Linear regulator
Encyclopedia
In electronics, a linear regulator is a voltage regulator
based on an active device (such as a bipolar junction transistor
, field effect transistor or vacuum tube
) operating in its "linear region" (in contrast, a switching regulator
is based on a transistor forced to act as an on/off switch) or passive devices like Zener diode
s operated in their breakdown region. The regulating device is made to act like a variable resistor
, continuously adjusting a voltage divider network to maintain a constant output voltage. It is very inefficient compared to a switched-mode power supply
, since it sheds the difference voltage by dissipating heat.
, the output voltage is kept reasonably constant. Linear regulators are often inefficient: since the transistor is acting like a resistor, it will waste electrical energy by converting it to heat. In fact, the power loss due to heating in the transistor is the current times the voltage
dropped across the transistor. The same function can often be performed much more efficiently by a switched-mode power supply
, but a linear regulator may be preferred for light loads or where the desired output voltage approaches the source voltage. In these cases, the linear regulator may dissipate less power than a switcher. The linear regulator also has the advantage of not requiring megnetic devices (inductors or transformers) which can be relatively expensive or bulky, being often of simpler design, and being quieter
.
Linear regulators exist in two basic forms: series regulators and shunt regulators.
All linear regulators require an input voltage at least some minimum amount higher than the desired output voltage. That minimum amount is called the dropout voltage
. For example, a common regulator such as the 7805 has an output voltage of 5V, but can only maintain this if the input voltage remains above about 7V, before the output voltage begins sagging below the rated output. Its dropout voltage is therefore 7V - 5V = 2V. When the supply voltage is less than about 2V above the desired output voltage, as is the case in low-voltage microprocessor
power supplies, so-called low dropout regulator
s (LDOs) must be used.
When one wants an output voltage higher than the available input voltage, no linear regulator will work (not even an LDO
). In this situation, a switching regulator
must be used.
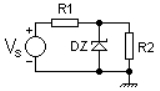
 The image shows a simple Zener voltage regulator. It is a shunt regulator and operates by way of the Zener diode
The image shows a simple Zener voltage regulator. It is a shunt regulator and operates by way of the Zener diode
's action of maintaining a constant voltage across itself when the current through it is sufficient to take it into the Zener breakdown region. The resistor
R1 supplies the Zener current IZ as well as the load current IR2 (R2 is the load). R1 can be calculated as -
 where, VZ is the Zener voltage, and IR2 is the required load current.
where, VZ is the Zener voltage, and IR2 is the required load current.
This regulator is used for very simple low power applications where the currents involved are very small and the load is permanently connected across the Zener diode (such as voltage reference
or voltage source
circuits). Once R1 has been calculated, removing R2 will cause the full load current (plus the Zener current) to flow through the diode and may exceed the diode's maximum current rating thereby damaging it. The regulation of this circuit is also not very good because the Zener current (and hence the Zener voltage) will vary depending on VS and inversely depending on the load current.
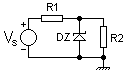
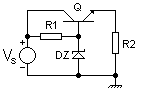 Adding an emitter follower
Adding an emitter follower
stage to the simple Zener regulator forms a simple series voltage regulator and substantially improves the regulation of the circuit. Here, the load current IR2 is supplied by the transistor whose base is now connected to the Zener diode. Thus the transistor's base current (IB) forms the load current for the Zener diode and is much smaller than the current through R2. This regulator is classified as "series" because the regulating element, viz., the transistor, appears in series with the load.
R1 sets the Zener current (IZ) and is determined as -
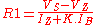 where, VZ is the Zener voltage, IB is the transistor's base current and K = 1.2 to 2 (to ensure that R1 is low enough for adequate IB).
where, VZ is the Zener voltage, IB is the transistor's base current and K = 1.2 to 2 (to ensure that R1 is low enough for adequate IB).
 where,
where,
IR2 is the required load current and is also the transistor's emitter current (assumed to be equal to the collector current) and hFE(min) is the minimum acceptable DC current gain for the transistor.
This circuit has much better regulation than the simple Zener regulator, since the base current of the transistor forms a very light load on the Zener, thereby minimising variation in Zener voltage due to variation in the load. Note that the output voltage will always be about 0.65V less than the Zener due to the transistor's VBE drop. Although this circuit has good regulation, it is still sensitive to the load and supply variation. This can be resolved by incorporating negative feedback circuitry into it. This regulator is often used as a "pre-regulator" in more advanced series voltage regulator circuits.
