Method of images
Encyclopedia
See also Method of image charges
for applications in electrostatics
and magnetostatics
Method of images (or mirror images) is a mathematical tool for solving differential equation
s in which the domain of the sought function
is extended by the addition of its mirror image with respect to a symmetry hyperplane
, with the purpose of facilitating the solution of the original problem. It is used in electrostatics
to simply calculate or visualize the distribution of the electric field of a charge in the vicinity of the conducting surface. It is based on the fact that the tangential component of the electrical field to the surface of a conductor
is zero, and that some field E with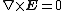 and
and 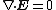 in some region is uniquely defined by its normal component over the surface which confines this region (the uniqueness theorem).
in some region is uniquely defined by its normal component over the surface which confines this region (the uniqueness theorem).
The method may also be used in magnetostatics
for calculating the magnetic field of a magnet which is close to a superconducting surface. Here, the component of the magnetic field normal to the superconductor is zero. Another use is in fluid dynamics
: the movement of a vortex
near a wall may be calculated using an image vortex.
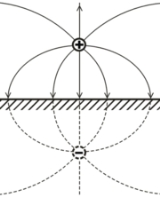
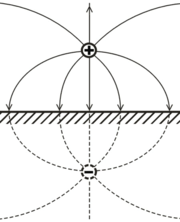 A textbook example is an infinite flat conducting surface (see Fig. 1). In this case the field distribution between the surface and a charge is the same as between this charge and another charge (imaginary charge), which is the mirror image of the real charge in respect to the surface but has the opposite sign. Evidently, in case of an electrical dipole, the vector of the mirrored dipole will have the opposite sign. Therefore, the force between the electrical charge or system of charges and the conducting surface is attractive. It is also interesting (but not obvious) that the total surface charge influenced on the conducting surface (which can be obtained by integration of the surface charge, for example) exactly matches the opposite value of the point charge (-q).
A textbook example is an infinite flat conducting surface (see Fig. 1). In this case the field distribution between the surface and a charge is the same as between this charge and another charge (imaginary charge), which is the mirror image of the real charge in respect to the surface but has the opposite sign. Evidently, in case of an electrical dipole, the vector of the mirrored dipole will have the opposite sign. Therefore, the force between the electrical charge or system of charges and the conducting surface is attractive. It is also interesting (but not obvious) that the total surface charge influenced on the conducting surface (which can be obtained by integration of the surface charge, for example) exactly matches the opposite value of the point charge (-q).
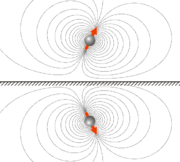 In case of magnet-superconductor pair (the superconductor here is ideal, into which the magnetic field does not penetrate), the mirror image of the magnet will have a magnetization
In case of magnet-superconductor pair (the superconductor here is ideal, into which the magnetic field does not penetrate), the mirror image of the magnet will have a magnetization
vector which is mirrored but of the same sign (see Fig. 2). This can be thought as due to additional sign change upon mirroring of an axial vector which the magnetization is. The force between the magnet and the superconducting surface is therefore repulsive.
Method of image charges
The method of image charges is a basic problem-solving tool in electrostatics...
for applications in electrostatics
Electrostatics
Electrostatics is the branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges....
and magnetostatics
Magnetostatics
Magnetostatics is the study of magnetic fields in systems where the currents are steady . It is the magnetic analogue of electrostatics, where the charges are stationary. The magnetization need not be static; the equations of magnetostatics can be used to predict fast magnetic switching events that...
Method of images (or mirror images) is a mathematical tool for solving differential equation
Differential equation
A differential equation is a mathematical equation for an unknown function of one or several variables that relates the values of the function itself and its derivatives of various orders...
s in which the domain of the sought function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
is extended by the addition of its mirror image with respect to a symmetry hyperplane
Hyperplane
A hyperplane is a concept in geometry. It is a generalization of the plane into a different number of dimensions.A hyperplane of an n-dimensional space is a flat subset with dimension n − 1...
, with the purpose of facilitating the solution of the original problem. It is used in electrostatics
Electrostatics
Electrostatics is the branch of physics that deals with the phenomena and properties of stationary or slow-moving electric charges....
to simply calculate or visualize the distribution of the electric field of a charge in the vicinity of the conducting surface. It is based on the fact that the tangential component of the electrical field to the surface of a conductor
Electrical conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is a material which contains movable electric charges. In metallic conductors such as copper or aluminum, the movable charged particles are electrons...
is zero, and that some field E with
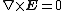 and
and 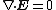 in some region is uniquely defined by its normal component over the surface which confines this region (the uniqueness theorem).
in some region is uniquely defined by its normal component over the surface which confines this region (the uniqueness theorem).The method may also be used in magnetostatics
Magnetostatics
Magnetostatics is the study of magnetic fields in systems where the currents are steady . It is the magnetic analogue of electrostatics, where the charges are stationary. The magnetization need not be static; the equations of magnetostatics can be used to predict fast magnetic switching events that...
for calculating the magnetic field of a magnet which is close to a superconducting surface. Here, the component of the magnetic field normal to the superconductor is zero. Another use is in fluid dynamics
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
: the movement of a vortex
Vortex
A vortex is a spinning, often turbulent,flow of fluid. Any spiral motion with closed streamlines is vortex flow. The motion of the fluid swirling rapidly around a center is called a vortex...
near a wall may be calculated using an image vortex.


Magnetization
In classical electromagnetism, magnetization or magnetic polarization is the vector field that expresses the density of permanent or induced magnetic dipole moments in a magnetic material...
vector which is mirrored but of the same sign (see Fig. 2). This can be thought as due to additional sign change upon mirroring of an axial vector which the magnetization is. The force between the magnet and the superconducting surface is therefore repulsive.
Further reading
- James Jeans (1908) The Mathematical Theory of Electricity and Magnetism, Chapter 8, Cambridge University PressCambridge University PressCambridge University Press is the publishing business of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII in 1534, it is the world's oldest publishing house, and the second largest university press in the world...
.

