
Minimum resolvable temperature difference
Encyclopedia
Minimum resolvable temperature difference (MRTD) is a measure for assessing the performance of infrared cameras, and is inversely proportional to the modulation transfer function
.
Typically, an operator is asked to assess the minimum temperature
difference at which a 4 bar target can be resolved
. This minimum difference will change with the spatial frequency
of the bar target used. A curve of MRTD against spatial frequency
is obtained which characterises the performance of the imaging system.
Modern infrared imaging systems can have low spatial frequency MRTDs of tens of millikelvins.
best fit
is calculated and the result is the MRTD curve which gives direct insight into the quality of the image. i.e. the infrared camera's ability to resolve detail, in this case temperature.
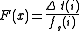 , the MRTD curve
, the MRTD curve
However, MDT is a measure of visibility, not resovability.
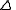 temperature versus spatial frequency.
temperature versus spatial frequency.
Modulation transfer function (infrared imaging)
The Modulation Transfer Function is used to approximate the position of best focus of an infrared imaging system. In an imaging system, best focus is typically achieved when the MTF is between 0.4 and 0.6; most often at 0.5 MTF is inversely related to the minimum resolvable temperature difference...
.
Typically, an operator is asked to assess the minimum temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
difference at which a 4 bar target can be resolved
Optical resolution
Optical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail in the object that is being imaged.An imaging system may have many individual components including a lens and recording and display components...
. This minimum difference will change with the spatial frequency
Spatial frequency
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, spatial frequency is a characteristic of any structure that is periodic across position in space. The spatial frequency is a measure of how often sinusoidal components of the structure repeat per unit of distance. The SI unit of spatial frequency is...
of the bar target used. A curve of MRTD against spatial frequency
Spatial frequency
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, spatial frequency is a characteristic of any structure that is periodic across position in space. The spatial frequency is a measure of how often sinusoidal components of the structure repeat per unit of distance. The SI unit of spatial frequency is...
is obtained which characterises the performance of the imaging system.
Modern infrared imaging systems can have low spatial frequency MRTDs of tens of millikelvins.
Manual test
A manual subjective test is implemented to determine the MRTD. An operator uses a series of 4-bar targets of different spatial frequencies. For each target he/she adjusts the blackbody, (source of Infrared radiation), temperature up and down until the pattern is "just resolvable." The positive and negative temperature differences are stored into a two dimensional array. The corresponding spatial frequencies used in each test are also stored into an array. The MRTD curve is a plot of these arrays (just resolvable temperature difference versus target spatial frequency). From the experimental MRTD data, a general polynomialPolynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
best fit
Curve fitting
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function...
is calculated and the result is the MRTD curve which gives direct insight into the quality of the image. i.e. the infrared camera's ability to resolve detail, in this case temperature.
Calculations
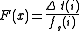 , the MRTD curve
, the MRTD curve
-
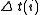 = array of just resolvable temperature differences
= array of just resolvable temperature differences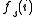 = array of spatial frequences
= array of spatial frequences
Minimum detectable temperature
Minimum detectable temperature (MDT), also called minimum detectable temperature difference (MDTD), is not the same phenomenon as MRTD and is only subtley different. Like MRTD, it is a measure of the performance of infrared cameras.However, MDT is a measure of visibility, not resovability.
Manual test
The manual subjective test for MDT is similar to the one for MRTD. A trained operator views a series of pinhole targets at different spatial frequencies. For each series of pinhole targets the operator ramps the blackbody (source of IR radiation) up and down until the targets are "just visible". The data at which the pinhole targets are "just visible" is stored into an array and plotted against spatial frequency, and a curve is fitted to the data. The MDT curve is thus defined as the temperature versus spatial frequency.
temperature versus spatial frequency.See also
- ThermographyThermographyInfrared thermography, thermal imaging, and thermal video are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermal imaging cameras detect radiation in the infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms...
- InfraredInfraredInfrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
- Minimum resolvable contrastMinimum Resolvable ContrastMinimum resolvable contrast is a subjective measure of a visible spectrum sensor’s or camera's sensitivity and ability to resolve data. A snapshot image of a series of three bar targets of selected spatial frequencies and various contrast coatings captured by the UUT are used to determine the...
- Modulation transfer function (infrared imaging)Modulation transfer function (infrared imaging)The Modulation Transfer Function is used to approximate the position of best focus of an infrared imaging system. In an imaging system, best focus is typically achieved when the MTF is between 0.4 and 0.6; most often at 0.5 MTF is inversely related to the minimum resolvable temperature difference...
- Optical transfer functionOptical transfer functionThe optical transfer function of an imaging system is the true measure of resolution that the system is capable of...
- Signal to noise ratio (image processing)Signal to noise ratio (image processing)The Signal to Noise Ratio is used in imaging as a physical measure of the sensitivity of a imaging system. Industry standards measure SNR in decibels of power and therefore apply the 20 log rule to the "pure" SNR ratio...

