
Minolta Dimage 7, 7i, 7hi
Encyclopedia

Minolta
Minolta Co., Ltd. was a Japanese worldwide manufacturer of cameras, camera accessories, photocopiers, fax machines, and laser printers. Minolta was founded in Osaka, Japan, in 1928 as . It is perhaps best known for making the first integrated autofocus 35mm SLR camera system...
DiMage 7, 7i, 7Hi series is a "pro-sumer" line of digital electronic viewfinder
Electronic viewfinder
An electronic viewfinder or EVF is a viewfinder where the image captured by the lens is projected electronically onto a miniature display. The image on this display is used to assist in aiming the camera at the scene to be photographed.-Operation:...
cameras from Minolta. These are also known as bridge digital camera
Bridge digital camera
Bridge cameras are cameras which fill the niche between the single-lens reflex cameras and the Point-and-shoot camera. They are often comparable in size and weight to the smallest Digital SLRs , but almost all digital bridge cameras lack an optical viewfinder system...
s. They are capable of capturing images in the 5 megapixel
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
range.
The DiMage 7 was announced 11 February 2001. The line uses a 2588 x 1960 pixel sensor coupled with a permanently attached optical 28-200mm (35mm equivalent) f/2.8W - f/3.5T zoom
Zoom lens
A zoom lens is a mechanical assembly of lens elements for which the focal length can be varied, as opposed to a fixed focal length lens...
lens
Photographic lens
A camera lens is an optical lens or assembly of lenses used in conjunction with a camera body and mechanism to make images of objects either on photographic film or on other media capable of storing an image chemically or electronically.While in principle a simple convex lens will suffice, in...
with a macro
Macro photography
Macrophotography is close-up photography, usually of very small subjects. Classically a macrophotograph is one in which the size of the subject on the negative is greater than life size. However in modern use it refers to a finished photograph of a subject at greater than life size...
switch (16 elements in 13 groups, includes two AD glass elements and two aspheric elements)
The DiMage 7/7i/7Hi series cameras were powered with four AA batteries, which discharged quickly; the 7-series was replaced by the DiMAGE A1
Minolta DiMage A1
The Minolta DiMAGE A1 is an electronic viewfinder bridge digital camera produced by Minolta, which was introduced in July 2003, replacing the DiMAGE 7/7h/7hi...
in July 2003.
| 7Hi/7i | ||||
| CCD Charge-coupled device A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time... |
ICX282AQF 2/3-type interline interlaced primary-color Super HAD CCD Charge-coupled device A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time... Total pixels: approx. 5.24 million Number of effective pixels: approx. 5.07 million Number of active pixels: approx. 5.02 million Chip size: 9.74 mm (H) X 7.96 mm (V) Unit cell size: 3.4 μm (H) X 3.4 μm (V) Saturation signal: 450 mV Sensitivity: 270 mV (G signal, 3200 K, 706 cd/m2, F5.6, 1/30 s accumulation) Dark signal: 16 mV (Ta=60 °C, 3.75 frame/s) Smear: -92 dB (without a mechanical shutter Shutter (photography) In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene... , frame readout mode) |
|||
| Image processing | CxProcess | |||
| Operating sysytem | iTRON Itron Itron Inc. is a provider of intelligent metering, data collection and utility software. It has nearly 8,000 utilities worldwide relying on their technology to optimize the delivery and use of energy and water... |
|||
| Camera sensitivity Film speed Film speed is the measure of a photographic film's sensitivity to light, determined by sensitometry and measured on various numerical scales, the most recent being the ISO system.... |
JPEG JPEG In computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality.... , TIFF Tagged Image File Format TIFF is a file format for storing images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry, and both amateur and professional photographers in general. As of 2009, it is under the control of Adobe Systems... , Motion JPEG (MOV): Auto (100 - 400), ISO 100, 200, 400, 800 equivalents RAW RAW image format A camera raw image file contains minimally processed data from the image sensor of either a digital camera, image scanner, or motion picture film scanner. Raw files are so named because they are not yet processed and therefore are not ready to be printed or edited with a bitmap graphics editor... : ISO 100 equivalent |
|||
| Aspect ratio | 4:3 | |||
| Lens Photographic lens A camera lens is an optical lens or assembly of lenses used in conjunction with a camera body and mechanism to make images of objects either on photographic film or on other media capable of storing an image chemically or electronically.While in principle a simple convex lens will suffice, in... construction |
