
Melilite
Encyclopedia
Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
of the melilite group. Minerals of the group are solid solution
Solid solution
A solid solution is a solid-state solution of one or more solutes in a solvent. Such a mixture is considered a solution rather than a compound when the crystal structure of the solvent remains unchanged by addition of the solutes, and when the mixture remains in a single homogeneous phase...
s of several endmembers, the most important of which are gehlenite
Gehlenite
Gehlenite, , is a sorosilicate, Al-rich endmember of the melilite complete solid solution series with akermanite.The type locality is in the Monzoni Mountains, Fassa Valley in Trentino in Italy, and is named after Adolf Ferdinand Gehlen by A.J...
and åkermanite
Åkermanite
Åkermanite is a melilite mineral of the sorosilicate group, containing calcium, magnesium, silicon, and oxygen. It is a product of contact metamorphism of siliceous limestones and dolostones, and rocks of sanidinite facies. Sanidinite facies represent the highest conditions of temperature of...
. A generalized formula for common melilite is (Ca
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
,Na
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
)2(Al
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
,Mg
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
,Fe
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
2+)[(Al
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
,Si
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
)Si
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
O
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
7]. Discovered in 1793 near Rome, it has a yellowish, greenish brown color. The name derives from the Greek words meli (μέλι) "honey" and lithos (λίθους) "stone".
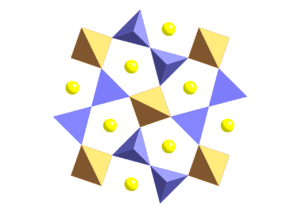
Minerals of the melilite group are sorosilicates. They have the same basic structure, of general formula A2B(T2O7). The melilite structure consist of pairs of fused TO4, where T may be Si, Al, B, in bow-tie form. Sharing one corner, the formula of the pair is T2O7. These bow-ties are linked together into sheets by the B cations. The sheets are held together by the A cations, most commonly calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
and sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
. Aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
may sit on either the T or the B site.
Minerals with the melilite structure may show a cleavage
Cleavage (geology)
This article is about rock cleavage, for cleavage in minerals see Cleavage Cleavage, in structural geology and petrology, describes a type of planar rock feature that develops as a result of deformation and metamorphism. The degree of deformation and metamorphism along with rock type determines the...
parallel to the (001) crystallographic directions and may show weaker cleavage perpendicular to this, in the {110} directions. Melilite is tetragonal.
The important endmembers of common melilite are
åkermanite Ca2Mg(Si2O7) and
gehlenite Ca2Al[AlSiO7]. Many melilites also contain appreciable iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
and sodium.
Some other compositions with the melilite structure include: alumoåkermanite (Ca,Na)2(Al,Mg,Fe2+)(Si2O7), okayamalite Ca2B[BSiO7], gugiaite Ca2Be[Si2O7],
hardystonite
Hardystonite
Hardystonite is a rare calcium zinc silicate mineral first described from the Franklin, New Jersey, USA zinc deposits. It often contains lead, which was detrimental to the zinc smelting process, so it was not a useful ore mineral...
Ca2Zn[Si2O7], barylite BaBe2[Si2O7],
andremeyerite BaFe2+2[Si2O7].
Some structures formed by replacing one oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
by F or OH: leucophanite
Leucophanite
Leucophanite is a sorosilicate mineral with a complex composition, 2BeSi27. It may contain cerium substituting in the calcium position....
(Ca,Na)2(Be,Al)[Si2O6(F,OH)],
jeffreyite (Ca,Na)2(Be,Al)[Si2O6(O,OH)], and meliphanite (Ca,Na)2(Be,Al)[Si2O6(OH,F)]
Occurrences
Melilite with compositions dominated by the endmembers akermanite and gehlenite is widely distributed but uncommon. It occurs in metamorphicMetamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock is the transformation of an existing rock type, the protolith, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The protolith is subjected to heat and pressure causing profound physical and/or chemical change...
and igneous rocks and in meteorite
Meteorite
A meteorite is a natural object originating in outer space that survives impact with the Earth's surface. Meteorites can be big or small. Most meteorites derive from small astronomical objects called meteoroids, but they are also sometimes produced by impacts of asteroids...
s.
Typical metamorphic occurrences are in high-temperature metamorphosed impure limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
s. For instance, melilite occurs in some high-temperature skarn
Skarn
Skarn is an old Swedish mining term originally used to describe a type of silicate gangue, or waste rock, associated with iron-ore bearing sulfide deposits apparently replacing Archean age limestones in Sweden's Persberg mining district. In modern usage the term "skarn" has been expanded to refer...
s.
Melilite also occurs in unusual silica-undersaturated
Normative mineralogy
Normative mineralogy is a geochemical calculation of the whole rock geochemistry of a rock sample that estimates the idealised mineralogy of a rock according to the principles of geochemistry....
igneous rock
Igneous rock
Igneous rock is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic rock. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava...
s. Some of these rocks appear to have formed by reaction of magma
Magma
Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and is expected to exist on other terrestrial planets. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and dissolved gas and sometimes also gas bubbles. Magma often collects in...
s with limestone. Other igneous rocks containing melilite crystallize from magma derived from the Earth's mantle and apparently uncontaminated by the Earth's crust. The presence of melilite is an essential constituent in some rare igneous rocks, such as olivine melilitite. Extremely rare igneous rocks contain as much as 70% melilite, together with minerals such as pyroxene
Pyroxene
The pyroxenes are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. They share a common structure consisting of single chains of silica tetrahedra and they crystallize in the monoclinic and orthorhombic systems...
and perovskite
Perovskite
A perovskite structure is any material with the same type of crystal structure as calcium titanium oxide , known as the perovskite structure, or XIIA2+VIB4+X2−3 with the oxygen in the face centers. Perovskites take their name from this compound, which was first discovered in the Ural mountains of...
.
Melilite is a constituent of some calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
- and aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
-rich inclusions (CAIs
Ca-Al-rich inclusions
A calcium-aluminium-rich inclusion or Ca-Al-rich Inclusion is a submillimeter to centimeter-sized light-colored calcium- and aluminium-rich inclusion found in carbonaceous chondrite meteorites...
) in chondritic meteorites
Chondrite
Chondrites are stony meteorites that have not been modified due to melting or differentiation of the parent body. They formed when various types of dust and small grains that were present in the early solar system accreted to form primitive asteroids...
. Isotope
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
ratios of magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
and some other elements in these inclusions are of great importance in deducing processes that formed our solar system
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
.

