
List of centroids
Encyclopedia
The following diagrams depict a list of centroid
s. A centroid of an object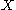 in
in  -dimension
-dimension
al space is the intersection of all hyperplane
s that divide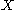 into two parts of equal moment
into two parts of equal moment
about the hyperplane. Informally, it is the "average
" of all points of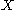 . For an object of uniform composition (mass, density, etc.) the centroid of a body is also its centre of mass.
. For an object of uniform composition (mass, density, etc.) the centroid of a body is also its centre of mass.
Centroid
In geometry, the centroid, geometric center, or barycenter of a plane figure or two-dimensional shape X is the intersection of all straight lines that divide X into two parts of equal moment about the line. Informally, it is the "average" of all points of X...
s. A centroid of an object
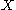 in
in  -dimension
-dimensionDimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a space or object is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus a line has a dimension of one because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on it...
al space is the intersection of all hyperplane
Hyperplane
A hyperplane is a concept in geometry. It is a generalization of the plane into a different number of dimensions.A hyperplane of an n-dimensional space is a flat subset with dimension n − 1...
s that divide
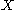 into two parts of equal moment
into two parts of equal momentMoment (physics)
In physics, the term moment can refer to many different concepts:*Moment of force is the tendency of a force to twist or rotate an object; see the article torque for details. This is an important, basic concept in engineering and physics. A moment is valued mathematically as the product of the...
about the hyperplane. Informally, it is the "average
Average
In mathematics, an average, or central tendency of a data set is a measure of the "middle" value of the data set. Average is one form of central tendency. Not all central tendencies should be considered definitions of average....
" of all points of
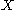 . For an object of uniform composition (mass, density, etc.) the centroid of a body is also its centre of mass.
. For an object of uniform composition (mass, density, etc.) the centroid of a body is also its centre of mass.| Shape | Figure | 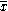 | 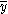 | Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right-triangular Triangle A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted .... area |
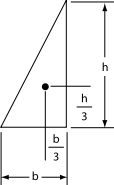 |
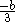 |
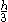 |
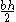 |
| Quarter-circular area | 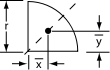 |
 |
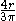 |
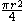 |
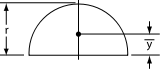
| Semicircular Semicircle In mathematics , a semicircle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that forms half of a circle. Being half of a circle's 360°, the arc of a semicircle always measures 180° or a half turn... area |
 |
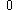 |
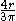 |
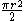 |
| Quarter-elliptical area | 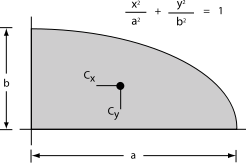 |
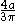 |
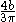 |
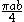 |
| Semielliptical area | 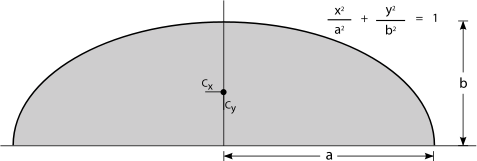 |
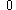 |
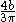 |
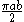 |
| Semiparabolic area | The area between the curve 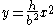 and the and the 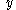 axis, from axis, from 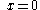 to to 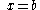 |
 |
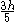 |
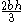 |
| Parabolic Parabola In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface... area |
The area between the curve 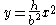 and the line and the line 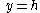 |
 |
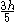 |
 |
| Parabolic spandrel | The area between the curve 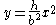 and the and the  axis, from axis, from 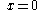 to to  |
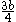 |
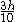 |
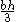 |
| General spandrel | The area between the curve  and the and the  axis, from axis, from 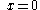 to to  |
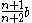 |
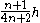 |
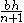 |
| Circular sector Circular sector A circular sector or circle sector, is the portion of a disk enclosed by two radii and an arc, where the smaller area is known as the minor sector and the larger being the major sector. In the diagram, θ is the central angle in radians, r the radius of the circle, and L is the arc length of the... |
The area between the curve (in polar coordinates) 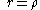 and the pole, from and the pole, from  to to  |
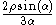 |
 |
 |
| Circular segment Circular segment In geometry, a circular segment is an area of a circle informally defined as an area which is "cut off" from the rest of the circle by a secant or a chord. The circle segment constitutes the part between the secant and an arc, excluding the circle's center... |
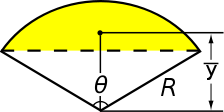 |
 |
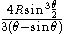 |
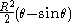 |
| Quarter-circular arc | The points on the circle 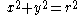 and in the first quadrant and in the first quadrant |
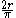 |
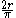 |
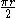 |
| Semicircular arc | The points on the circle 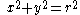 and above the and above the 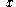 axis axis |
 |
 |
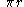 |
| Arc of circle Circle A circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius.... |
The points on the curve (in polar coordinates) 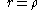 , from , from 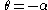 to to 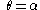 |
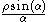 |
 |
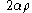 |
External links
- http://www.engineering.com/Library/ArticlesPage/tabid/85/articleType/ArticleView/articleId/109/Centroids-of-Common-Shapes.aspx
- http://www.efunda.com/math/areas/IndexArea.cfm

