, the category Ab has the abelian groups as objects and group homomorphisms as morphisms. This is the prototype of an abelian category....
, ⊗Z, Z) is a ringRing (mathematics)In mathematics, a ring is an algebraic structure consisting of a set together with two binary operations usually called addition and multiplication, where the set is an abelian group under addition and a semigroup under multiplication such that multiplication distributes over addition...
. - For a commutative ring R, a monoid object in (R-Mod, ⊗R, R) is an R-algebra.
- A monoid object in K-VectCategory of vector spacesIn mathematics, especially category theory, the category K-Vect has all vector spaces over a fixed field K as objects and K-linear transformations as morphisms...
(again, with the tensor product) is a K-algebraAlgebra over a fieldIn mathematics, an algebra over a field is a vector space equipped with a bilinear vector product. That is to say, it isan algebraic structure consisting of a vector space together with an operation, usually called multiplication, that combines any two vectors to form a third vector; to qualify as...
, a comonoid object is a K-coalgebraCoalgebraIn mathematics, coalgebras or cogebras are structures that are dual to unital associative algebras. The axioms of unital associative algebras can be formulated in terms of commutative diagrams...
. - For any category C, the category [C,C] of its endofunctors has a monoidal structure induced by the composition. A monoid object in [C,C] is a monadMonad (category theory)In category theory, a branch of mathematics, a monad, Kleisli triple, or triple is an functor, together with two natural transformations...
on C.
Categories of monoids
Given two monoids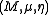 and
and 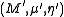 in a monoidal category C, a morphism
in a monoidal category C, a morphism 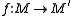 is a morphism of monoids when
is a morphism of monoids when
-
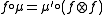 ,
, -
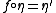 .
.
The category of monoids in C and their monoid morphisms is written
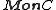 .
.See also
- monoidMonoidIn abstract algebra, a branch of mathematics, a monoid is an algebraic structure with a single associative binary operation and an identity element. Monoids are studied in semigroup theory as they are naturally semigroups with identity. Monoids occur in several branches of mathematics; for...
(non-categorical definition) - Act-S, the category of monoids acting on sets

