Mercury coulometer
Encyclopedia
Mercury coulometer is an electroanalytical chemistry device
using mercury
to determine the amount of matter transformed (in coulombs) during the following reaction:
These oxidation/reduction processes have 100% efficiency with the wide range of the current densities. Measuring of the quantity of electricity
(coulombs) is based on the changes of the mass of the mercury electrode
. Mass of the electrode
can be increased during cathodic
deposition of the mercury ions or decreased during the anodic
dissolution of the metal.
where
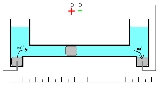
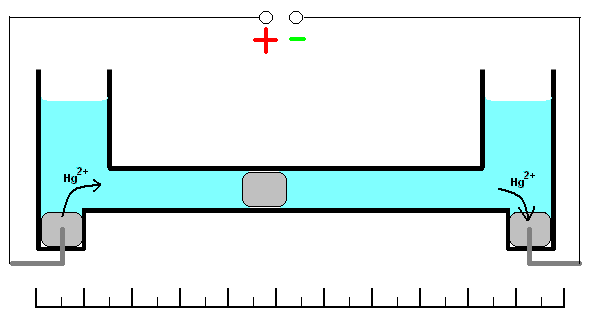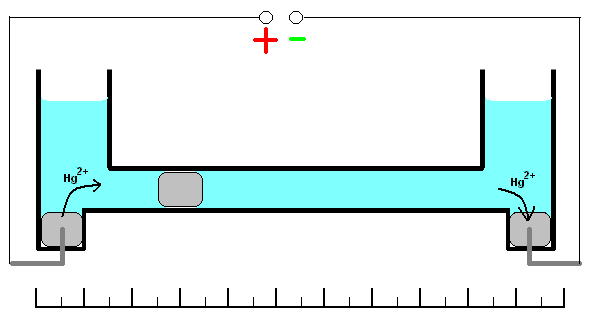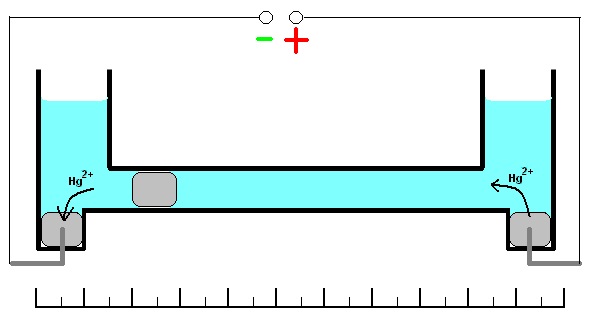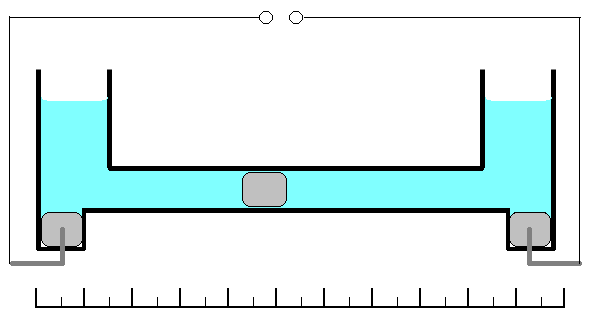 This coulometer has different constructions but all of them are based on mass measurements. One of the most significant construction is shown on the picture. It consists of two reservoirs connected by a thin graduated capillary. All system contains solution of the mercury(II)-ions solution. Each of the reservoirs have an electrode immersed into a drop of mercury. Another small drop of mercury is inserted into the capillary. When the current is turned on, it will initiate dissolution of the metallic mercury on the one side of the drop in the capillary and deposition on the other side of the same drop. This drop starts to move. Because of the 100% efficiency of the deposition/dissolution of the mercury under the current influence, mass or volume of this small drop will be a constant and its movement will be linearly correlated with the passed charge
This coulometer has different constructions but all of them are based on mass measurements. One of the most significant construction is shown on the picture. It consists of two reservoirs connected by a thin graduated capillary. All system contains solution of the mercury(II)-ions solution. Each of the reservoirs have an electrode immersed into a drop of mercury. Another small drop of mercury is inserted into the capillary. When the current is turned on, it will initiate dissolution of the metallic mercury on the one side of the drop in the capillary and deposition on the other side of the same drop. This drop starts to move. Because of the 100% efficiency of the deposition/dissolution of the mercury under the current influence, mass or volume of this small drop will be a constant and its movement will be linearly correlated with the passed charge
. If you change direction of the current, the drop starts move in opposite direction. Sensitivity of this type of coulometer
s depends on the diameter of the capillary.
Coulometry
Coulometry is the name given to a group of techniques in analytical chemistry that determine the amount of matter transformed during an electrolysis reaction by measuring the amount of electricity consumed or produced....
using mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
to determine the amount of matter transformed (in coulombs) during the following reaction:
-
- Hg2+ + 2e– = Hgo
These oxidation/reduction processes have 100% efficiency with the wide range of the current densities. Measuring of the quantity of electricity
Quantity of electricity
In physics the term quantity of electricity refers to the quantity of electric charge. It is designated by the letter Q and in the SI system is measured in derived units called Coulombs.- Pre-English origins :...
(coulombs) is based on the changes of the mass of the mercury electrode
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
. Mass of the electrode
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
can be increased during cathodic
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
deposition of the mercury ions or decreased during the anodic
Anode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
dissolution of the metal.
-
 ,
,
where
- Q-quantity of electricity (coulombs);
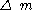 -mass changes (gr);
-mass changes (gr); - F-Faraday constant (96485 Coulomb.MolMol-Places:* City Municipality of Ljubljana, known after the acronym MOL in Slovene language * Märkisch-Oderland, a rural district of Brandenburg, Germany* Mol, Belgium, a municipality in Belgium* Mol, Serbia, a town in Serbia...
– 1) and - M the molar mass of mercuryMercury (element)Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
: (200.59 gr.MolMol-Places:* City Municipality of Ljubljana, known after the acronym MOL in Slovene language * Märkisch-Oderland, a rural district of Brandenburg, Germany* Mol, Belgium, a municipality in Belgium* Mol, Serbia, a town in Serbia...
– 1);
Construction

Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
. If you change direction of the current, the drop starts move in opposite direction. Sensitivity of this type of coulometer
Coulometry
Coulometry is the name given to a group of techniques in analytical chemistry that determine the amount of matter transformed during an electrolysis reaction by measuring the amount of electricity consumed or produced....
s depends on the diameter of the capillary.