16 elements in 13 groups (includes two AD glass elements and two aspheric elements) | |||
| Maximum aperture Aperture In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture of an optical system is the opening that determines the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. The aperture determines how collimated the admitted rays are,... |
f/2.8 - f/3.5 | |||
| Aperture Aperture In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture of an optical system is the opening that determines the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. The aperture determines how collimated the admitted rays are,... steps |
f/2.8, 3.5, 4, 4.5, 5.6, 6.7, 8, 9.5 | |||
| Focal length Focal length The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light. For an optical system in air, it is the distance over which initially collimated rays are brought to a focus... |
7.2 - 50.8 mm (35 mm equivalent: 28 – 200 mm) Macro Macro photography Macrophotography is close-up photography, usually of very small subjects. Classically a macrophotograph is one in which the size of the subject on the negative is greater than life size. However in modern use it refers to a finished photograph of a subject at greater than life size... : 7.2 and 43 - 50.8 mm (35 mm equivalent: 28 and 170 – 200 mm) |
|||
| Focusing range (from CCD Charge-coupled device A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time... ) |
0.5 m / 19.7 inch to infinity Macro Macro photography Macrophotography is close-up photography, usually of very small subjects. Classically a macrophotograph is one in which the size of the subject on the negative is greater than life size. However in modern use it refers to a finished photograph of a subject at greater than life size... : Wide 30 – 60 cm / 11.8 - 23.6 inch, Telephoto 25 – 60 cm / 9.8 - 23.6 inch |
|||
| Maximum magnification | 0.177x (Equivalent to 0.7x in 35 mm format) (With a focal length Focal length The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light. For an optical system in air, it is the distance over which initially collimated rays are brought to a focus... of 50.8 mm. Distance at 25 cm) Area covered at maximum magnification: 50 x 37 mm / 2 x 1.5 inch (approx.) |
|||
| Optical zooming control | Manual zooming ring | |||
| Optical focus control | Precision Focus-by-wire rotating focusing ring | |||
| Autofocus Autofocus An autofocus optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus fully automatic or on a manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system has to be done manually until indication... system |
Video AF | |||
| Focus lock | By pressing shutter Shutter (photography) In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene... -release button partway down. Also possible with spot-AE lock button (The function of the spot-AE lock button can be changed with the recording menu) |
|||
| Autofocus Autofocus An autofocus optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus fully automatic or on a manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system has to be done manually until indication... areas |
Wide focus area, Spot focus point
|
|||
| Focus modes | Autofocus Autofocus An autofocus optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus fully automatic or on a manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system has to be done manually until indication... : Single-shot AF (DMF), Continuous AF (DMF) Manual focus |
|||
| Focus features | Pixel binning in low light conditions Center scan mode for 4x electronic zoom image (EVF/LCD, manual focus) 2x Digital zoom (LCD, manual focus) |
|||
| Exposure Exposure (photography) In photography, exposure is the total amount of light allowed to fall on the photographic medium during the process of taking a photograph. Exposure is measured in lux seconds, and can be computed from exposure value and scene luminance over a specified area.In photographic jargon, an exposure... modes |
P (Programmed AE) (with program shift), A (Aperture Aperture In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture of an optical system is the opening that determines the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. The aperture determines how collimated the admitted rays are,... priority), S (shutter Shutter (photography) In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene... priority), M (Manual). |
|||
| AE lock | With Spot-AE lock button or by pressing the shutter Shutter (photography) In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene... -release button partway down |
|||
| Metering | Multi-segment (300 segments), Center-weighted, Spot | |||
| Exposure Exposure (photography) In photography, exposure is the total amount of light allowed to fall on the photographic medium during the process of taking a photograph. Exposure is measured in lux seconds, and can be computed from exposure value and scene luminance over a specified area.In photographic jargon, an exposure... control range |
