
Microactuator
Encyclopedia
A microactuator is a microscopic
servomechanism
that supplies and transmits a measured amount of energy for the operation of another mechanism or system. As a general actuator
, following standards have to be met.
For microactuator, there are two in addition
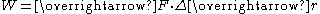
since an actuator is to manipulate positions and therefore force is needed. For different kind of microactuators, different physical principles are applied.
Microscopic
The microscopic scale is the scale of size or length used to describe objects smaller than those that can easily be seen by the naked eye and which require a lens or microscope to see them clearly.-History:...
servomechanism
Servomechanism
thumb|right|200px|Industrial servomotorThe grey/green cylinder is the [[Brush |brush-type]] [[DC motor]]. The black section at the bottom contains the [[Epicyclic gearing|planetary]] [[Reduction drive|reduction gear]], and the black object on top of the motor is the optical [[rotary encoder]] for...
that supplies and transmits a measured amount of energy for the operation of another mechanism or system. As a general actuator
Actuator
An actuator is a type of motor for moving or controlling a mechanism or system. It is operated by a source of energy, usually in the form of an electric current, hydraulic fluid pressure or pneumatic pressure, and converts that energy into some kind of motion. An actuator is the mechanism by which...
, following standards have to be met.
- Large travel
- High precision
- Fast switching
- Low power consumption
- Power free force sustainability
For microactuator, there are two in addition
- Microstructurability
- IntegrabilityIntegrabilityIntegrability may refer to:* Riemann integrability; see Riemann integral* Lebesgue integrability; see Lebesgue integral* Darboux integrability; see Darboux integral* System integration * Interoperability...
Principle of microactuators
The basic principle can be described as the expression for mechanical workMechanical work
In physics, work is a scalar quantity that can be described as the product of a force times the distance through which it acts, and it is called the work of the force. Only the component of a force in the direction of the movement of its point of application does work...
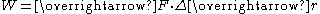
since an actuator is to manipulate positions and therefore force is needed. For different kind of microactuators, different physical principles are applied.
Classes of microactuators
- Electrostatic
- ElectromagneticElectromagneticElectromagnetic may refer to:* Electromagnetism* Electromagnetic field* Electromagnetic force* Electromagnetic radiation* Electromagnetic induction* Electromagnetic spectrum...
- Piezoelectric
- FluidFluidIn physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
- ThermalThermalA thermal column is a column of rising air in the lower altitudes of the Earth's atmosphere. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of the Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example of convection. The sun warms the ground, which in turn warms the air directly above it...
See also
- Newton's laws
- Euler-Bernoulli beam equationEuler-Bernoulli beam equationEuler–Bernoulli beam theory is a simplification of the linear theory of elasticity which provides a means of calculating the load-carrying and deflection characteristics of beams. It covers the case for small deflections of a beam which is subjected to lateral loads only...
- ElectrostaticsElectrostaticsElectrostatics is the branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges....
- ElectromagneticElectromagneticElectromagnetic may refer to:* Electromagnetism* Electromagnetic field* Electromagnetic force* Electromagnetic radiation* Electromagnetic induction* Electromagnetic spectrum...
- PiezoelectricityPiezoelectricityPiezoelectricity is the charge which accumulates in certain solid materials in response to applied mechanical stress. The word piezoelectricity means electricity resulting from pressure...
- MicrofluidicsMicrofluidicsMicrofluidics deals with the behavior, precise control and manipulation of fluids that are geometrically constrained to a small, typically sub-millimeter, scale.Typically, micro means one of the following features:* small volumes...
- Sensors
- Nanotube nanomotorNanotube nanomotorA device generating linear or rotational motion using carbon nanotube as the primary component, is termed a nanotube nanomotor. Nature already has some of the most efficient and powerful kinds of nanomotors. Some of these natural biological nanomotors have been re-engineered to serve desired purposes...

