
Mirror mount
Encyclopedia

Mirror
A mirror is an object that reflects light or sound in a way that preserves much of its original quality prior to its contact with the mirror. Some mirrors also filter out some wavelengths, while preserving other wavelengths in the reflection...
. In optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
research, these can be quite sophisticated devices, due to the need to be able to tip and tilt the mirror by controlled amounts, while still holding it in a precise position when it is not being adjusted.
Precision mirror mounts can be quite expensive, and a notable amount of engineering goes into their design. Such sophisticated mounts are often required for lasers, interferometers, and optical delay lines.
Types of mirror mount

Kinematics
Kinematics is the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies and systems without consideration of the forces that cause the motion....
mount. This type of mount is designed according to the principles of kinematic determinacy
Kinematic determinacy
Kinematic determinacy is a term used in structural mechanics to describe a structure where material compatibility conditions alone can be used to calculate deflections....
. Typically, the movable frame that holds the mirror pivots on a ball bearing
Ball bearing
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this by using at least two races to contain the balls and transmit...
which is set into a hole in the fixed frame. Ideally this hole should be trihedral (pyramid-shaped). Often a conical hole is used due to easier manufacture. The frame is pivoted by means of two micrometer
Micrometer
A micrometer , sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge, is a device incorporating a calibrated screw used widely for precise measurement of small distances in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades, along with other metrological instruments such as dial, vernier,...
s or fine-thread screws, tipped with steel ball bearings. One of these ball bearings rests in a V-groove, the other rests on a flat surface. On cheaper mounts, the flat surface may be simply the material of the mount. In more expensive mounts, the flat surface (and perhaps the hole and v-groove too) may be made out of a much harder material (often sapphire
Sapphire
Sapphire is a gemstone variety of the mineral corundum, an aluminium oxide , when it is a color other than red or dark pink; in which case the gem would instead be called a ruby, considered to be a different gemstone. Trace amounts of other elements such as iron, titanium, or chromium can give...
), set into the frame.
The reason for this strange mechanism, is that the first ball (ideally) makes contact with the fixed frame at exactly three points, the second ball at two, and the third ball at just one. These six points of contact exactly constrain the six degrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom (engineering)
In mechanics, degrees of freedom are the set of independent displacements and/or rotations that specify completely the displaced or deformed position and orientation of the body or system...
for motion of the movable frame. This leads to precise movement of the frame when the micrometers or screws are turned, without unnecessary wobble or friction.
A disadvantage of kinematic mounts is that the center of the mirror moves along its normal
Surface normal
A surface normal, or simply normal, to a flat surface is a vector that is perpendicular to that surface. A normal to a non-flat surface at a point P on the surface is a vector perpendicular to the tangent plane to that surface at P. The word "normal" is also used as an adjective: a line normal to a...
axis, when the mirror is rotated. This is because the center of rotation is the middle of the first ball bearing, not the center of the mirror. For optical cavities
Optical cavity
An optical cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors that forms a standing wave cavity resonator for light waves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light. They are also used in optical parametric...
and interferometers, it is often desirable to be able to align the mirrors separately from adjustments to the length of the cavity. For these applications and others, a more sophisticated mount is required.
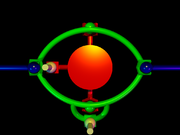
Stepper motor
A stepper motor is a brushless, electric motor that can divide a full rotation into a large number of steps. The motor's position can be controlled precisely without any feedback mechanism , as long as the motor is carefully sized to the application...
under computer control to make this seem to the operator like simple rotation about a virtual pivot point in the center of the mirror surface. The translation can instead be eliminated mechanically by using a gimbal
Gimbal
A gimbal is a pivoted support that allows the rotation of an object about a single axis. A set of two gimbals, one mounted on the other with pivot axes orthogonal, may be used to allow an object mounted on the innermost gimbal to remain immobile regardless of the motion of its support...
mount, which uses two rings that each pivot about a line running through the center of the mirror. This gives kinematically-correct two-axis rotation about the center of the mirror.
With both types of mount, springs are needed to keep the frame pressed against the ball bearings, unless the mount is designed to be used only in an orientation where gravity will keep the frame in place. Following the cantilever
Cantilever
A cantilever is a beam anchored at only one end. The beam carries the load to the support where it is resisted by moment and shear stress. Cantilever construction allows for overhanging structures without external bracing. Cantilevers can also be constructed with trusses or slabs.This is in...
principle, a large mount allows finer control than a smaller one. The frames are ideally made of a light material, to make the resonant
Resonance
In physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate at a greater amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as the system's resonant frequencies...
frequency of the structure high. This reduces vibration, since many common sources of vibration are relatively low frequency. For stability, the fixed frame is supported by a rigid mount that is securely bolted to a supporting surface. In a laboratory environment, this is typically an optical table
Optical table
An optical table is platform that is used to support systems used for optics experiments and engineering.-Explanation:In optical systems, especially those involving interferometry, the alignment of each component must be extremely accurate—precise down to a fraction of a wavelength—usually a few...
.
The mount itself has to avoid deformation of the mounted optics. Stress from mounting can introduce aberration in the light reflected from a mirror, or photoelasticity
Photoelasticity
Photoelasticity is an experimental method to determine the stress distribution in a material. The method is mostly used in cases where mathematical methods become quite cumbersome. Unlike the analytical methods of stress determination, photoelasticity gives a fairly accurate picture of stress...
inside a lens. In some lasers the mirrors have to be easily replaced, in which case the mount needs to be designed to allow the mirror to be removed and replaced without losing correct alignment.
Operation
The fine-thread screws show a slip and stick behaviour. So when used manually, a torque is applied with two fingers until the thread slips a bit. Then the new position is read on a scale. Inexpensive screws do long slips and lack a scale. Precision micrometers perform better and provide a scale for reference. When used remotely, an electric motorElectric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
is used to apply short pulses of torque. The motor is firmly connected with the screw and the thread and nothing else so that the pulse is absorbed by friction. A small camera
Camera
A camera is a device that records and stores images. These images may be still photographs or moving images such as videos or movies. The term camera comes from the camera obscura , an early mechanism for projecting images...
reads a Gray code
Gray code
The reflected binary code, also known as Gray code after Frank Gray, is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit. It is a non-weighted code....
scale. When the ball is not completely centered on the screw and the axis is not normal to the mirror surface (which is an explicit feature of some convenience mirror mounts), a small sinus movement of the mirror is overlayed onto the linear movement, which a controller could compensate for. For analog fine control (5 nm) piezos
Piezoelectricity
Piezoelectricity is the charge which accumulates in certain solid materials in response to applied mechanical stress. The word piezoelectricity means electricity resulting from pressure...
are built into the mobile frame.
Applications