P / A modes: Wide; Ev - 1 - 18, Telephoto; Ev - 0.4 (7Hi) / 1.6 (7i) - 18.7 S / M modes: Wide; Ev - 1 - 17, Telephoto; Ev - 0.4 (7Hi) / 1.6 (7i) - 17.7 |
|||
| shutter Shutter (photography) In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene... |
CCD Charge-coupled device A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time... electronic shutter Shutter (photography) In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene... and mechanical shutter Shutter (photography) In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene... |
|||
| shutter Shutter (photography) In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene... speed range |
7Hi: 15 - 1/4000 seconds (in P / A modes, ISO 100), Bulb Bulb (photography) Bulb, abbreviated B, is a shutter speed setting on an adjustable camera that allows for long exposure times under the direct control of the photographer. With this setting, the shutter simply stays open as long as the shutter release button remains depressed... (max. 30 seconds) 7i: 4 - 1/4000 seconds (in P / A modes), 4 - 1/2000 seconds (in S / M modes), Bulb (max. 30 seconds) |
|||
| White-balance control | 7Hi: Automatic, Preset {Daylight, Tungsten, Fluorescent 1, 2 (white / cool white), Cloudy}, Custom (3 positions) 7i: Automatic, Preset (Daylight, Tungsten, Fluorescent, Cloudy), Custom |
|||
| Digital Subject Programs | Portrait, Sports action, Sunset, Night portrait, Text | |||
| Digital Effects Control | Exposure Exposure (photography) In photography, exposure is the total amount of light allowed to fall on the photographic medium during the process of taking a photograph. Exposure is measured in lux seconds, and can be computed from exposure value and scene luminance over a specified area.In photographic jargon, an exposure... , Color saturation, Contrast compensation, Filter |
|||
| Exposure compensation Exposure compensation Exposure compensation is a technique for adjusting the exposure indicated by a photographic exposure meter, in consideration of factors that may cause the indicated exposure to result in a less-than-optimal image. Factors considered may include unusual lighting distribution, variations within a... |
+/- 2 Ev in 1/3 increments | |||
| Flash Flash (photography) A flash is a device used in photography producing a flash of artificial light at a color temperature of about 5500 K to help illuminate a scene. A major purpose of a flash is to illuminate a dark scene. Other uses are capturing quickly moving objects or changing the quality of light... metering |
ADI, Pre-flash TTL, Manual flash control
|
|||
| Flash-sync speeds | All shutter Shutter (photography) In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene... speeds |
|||
| Flash Flash (photography) A flash is a device used in photography producing a flash of artificial light at a color temperature of about 5500 K to help illuminate a scene. A major purpose of a flash is to illuminate a dark scene. Other uses are capturing quickly moving objects or changing the quality of light... modes |
Fill-flash, Red-eye reduction, Rear flash sync, Wireless / Remote flash | |||
| Built-in flash range* (approx.) | able class="wikitable" style="text-align: left; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ISO setting | Flash range (wide angle) | Flash range (telephoto) |
| AUTO | 0.5m - 3.8m / 1.6 ft. - 12.5 ft. | 0.5m - 3.0m / 1.6 ft. - 9.8 ft. | ||
| 100 | 0.5m - 2.7m / 1.6 ft. - 8.8 ft. | 0.5m - 2.1m / 1.6 ft. - 6.9 ft. | ||
| 200 | 0.5m - 3.8m / 1.6 ft. - 12.5 ft. | 0.5m - 3.0m / 1.6 ft. - 9.8 ft. | ||
| 400 | 0.5m - 5.4m / 1.6 ft. - 17.6 ft. | 0.5m - 4.2m / 1.6 ft. - 13.8 ft. | ||
| 800 | 0.5m - 7.6m / 1.6 ft. - 25 ft. | 0.5m - 6.0m / 1.6 ft. - 19.6 ft. |
Flash sync terminal (7Hi)
Electronic viewfinder
An electronic viewfinder or EVF is a viewfinder where the image captured by the lens is projected electronically onto a miniature display. The image on this display is used to assist in aiming the camera at the scene to be photographed.-Operation:...
type
Electronic viewfinder
An electronic viewfinder or EVF is a viewfinder where the image captured by the lens is projected electronically onto a miniature display. The image on this display is used to assist in aiming the camera at the scene to be photographed.-Operation:...
), Variable-position: 0 - 90 degrees
Automatic monitor amplification, Electronic magnification for manual focusing
Electronic viewfinder
An electronic viewfinder or EVF is a viewfinder where the image captured by the lens is projected electronically onto a miniature display. The image on this display is used to assist in aiming the camera at the scene to be photographed.-Operation:...
display
Equivalent visual resolution: 220,000 pixels (approx.), Field of view: 100% (approx.)
