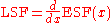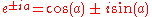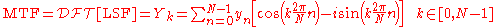.gif)
Modulation transfer function (infrared imaging)
Encyclopedia
The Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) is used to approximate the position of best focus
of an infrared
imaging
system. In an imaging system, best focus
is typically achieved when the MTF is between 0.4 and 0.6; most often at 0.5 (50% cutoff frequency of the MTF) MTF is inversely related to the minimum resolvable temperature difference
(MRTD), which is a measure of an infrared sensor's ability to resolve
temperature difference. MTF is defined as the discrete fourier transform of the Line Spread Function (LSF). The LSF can be calculated by two different methods. One includes measuring the LSF directly from an idealized line approximation provided by an image of a slit target. The other involves differentiating the Edge Spread Function (ESF).
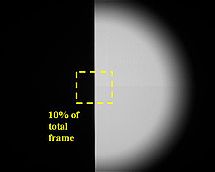 An operator defines a box area encompassing the edge of a knife-edge test target image back-illuminated by a blackbody. The box area is defined to be approximately 10% of the total frame area. The image pixel
An operator defines a box area encompassing the edge of a knife-edge test target image back-illuminated by a blackbody. The box area is defined to be approximately 10% of the total frame area. The image pixel
data is translated into a two-dimensional array (pixel intensity
and pixel position
). The amplitude (pixel intensity) of each line within the array is normalized
and averaged. This yields the edge spread function (ESF)
where
of the ESF, which is differentiated using numerical methods
.
Since the ESF can not be differentiated analytically, it is numerically approximated using the finite difference
:
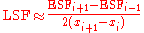
where
data. A sixth order polynomial is fitted to the MTF vs. spatial frequency curve to remove any trends. The 50% cutoff frequency is determined to yield the corresponding spatial frequency. Thus, the approximate position of best focus of the Unit Under Test is determined from this data.
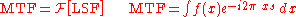
Therefore, the Fourier Transform is numerically approximated using the discrete Fourier transform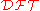 .
.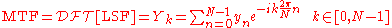
 where
where
Since most computer software is not able to compute complex numbers directly, Euler's identity is implemented to break the transform into separate real and complex terms.
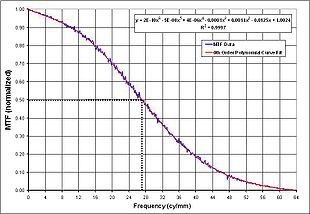
The MTF is then plotted against spatial frequency and all relevant data concerning this test can be determined from that graph.
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by...
of an infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
imaging
Digital imaging
Digital imaging or digital image acquisition is the creation of digital images, typically from a physical scene. The term is often assumed to imply or include the processing, compression, storage, printing, and display of such images...
system. In an imaging system, best focus
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by...
is typically achieved when the MTF is between 0.4 and 0.6; most often at 0.5 (50% cutoff frequency of the MTF) MTF is inversely related to the minimum resolvable temperature difference
Minimum resolvable temperature difference
Minimum resolvable temperature difference is a measure for assessing the performance of infrared cameras, and is inversely proportional to the modulation transfer function....
(MRTD), which is a measure of an infrared sensor's ability to resolve
Image resolution
Image resolution is an umbrella term that describes the detail an image holds. The term applies to raster digital images, film images, and other types of images. Higher resolution means more image detail....
temperature difference. MTF is defined as the discrete fourier transform of the Line Spread Function (LSF). The LSF can be calculated by two different methods. One includes measuring the LSF directly from an idealized line approximation provided by an image of a slit target. The other involves differentiating the Edge Spread Function (ESF).
ESF evaluation

Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
data is translated into a two-dimensional array (pixel intensity
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
and pixel position
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
). The amplitude (pixel intensity) of each line within the array is normalized
Normalization (statistics)
In one usage in statistics, normalization is the process of isolating statistical error in repeated measured data. A normalization is sometimes based on a property...
and averaged. This yields the edge spread function (ESF)
where
- ESF = the output array of normalized pixel intensity data
-
 = the input array of pixel intensity data
= the input array of pixel intensity data -
 = the ith element of
= the ith element of 
-
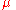 = the average value of the pixel intensity data
= the average value of the pixel intensity data -
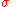 = the standard deviation of the pixel intensity data
= the standard deviation of the pixel intensity data -
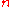 = number of pixels used in average
= number of pixels used in average
LSF evaluation
The line spread function (LSF) can be found using two different methods. It can be found directly from an ideal line approximation provided by a slit test target or it can be derived from the ESF. Using the latter method, the LSF is defined as the first derivativeDerivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
of the ESF, which is differentiated using numerical methods
Numerical analysis
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation for the problems of mathematical analysis ....
.
Since the ESF can not be differentiated analytically, it is numerically approximated using the finite difference
Finite difference
A finite difference is a mathematical expression of the form f − f. If a finite difference is divided by b − a, one gets a difference quotient...
:

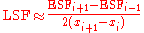
where
-
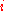 = the index
= the index 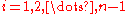
-
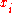 =
= 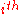 position of the
position of the 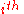 pixel
pixel -
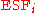 = ESF of the
= ESF of the 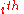 pixel
pixel
MTF Evaluation
The Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) is defined as the discrete fourier transform of the Line Spread Function. Thus, given the LSF, the MTF is approximated numerically. This data is graphed against the spatial frequencySpatial frequency
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, spatial frequency is a characteristic of any structure that is periodic across position in space. The spatial frequency is a measure of how often sinusoidal components of the structure repeat per unit of distance. The SI unit of spatial frequency is...
data. A sixth order polynomial is fitted to the MTF vs. spatial frequency curve to remove any trends. The 50% cutoff frequency is determined to yield the corresponding spatial frequency. Thus, the approximate position of best focus of the Unit Under Test is determined from this data.
MTF calculations
The Fourier transform of the LSF can not be determined analytically by the following equations: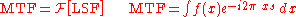
Therefore, the Fourier Transform is numerically approximated using the discrete Fourier transform
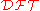 .
.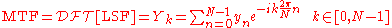

-
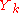 = the
= the 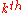 value of the MTF
value of the MTF -
 = number of data points
= number of data points -
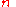 = index
= index -
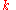 =
= 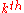 term of the LSF data
term of the LSF data -
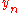 =
= 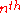 pixel position
pixel position -
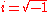
Since most computer software is not able to compute complex numbers directly, Euler's identity is implemented to break the transform into separate real and complex terms.
The MTF is then plotted against spatial frequency and all relevant data concerning this test can be determined from that graph.
See also
- Minimum Resolvable ContrastMinimum Resolvable ContrastMinimum resolvable contrast is a subjective measure of a visible spectrum sensor’s or camera's sensitivity and ability to resolve data. A snapshot image of a series of three bar targets of selected spatial frequencies and various contrast coatings captured by the UUT are used to determine the...
- Minimum resolvable temperature differenceMinimum resolvable temperature differenceMinimum resolvable temperature difference is a measure for assessing the performance of infrared cameras, and is inversely proportional to the modulation transfer function....
- Optical transfer functionOptical transfer functionThe optical transfer function of an imaging system is the true measure of resolution that the system is capable of...
- Signal transfer functionSignal transfer functionThe signal transfer function is a measure of the signal output versus the signal input of a system such as an infrared system or sensor. There are many general applications of the SiTF...
External links
- SPIE international society advancing light based research.
- Electro Optical Industries infrared and visible light spectrum test and calibration equipment.
- MTF expressing the imaging quality.
- Quick MTF software for measuring resolution, including ESF, LSF and MTF.
- MTF on Optipedia Modulation transfer function written by Glenn D. Boreman on Optipedia.
- How to Measure MTF How to Measure MTF and other Properties of Lenses written by Optikos Corporation.