Coma (optics)
In optics , the coma in an optical system refers to aberration inherent to certain optical designs or due to imperfection in the lens or other components which results in off-axis point sources such as stars appearing distorted, appearing to have a tail like a comet...
. Sometimes prism
Prism (optics)
In optics, a prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. The exact angles between the surfaces depend on the application. The traditional geometrical shape is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use...
s only need two axes alignment and can be mounted on a mirror mount rather than a three-axis prism table.
Critical phase matched crystals can be aligned and tuned precisely with a standard mirror mount. The same is true for small etalons, retarder
Wave plate
A wave plate or retarder is an optical device that alters the polarization state of a light wave travelling through it.- Operation :A wave plate works by shifting the phase between two perpendicular polarization components of the light wave. A typical wave plate is simply a birefringent crystal...
s and polarizer
Polarizer
A polarizer is an optical filter that passes light of a specific polarization and blocks waves of other polarizations. It can convert a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam with well-defined polarization. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular...
s. Furthermore, mirror mounts using magnet
Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object...
s instead of springs allow the mobile frame to be removed and later replaced in exactly the same position.
Related devices
- Although rotationRotationA rotation is a circular movement of an object around a center of rotation. A three-dimensional object rotates always around an imaginary line called a rotation axis. If the axis is within the body, and passes through its center of mass the body is said to rotate upon itself, or spin. A rotation...
can be achieved by a semi gimbal mount most rotation stages are not designed based on the principles of kinematic determinacy. - A linear motion bearingLinear motion bearingA linear-motion bearing or linear slide is a bearing designed to provide free motion in one dimension. There are many different types of linear motion bearings and this family of products is generally broken down into two sub-categories: rolling-element and plane.Motorized linear slides such as...
or linear stageLinear stageA linear stage or translation stage is a component of a motion system used to restrict an object to a single axis of motion. The term linear slide is often used interchangeably with "linear stage", though technically "linear slide" refers to a linear motion bearing, which is only a component of a...
having kinematic determinacy uses two V-grooves sliding on a cylinder, a flat surface sliding on a second parallel cylinder, and a flat surface joining the screw. - The hexapod known from flight simulatorFlight simulatorA flight simulator is a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and various aspects of the flight environment. This includes the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they react to applications of their controls and other aircraft systems, and how they react to the external...
s allows motion with six degrees of freedom. For kinematic determinacy each leg consists of a ball set in a trihedral hole in the fixed frame, a ball joining a flat plate in the fixed frame, and a ball joing a trihedral hole in the mobile frame. The mobile part of the leg is connected with a thread which runs in thread of the fixed part. - A screw-thread join gets kinematic determinacy the same way as any other rotation bearingBearing (mechanical)A bearing is a device to allow constrained relative motion between two or more parts, typically rotation or linear movement. Bearings may be classified broadly according to the motions they allow and according to their principle of operation as well as by the directions of applied loads they can...
. - The ball bearingBall bearingA ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this by using at least two races to contain the balls and transmit...
and cylindrical roller bearing are over-determined, having more points of contact than required for kinematic determinacy. This leads to decreased precision as the joints wear. - The flexure bearingFlexure bearingA flexure bearing is a bearing which allows motion by bending a load element.A typical flexure bearing is just one part, joining two other parts. For example, a hinge may be made by attaching a long strip of a flexible element to a door and to the door frame...
and piezoelectric elementPiezoelectricityPiezoelectricity is the charge which accumulates in certain solid materials in response to applied mechanical stress. The word piezoelectricity means electricity resulting from pressure...
offer higher precision than other mechanical bearings.