The circuit is readily made adjustable by adding a pot across the Zener, moving the transistor base connection from the top of the Zener to the pot wiper. It may be made step adjustable by switching in different Zeners. Finally it is occasionally made microadjustable by adding a low value pot in series with the Zener; this allows a little voltage adjustment, but degrades regulation.
forms. The most common linear regulators are three-terminal integrated circuit
s in the TO220
package. (The TO-220 package is the same kind that many medium-power transistors commonly come in: three legs in a straight line protruding from a black plastic molded case with a metal backplate which has a hole for bolting to a heatsink).
Common solid-state series voltage regulators are the LM78xx
(for positive voltages) and LM79xx (for negative voltages), and common fixed voltages are 5 V (for transistor-transistor logic
circuits) and 12 V (for communications circuits and peripheral devices such as disk drives). In fixed voltage regulators the reference pin is tied to ground
, whereas in variable regulators the reference pin is connected to the centre point of a fixed or variable voltage divider fed by the regulator's output. A variable voltage divider (such as a potentiometer
) allows the user to adjust the regulated voltage.
 "Fixed" three-terminal linear regulators are commonly available to generate fixed voltages of plus 3 V, and plus or minus 5 V, 6V, 9 V, 12 V, or 15 V
"Fixed" three-terminal linear regulators are commonly available to generate fixed voltages of plus 3 V, and plus or minus 5 V, 6V, 9 V, 12 V, or 15 V
when the load is less than 1.5 ampere
s.
The "78xx
" series (7805, 7812, etc.) regulate positive voltages while the "79xx" series (7905, 7912, etc.) regulate negative voltages. Often, the last two digits of the device number are the output voltage; e.g., a 7805 is a +5 V regulator, while a 7915 is a -15 V regulator. There are variants on the 78xx series ICs, such as 78L and 78S, some of which can supply up to 1.5 Amps.
A Zener diode or resistor is added between the IC's ground terminal and ground. Resistors are acceptable where ground current is constant, but are ill-suited to regulators with varying ground current. Switching in different Zeners, diodes or resistors can be used to obtain stepwise adjustment.
A potentiometer can be placed in series with the ground terminal to variably increase the output voltage. This degrades regulation, and is not suitable for regulators with varying ground current.
article entitled "Break Loose from Fixed IC Regulators". The article was written by Robert Dobkin, an IC
designer then working for National Semiconductor
. Dobkin later left National in 1981 to found Linear Technology
where he is currently chief technology officer.
s, commonly available "adjustable" three-terminal linear regulators may be used. An adjustable regulator generates a fixed low nominal voltage between its output and its 'adjust' terminal (equivalent to the ground terminal in a fixed regulator). The "317
" series (+1.25V) regulates positive voltages while the "337" series (-1.25V) regulates negative voltages.
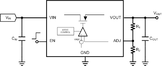 The adjustment is performed by constructing a potential divider with its ends between the regulator output and ground, and its centre-tap connected to the 'adjust' terminal of the regulator. The ratio of resistances determines the output voltage using the same feedback mechanisms described earlier.
The adjustment is performed by constructing a potential divider with its ends between the regulator output and ground, and its centre-tap connected to the 'adjust' terminal of the regulator. The ratio of resistances determines the output voltage using the same feedback mechanisms described earlier.
Complex power requirements (e.g., op-amp circuits needing matched positive and negative DC supplies) are more difficult, but single IC dual tracking adjustable regulators are available. Some even have selectable current limiting as well. An example is the 419x series.
Note that some regulators, like the LM317, require a minimum load.
Sometimes external protection is used, such as crowbar protection
s.
Voltage regulator
A voltage regulator is an electrical regulator designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage level. A voltage regulator may be a simple "feed-forward" design or may include negative feedback control loops. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components...
based on an active device (such as a bipolar junction transistor
Bipolar junction transistor
|- align = "center"| || PNP|- align = "center"| || NPNA bipolar transistor is a three-terminal electronic device constructed of doped semiconductor material and may be used in amplifying or switching applications. Bipolar transistors are so named because their operation involves both electrons...
, field effect transistor or vacuum tube
Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
) operating in its "linear region" (in contrast, a switching regulator
Switched-mode power supply
A switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator in order to be highly efficient in the conversion of electrical power...
is based on a transistor forced to act as an on/off switch) or passive devices like Zener diode
Zener diode
A Zener diode is a special kind of diode which allows current to flow in the forward direction in the same manner as an ideal diode, but will also permit it to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value known as the breakdown voltage, "Zener knee voltage" or "Zener...
s operated in their breakdown region. The regulating device is made to act like a variable resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
, continuously adjusting a voltage divider network to maintain a constant output voltage. It is very inefficient compared to a switched-mode power supply
Switched-mode power supply
A switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator in order to be highly efficient in the conversion of electrical power...
