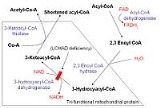
Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency
Encyclopedia
Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency, often shortened to LCHAD deficiency, is a rare autosomal recessive fatty acid oxidation disorder that prevents the body from converting certain fat
s into energy. This can become life-threatening, particularly during periods of fasting
.
 Mutation
Mutation
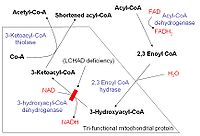
s in the HADHA
gene lead to inadequate levels of an enzyme called long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A (CoA
) dehydrogenase, which is part of a protein complex known as mitochondrial trifunctional protein
. Long-chain fatty acid
s from food and body fat cannot be metabolized
and processed without sufficient levels of this enzyme
. As a result, these fatty acids are not converted to energy, which can lead to characteristic features of this disorder, such as lethargy and hypoglycemia
. Long-chain fatty acids or partially metabolized fatty acids may build up in tissues and damage the liver
, heart
, retina
, and muscles, causing more serious complications.
, hypotonia
, liver problems, and abnormalities in the retina
. Muscle pain, a breakdown of muscle tissue, and abnormalities in the nervous system
that affect arms and legs (peripheral neuropathy
) may occur later in childhood. There is also a risk for complications such as life-threatening heart and breathing problems, coma
, and sudden unexpected death. Episodes of LCHAD deficiency can be triggered by periods of fasting or by illnesses such as viral
infections.
Lipid
Lipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
s into energy. This can become life-threatening, particularly during periods of fasting
Fasting
Fasting is primarily the act of willingly abstaining from some or all food, drink, or both, for a period of time. An absolute fast is normally defined as abstinence from all food and liquid for a defined period, usually a single day , or several days. Other fasts may be only partially restrictive,...
.

Genetics

Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s in the HADHA
HADHA
HADHA is a gene associated with long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency.-See also:* Mitochondrial trifunctional protein...
gene lead to inadequate levels of an enzyme called long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A (CoA
COA
COA can refer to:*Codename Amscray*Cash on Arrival*Cause of action*CedarOpenAccounts*Center of Attention*Certificate of Appealability*Certificate of Approval for marriage or civil partnership in the United Kingdom*Certificate of Authenticity...
) dehydrogenase, which is part of a protein complex known as mitochondrial trifunctional protein
Mitochondrial trifunctional protein
Mitochondrial trifunctional protein is a protein which catalyzes several reactions in beta oxidation. It has two subunits:* HADHA* HADHBThe three functions are long-chain 3-hydroxy acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase, 2-enoyl coenzyme A hydratase, and long-chain 3-ketoacyl CoA...
. Long-chain fatty acid
Fatty acid
In chemistry, especially biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long unbranched aliphatic tail , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have a chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are usually derived from...
s from food and body fat cannot be metabolized
Fatty acid metabolism
Fatty acids are an important source of energy and adenosine triphosphate for many cellular organisms. Excess fatty acids, glucose, and other nutrients can be stored efficiently as fat. Triglycerides yield more than twice as much energy for the same mass as do carbohydrates or proteins. All cell...
and processed without sufficient levels of this enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
. As a result, these fatty acids are not converted to energy, which can lead to characteristic features of this disorder, such as lethargy and hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia or hypoglycæmia is the medical term for a state produced by a lower than normal level of blood glucose. The term literally means "under-sweet blood"...
. Long-chain fatty acids or partially metabolized fatty acids may build up in tissues and damage the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
, retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
, and muscles, causing more serious complications.
Symptoms
Typically, initial signs and symptoms of this disorder occur during infancy or early childhood and can include feeding difficulties, lethargy, hypoglycemiaHypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia or hypoglycæmia is the medical term for a state produced by a lower than normal level of blood glucose. The term literally means "under-sweet blood"...
, hypotonia
Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone , often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength...
, liver problems, and abnormalities in the retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
. Muscle pain, a breakdown of muscle tissue, and abnormalities in the nervous system
Nervous system
The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. In most animals the nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The central nervous...
that affect arms and legs (peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is the term for damage to nerves of the peripheral nervous system, which may be caused either by diseases of or trauma to the nerve or the side-effects of systemic illness....
) may occur later in childhood. There is also a risk for complications such as life-threatening heart and breathing problems, coma
Coma
In medicine, a coma is a state of unconsciousness, lasting more than 6 hours in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light or sound, lacks a normal sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. A person in a state of coma is described as...
, and sudden unexpected death. Episodes of LCHAD deficiency can be triggered by periods of fasting or by illnesses such as viral
Virus
A virus is a small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the living cells of organisms. Viruses infect all types of organisms, from animals and plants to bacteria and archaea...
infections.