Display format: 300 (H) X 224 (V)
Pixel dimensions: 0.0135 mm (pixel dimensions include a 0.0005 mm interpixel gap)
Color depth: 18 bit (6 bit RGB)
Brightness: 250 cd/m2
Contrast ratio: 80:1
Electronic viewfinder
An electronic viewfinder or EVF is a viewfinder where the image captured by the lens is projected electronically onto a miniature display. The image on this display is used to assist in aiming the camera at the scene to be photographed.-Operation:...
magnification
Eye relief
-Eye Relief and Exit Pupil:The eye relief of a telescope, a microscope, or binoculars is the distance from the last surface of an eyepiece at which the eye can obtain the full viewing angle. If a viewer's eye is outside this distance, a reduced field of view will be obtained...
Total pixels: 118,000, Field of view: 100% (approx.)
Number of colors: Analog full color
Pixel arrangement: RGB delta
Effective pixels per unit area: 115.4 dots/mm2
Optical transmittance: 8.6%
Contrast ratio: 200:1
Playback mode: Single-frame, Index, Enlarged playback, Slide show, Histogram of recorded image, Various statuses
Electronic viewfinder
An electronic viewfinder or EVF is a viewfinder where the image captured by the lens is projected electronically onto a miniature display. The image on this display is used to assist in aiming the camera at the scene to be photographed.-Operation:...
proximity sensor), Electronic viewfinder
Electronic viewfinder
An electronic viewfinder or EVF is a viewfinder where the image captured by the lens is projected electronically onto a miniature display. The image on this display is used to assist in aiming the camera at the scene to be photographed.-Operation:...
display, LCD-monitor display
Correlated Double Sampling
Correlated Double Sampling
Correlated Double Sampling is a technique for measuring electrical values such as voltages or currents that allows for removal of an undesired offset. It is used quite frequently when measuring sensor outputs. The output of the sensor is measured twice: once in a known condition and once in an...
(CDS)
79 dB SNR
SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random access memory is dynamic random access memory that is synchronized with the system bus. Classic DRAM has an asynchronous interface, which means that it responds as quickly as possible to changes in control inputs...
)
7i: 32MB (SDRAM
SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random access memory is dynamic random access memory that is synchronized with the system bus. Classic DRAM has an asynchronous interface, which means that it responds as quickly as possible to changes in control inputs...
)
JPEG
In computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality....
, TIFF
Tagged Image File Format
TIFF is a file format for storing images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry, and both amateur and professional photographers in general. As of 2009, it is under the control of Adobe Systems...
, Motion JPEG (MOV), RAW. DCF 1.0 / DPOF 1.1-compliant
7i: Exif Print, PRINT Image Matching
CompactFlash
CompactFlash is a mass storage device format used in portable electronic devices. Most CompactFlash devices contain flash memory in a standardized enclosure. The format was first specified and produced by SanDisk in 1994...
cards (max. 2 GB) IBM Microdrive
Microdrive
Microdrive is a brand name for a miniature, 1-inch hard disk designed to fit in a CompactFlash Type II slot. The release of similar drives by other makers has led to them often being referred to as 'microdrives'...
(170MB, 340MB, 512MB, 1 GB)
Still images (RAW): 2568 x 1928
Movie clips: 640 x 480 (UHS continuous-advance mode), 320 x 240 (standard, night movie modes), Time-lapse movie at all image sizes
ICC profile
In color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium...
s are available for all formats except RAW
High Speed continuous advance (with 2560 x 1920 size images) (7Hi)
UHS (Ultra High Speed) continuous advance (with 1280 x 960 size images)
Standard continuous advance
- UHS and standard continuous advance cannot be used with Super Fine or RAW images.
Speeds :
High Speed continuous advance: max. 3 frame/s (approx.) (7Hi)
UHS (Ultra High Speed) continuous advance: 7 frame/s (approx.)
Standard continuous advance: max. 2 frame/s
- Actual speeds may vary depending upon subjects and shooting conditions.
Exposure: 1.0, 0.5, 0.3 Ev increments
Contrast, Color saturation, Filter: fixed increments
Number of brackets: 3 frames
60 s (max.) with and without monaural audio
Number of recorded pixels: 320 x 240
Frame rate: 15 frame/s
Night movie mode (Images is monochrome.):
60 s (max.) with and without monaural audio
Number of recorded pixels: 320 x 240
Frame rate: 15 frame/s
UHS (Ultra High Speed) continuous-advance movie mode:
Number of recorded pixels: 640 x 480
Frame rate: approx. 7 frame/s without audio
Time-lapse movie mode:
Number of recorded pixels: 2560 x 1920, 1600 x 1200, 1280 x 960, 640 x 480
Frame rate: 4 frame/s without audio
File format: WAVE
Shutter (photography)
In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene...
sound effect settings
Shutter (photography)
In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene...
speed, Aperture
Aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture of an optical system is the opening that determines the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. The aperture determines how collimated the admitted rays are,...
value, Exposure compensation
Exposure compensation
Exposure compensation is a technique for adjusting the exposure indicated by a photographic exposure meter, in consideration of factors that may cause the indicated exposure to result in a less-than-optimal image. Factors considered may include unusual lighting distribution, variations within a...
value, Metering method, Flash on / off, Camera sensitivity, White balance setting, Focal length
Focal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light. For an optical system in air, it is the distance over which initially collimated rays are brought to a focus...