, since it sheds the difference voltage by dissipating heat.
Overview
The transistor (or other device) is used as one half of a potential divider to establish the regulated output voltage. The output voltage is compared to a reference voltage to produce a control signal to the transistor which will drive its gate or base. With negative feedback and good choice of compensationFrequency compensation
In electrical engineering, frequency compensation is a technique used in amplifiers, and especially in amplifiers employing negative feedback. It usually has two primary goals: To avoid the unintentional creation of positive feedback, which will cause the amplifier to oscillate, and to control...
, the output voltage is kept reasonably constant. Linear regulators are often inefficient: since the transistor is acting like a resistor, it will waste electrical energy by converting it to heat. In fact, the power loss due to heating in the transistor is the current times the voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
dropped across the transistor. The same function can often be performed much more efficiently by a switched-mode power supply
Switched-mode power supply
A switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator in order to be highly efficient in the conversion of electrical power...
, but a linear regulator may be preferred for light loads or where the desired output voltage approaches the source voltage. In these cases, the linear regulator may dissipate less power than a switcher. The linear regulator also has the advantage of not requiring megnetic devices (inductors or transformers) which can be relatively expensive or bulky, being often of simpler design, and being quieter
Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
.
Linear regulators exist in two basic forms: series regulators and shunt regulators.
- Series regulators are the more common form. The series regulator works by providing a path from the supply voltage to the load through a variable resistance (the main transistor is in the "top half" of the voltage divider). The power dissipated by the regulating device is equal to the power supply output current times the voltage drop in the regulating device.
- The shunt regulator works by providing a path from the supply voltage to ground through a variable resistance (the main transistor is in the "bottom half" of the voltage divider). The current through the shunt regulator is diverted away from the load and flows uselessly to ground, making this form even less efficient than the series regulator. It is, however, simpler, sometimes consisting of just a voltage-reference diodeDiodeIn electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
, and is used in very low-powerLow-power electronicsLow-power electronics means that the consumption of electric power is deliberately low, e.g. notebook processors.- Computing elements :The density and speed of integrated-circuit computing elements have increased exponentially for several decades, following a trend described by Moore's Law...
ed circuits where the wasted current is too small to be of concern. This form is very common for voltage reference circuits.
All linear regulators require an input voltage at least some minimum amount higher than the desired output voltage. That minimum amount is called the dropout voltage
Dropout voltage
In electronics, the dropout voltage of a voltage regulator is the smallest possible difference between the input voltage and output voltage to remain inside the regulator's intended operating range....
. For example, a common regulator such as the 7805 has an output voltage of 5V, but can only maintain this if the input voltage remains above about 7V, before the output voltage begins sagging below the rated output. Its dropout voltage is therefore 7V - 5V = 2V. When the supply voltage is less than about 2V above the desired output voltage, as is the case in low-voltage microprocessor
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
power supplies, so-called low dropout regulator
Low dropout regulator
A low-dropout or LDO regulator is a DC linear voltage regulator which can operate with a very small input–output differential voltage.The advantages of a low dropout voltage include a lower minimum operating voltage, higher efficiency operation and lower heat dissipation.The main components are a...
s (LDOs) must be used.
When one wants an output voltage higher than the available input voltage, no linear regulator will work (not even an LDO
Low dropout regulator
A low-dropout or LDO regulator is a DC linear voltage regulator which can operate with a very small input–output differential voltage.The advantages of a low dropout voltage include a lower minimum operating voltage, higher efficiency operation and lower heat dissipation.The main components are a...
). In this situation, a switching regulator
Switched-mode power supply
A switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator in order to be highly efficient in the conversion of electrical power...
must be used.
Simple Zener regulator

Zener diode
A Zener diode is a special kind of diode which allows current to flow in the forward direction in the same manner as an ideal diode, but will also permit it to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value known as the breakdown voltage, "Zener knee voltage" or "Zener...
's action of maintaining a constant voltage across itself when the current through it is sufficient to take it into the Zener breakdown region. The resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
R1 supplies the Zener current IZ as well as the load current IR2 (R2 is the load). R1 can be calculated as -
 where, VZ is the Zener voltage, and IR2 is the required load current.
where, VZ is the Zener voltage, and IR2 is the required load current.This regulator is used for very simple low power applications where the currents involved are very small and the load is permanently connected across the Zener diode (such as voltage reference
Voltage reference
A voltage reference is an electronic device that produces a fixed voltage irrespective of the loading on the device, power supply variations, temperature changes, and the passage of time. