
Manganate
Encyclopedia
Molecular entity
According to the IUPAC Gold Book a molecular entity is "any constitutionally or isotopically distinct atom, molecule, ion, ion pair, radical, radical ion, complex, conformer, etc., identifiable as a separately distinguishable entity"....
with manganese
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals...
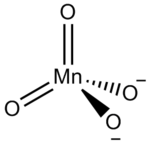
as the central atom. However, the name is usually used to refer to the tetraoxidomanganate(2−) anion, MnO, also known as manganate(VI) because it contains manganese in the +6 oxidation state
Oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state is an indicator of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. The formal oxidation state is the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Oxidation states are typically represented by...
. Manganates are the only known manganese(VI) compounds.
Manganate(VI)
The manganate(VI) ion is tetrahedral, similar to sulfate or chromate: indeed, manganates are often isostructural with sulfates and chromates, a fact first noted by MitscherlichEilhard Mitscherlich
Eilhard Mitscherlich was a German chemist, who is perhaps best remembered today for his law of isomorphism , which states that compounds crystallizing together probably have similar structures and compositions...
in 1831. The manganese
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals...
–oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
distance is 165.9 pm, about 3 pm longer than in permanganate
Permanganate
A permanganate is the general name for a chemical compound containing the manganate ion, . Because manganese is in the +7 oxidation state, the permanganate ion is a strong oxidizing agent. The ion has tetrahedral geometry...
. As a d1 ion, it is paramagnetic
Paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby the paramagnetic material is only attracted when in the presence of an externally applied magnetic field. In contrast with this, diamagnetic materials are repulsive when placed in a magnetic field...
, but any Jahn–Teller distortion is too small to be detected by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a...
. Manganates are dark green in colour, with a visible absorption maximum of λmax = 606 nm (ε = ). The Raman spectrum
Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy is a spectroscopic technique used to study vibrational, rotational, and other low-frequency modes in a system.It relies on inelastic scattering, or Raman scattering, of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range...
has also been reported.
Preparation
SodiumSodium manganate
Sodium manganate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2MnO4. This is a deep green solid is rarely encountered analogue of the related salt K2MnO4. Sodium manganate is rarely encountered because it cannot be readily prepared from by the oxidation of manganese dioxide and sodium hydroxide...
and potassium manganate
Potassium manganate
Potassium manganate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2MnO4. This green-colored salt is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of potassium permanganate , a common chemical...
s are usually prepared in the laboratory by stirring the equivalent permanganate
Permanganate
A permanganate is the general name for a chemical compound containing the manganate ion, . Because manganese is in the +7 oxidation state, the permanganate ion is a strong oxidizing agent. The ion has tetrahedral geometry...
in a concentrated solution (5–10 M) of the hydroxide
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carrying a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, as a ligand, a nucleophile, and a...
for 24 hours or with heating.
- + → + + O2
Potassium manganate is prepared industrially, as an intermediate to potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula KMnO4. It is a salt consisting of K+ and MnO4− ions. Formerly known as permanganate of potash or Condy's crystals, it is a strong oxidizing agent. It dissolves in water to give intensely purple solutions, the...
, by dissolving manganese dioxide in molten potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, commonly called caustic potash.Along with sodium hydroxide , this colorless solid is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications. Most applications exploit its reactivity toward acids and its corrosive...
with potassium nitrate
Potassium nitrate
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula KNO3. It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrate ions NO3−.It occurs as a mineral niter and is a natural solid source of nitrogen. Its common names include saltpetre , from medieval Latin sal petræ: "stone salt" or possibly "Salt...
or air as the oxidizing agent
Oxidizing agent
An oxidizing agent can be defined as a substance that removes electrons from another reactant in a redox chemical reaction...
.
- + + O2 → +
Uses
Manganates, particularly the insoluble barium manganate, BaMnO4, have been used as oxidizing agentOxidizing agent
An oxidizing agent can be defined as a substance that removes electrons from another reactant in a redox chemical reaction...
s in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
: they will oxidize primary alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
s to aldehyde
Aldehyde
An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group....
s and then to carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
s, and secondary alcohols to ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
s. Barium manganate has also been used to oxidize hydrazone
Hydrazone
Hydrazones are a class of organic compounds with the structure R1R2C=NNH2. They are related to ketones and aldehydes by the replacement of the oxygen with the NNH2 functional group...
s to diazo compounds.
Disproportionation
Manganates are unstable towards disproportionation in all but the most alkaline of aqueous solutionAqueous solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is usually shown in chemical equations by appending aq to the relevant formula, such as NaCl. The word aqueous means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in water...
s. The ultimate products are permanganate
Permanganate
A permanganate is the general name for a chemical compound containing the manganate ion, . Because manganese is in the +7 oxidation state, the permanganate ion is a strong oxidizing agent. The ion has tetrahedral geometry...
and manganese dioxide, but the kinetics
Chemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the study of rates of chemical processes. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how different experimental conditions can influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition...
are complex and the mechanism may involved protonated and/or manganese(V) species.
Manganic acid
Manganic acid cannot be formed because of its rapid disproportionation. However, its second acid dissociation constantAcid dissociation constant
An acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction known as dissociation in the context of acid-base reactions...
has been estimated by pulse radiolysis techniques:
- HMnO MnO + H+ pKa = 7.4 ± 0.1
Manganate(V)
The manganate(V) anion, MnO, known trivially as hypomanganate and systematically as tetraoxidomanganate(3−), is a bright blue species with a visible absorption maximum of λmax = 670 nm (ε = ). It is unstable towards dispropotionation to manganate(VI) and manganese dioxide, although the reaction is slow in very alkaline solution (c(OH−) = ).Hypomanganates may be prepared by the careful reduction of manganates with sulfite
Sulfite
Sulfites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion SO. The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although the acid itself is elusive, its salts are widely used.-Structure:...
, hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide and an oxidizer. Hydrogen peroxide is a clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. In dilute solution, it appears colorless. With its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent...
or mandelate
Mandelic acid
Mandelic acid is an aromatic alpha hydroxy acid with the molecular formula C6H5CHCO2H. It is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is a useful precursor to various drugs...
. Only potassium hypomanganate has been studied to any significant extent. Hypomanganic acid cannot be formed because of its rapid disproportionation, but its third acid dissociation constant
Acid dissociation constant
An acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction known as dissociation in the context of acid-base reactions...
has been estimated by pulse radiolysis techniques:
- HMnO MnO + H+ pKa =
Cyclic ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
s of hypomanganic acid are thought to be intermediates in the oxidation of alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
s by permanganate
Permanganate
A permanganate is the general name for a chemical compound containing the manganate ion, . Because manganese is in the +7 oxidation state, the permanganate ion is a strong oxidizing agent. The ion has tetrahedral geometry...
.
Manganate(IV) and manganate(III)
The manganate(IV) anion has been prepared by radiolysisRadiolysis
Radiolysis is the dissociation of molecules by nuclear radiation. It is the cleavage of one or several chemical bonds resulting from exposure to high-energy flux...
of dilute solutions of permanganate
Permanganate
A permanganate is the general name for a chemical compound containing the manganate ion, . Because manganese is in the +7 oxidation state, the permanganate ion is a strong oxidizing agent. The ion has tetrahedral geometry...
. It is mononuclear in dilute solution, and shows a strong absorption in the ultraviolet and a weaker absorption at 650 nm.
Most so-called "manganite
Manganite (disambiguation)
*The mineral Manganite of formula MnO*Mixed metal oxides containing manganese:**With manganese in a +3 oxidation state eg NiMn2O4**With manganese in a +4 oxidation state eg CaMnO3 or Ca2MnO4**Lanthanum strontium manganite...
s" do not contain discrete oxoanions, but are mixed oxide
Mixed oxide
In chemistry, a mixed oxide is a somewhat informal name for an oxide that contains more than one chemical element in its cation, or of a single element cation that has atoms in several states of oxidation....
s with perovskite (LaMnIIIO3, CaMnIVO3), spinel
Spinel
Spinel is the magnesium aluminium member of the larger spinel group of minerals. It has the formula MgAl2O4. Balas ruby is an old name for a rose-tinted variety.-Spinel group:...
(LiMnO4) or sodium chloride (LiMnIIIO2, NaMnIIIO2) structures. One exception is potassium dimanganate(III)
Potassium dimanganate(III)
Potassium dimanganate, K6Mn2O6, is a manganese compound. Unlike lithium and sodium manganites, MMnO2, which are best described as mixed oxides, potassium dimanganite contains discrete Mn2O anions in the solid state...
, K6Mn2O6, which contains discrete Mn2O anions.

