Signal transfer function
Encyclopedia
The signal transfer function (SiTF) is a measure of the signal output
versus the signal input
of a system such as an infrared
system or sensor
. There are many general applications of the SiTF. Specifically, in the field of image analysis, it gives a measure of the noise
of an imaging system, and thus yields one assement of its performance.
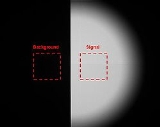
regions of the output image of the infrared sensor, i.e. of the Unit Under Test (UUT), (see "Half Moon" image below). The average signal and background are calculated by averaging the data of each arbitrarily defined region. A second order polynomial
curve is fitted
to the data of each line. Then, the polynomial is subtracted from the average signal and background data to yield the new signal and background. The difference of the new signal and background data is taken to yield the net signal. Finally, the net signal is plotted versus the signal input. The signal input of the UUT is within its own spectral response. (e.g. color-correlated temperature
, pixel
intensity, etc.). The slope of the linear portion of this curve is then found using the method of least squares
.
 The net signal is calculated from the average signal and background, as in signal to noise ratio (imaging)#Calculations.
The net signal is calculated from the average signal and background, as in signal to noise ratio (imaging)#Calculations.
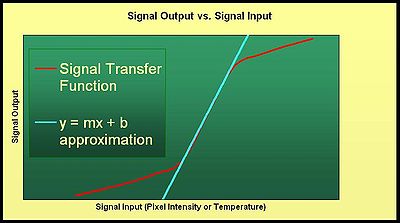
The SiTF curve is then given by the signal output data, (net signal data), plotted against the signal input data (see graph of SiTF to the right). All the data points in the linear region of the SiTF curve can be used in the method of least squares
to find a linear approximation. Given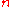 data points
data points 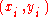 a best fit line parameterized as
a best fit line parameterized as 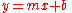 is given by:
is given by:
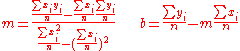
Signal (electrical engineering)
In the fields of communications, signal processing, and in electrical engineering more generally, a signal is any time-varying or spatial-varying quantity....
versus the signal input
Signal (electrical engineering)
In the fields of communications, signal processing, and in electrical engineering more generally, a signal is any time-varying or spatial-varying quantity....
of a system such as an infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
system or sensor
Sensor
A sensor is a device that measures a physical quantity and converts it into a signal which can be read by an observer or by an instrument. For example, a mercury-in-glass thermometer converts the measured temperature into expansion and contraction of a liquid which can be read on a calibrated...
. There are many general applications of the SiTF. Specifically, in the field of image analysis, it gives a measure of the noise
Noise
In common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
of an imaging system, and thus yields one assement of its performance.
SiTF evaluation
In evaluating the SiTF curve, the signal input and signal output are measured differentially; meaning, the differential of the input signal and differential of the output signal are calculated and plotted against each other. An operator, using computer software, defines an arbitrary area, with a given set of data points, within the signal and backgroundBackground radiation
Background radiation is the ionizing radiation constantly present in the natural environment of the Earth, which is emitted by natural and artificial sources.-Overview:Both Natural and human-made background radiation varies by location....
regions of the output image of the infrared sensor, i.e. of the Unit Under Test (UUT), (see "Half Moon" image below). The average signal and background are calculated by averaging the data of each arbitrarily defined region. A second order polynomial
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
curve is fitted
Curve fitting
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function...
to the data of each line. Then, the polynomial is subtracted from the average signal and background data to yield the new signal and background. The difference of the new signal and background data is taken to yield the net signal. Finally, the net signal is plotted versus the signal input. The signal input of the UUT is within its own spectral response. (e.g. color-correlated temperature
Color temperature
Color temperature is a characteristic of visible light that has important applications in lighting, photography, videography, publishing, manufacturing, astrophysics, and other fields. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal black-body radiator that radiates light of...
, pixel
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
intensity, etc.). The slope of the linear portion of this curve is then found using the method of least squares
Least squares
The method of least squares is a standard approach to the approximate solution of overdetermined systems, i.e., sets of equations in which there are more equations than unknowns. "Least squares" means that the overall solution minimizes the sum of the squares of the errors made in solving every...
.
SiTF curve


The SiTF curve is then given by the signal output data, (net signal data), plotted against the signal input data (see graph of SiTF to the right). All the data points in the linear region of the SiTF curve can be used in the method of least squares
Least squares
The method of least squares is a standard approach to the approximate solution of overdetermined systems, i.e., sets of equations in which there are more equations than unknowns. "Least squares" means that the overall solution minimizes the sum of the squares of the errors made in solving every...
to find a linear approximation. Given
 data points
data points 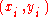 a best fit line parameterized as
a best fit line parameterized as 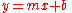 is given by:
is given by: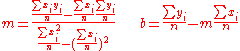
See also
- Optical transfer functionOptical transfer functionThe optical transfer function of an imaging system is the true measure of resolution that the system is capable of...
- DistortionDistortionA distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
- Minimum resolvable temperature differenceMinimum resolvable temperature differenceMinimum resolvable temperature difference is a measure for assessing the performance of infrared cameras, and is inversely proportional to the modulation transfer function....
- Noise equivalent temperature differenceNoise equivalent temperature differenceNoise-equivalent temperature is a measure of the sensitivity of a detector of thermal radiation in the infrared, terahertz or microwave portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It is the amount of incident signal temperature that would be needed to match the internal noise of the detector such...
- Power spectral density
- Minimum resolvable contrastMinimum Resolvable ContrastMinimum resolvable contrast is a subjective measure of a visible spectrum sensor’s or camera's sensitivity and ability to resolve data. A snapshot image of a series of three bar targets of selected spatial frequencies and various contrast coatings captured by the UUT are used to determine the...
- Signal to noise ratio (imaging)