, etc.
Dark frame subtraction
In digital photography, dark-frame subtraction is a way to minimize image noise for pictures taken with long exposure times. It takes advantage of the fact that a component of image noise, known as fixed-pattern noise, is the same from shot to shot: noise from the sensor, dead or hot pixels...
Continuous playback time: 120 minutes
- 1700 mAh Ni-MH batteries, EVF on, External LCD monitor off, Full-size images (2560 X 1920), Standard image quality, No instant playback, No voice memo, Flash used with 50 % of the frames
shutter
Shutter (photography)
In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period of time, for the purpose of exposing photographic film or a light-sensitive electronic sensor to light to capture a permanent image of a scene...
release time lag: 0.1 - 0.17 second
7i: 525 g / 18.5 ounce
without batteries or recording media

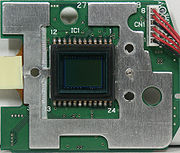
Parts List
- DSC Controller LSI /OS: micro iTRON, Nucleus+/ (7i/7Hi): MA07163 DSC-2
- Microcontroller (7i/7Hi): D78F0338
- Image sensor 2/3-type interline primary-color CCDCharge-coupled deviceA charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time...
(7i/7Hi): ICX282AQF - Timing Generator for Frame Readout CCD (7i/7Hi): CXD2498R
- CCD SIGNAL PROCESSOR (7i/7Hi): VSP2262
- LCD (7i/7Hi): ACX312AK
- EVF LightView QVGA Digital Display Module /Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal - FLC/(7i/7Hi): LDM-0201
- Driver/Timing Generator for LCD (7i/7Hi): CXA3572R
- CMOS SDRAM MEMORY (7i): TC59SM716, (7Hi) HY57V561620
- CMOS FLASH MEMORY (7i): TC58FVT160FT, (7Hi) MBM29LV320
- EEPROM (7i/7Hi): IS93C46D
- EEPROM PLD (7i/7Hi): EPM3064A
- DC-DC converter (7i/7Hi): AN8049SH
- Digital Camera Motor Driver (7i/7Hi): LB8649
- A/D & D/A converter for portable digital audio system (7i/7Hi): AK4550
- D/A converter (7i/7Hi): MB40C938V
- REAL TIME CLOCK (7i/7Hi): R4543_B
- Octal Bus Buffer (7i/7Hi): MC74VHC244
- IGBT for STROBE FLASHER (7i/7Hi): CY25AAJ-8F
- Triac (7Hi): BCR5AS
- Operational amplifier (7Hi): NJM4558
PCB
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
System accessories
- Case CS-DG7
- Leather Neck Strap NS-DG 1000 (7Hi)
- Neck Strap NS-DG 2000/3000 (7Hi)
- Neck Strap NS-DG7 (7i)
- Lens Shade DLS-7Hi (7Hi)
- Lens Shade DLS-7i (7i)
- Lens Cap LF-1249
- Shoe Cap SC-9
- USB Cable USB-100
- AV Cable AVC-300
- External Battery Pack kit EBP-100
- Battery Pack holder BH-100
- Li-ion Battery NP-100
- Li-ion Battery Charger BC-100
- AC Adapter AC-1L
- AC Adapter AC-2L
- Remote Cable RC-1000L
- Remote Cable RC-1000S
- Wide-angle Converter ACW-100
- Telephoto Converter ACT-100
- Close-up Lens CL-49-200
- PC Flash Adapter PCT-100
- Program/Maxxum Flash 3600HS(D)
- Program/Maxxum Flash 5600HS(D)
- Bounce Reflector V-Set
- External Battery Pack EP2 Set
- Macro Flash Controller
- Macro Twin Flash 2400
- Macro Ring Flash 1200
- Close-up Diffuser CD-1000
- Triple Connector TC-1000
- Cable CD
- Off-Camera Shoe OS-1100
- Off-camera Cable OC-1100

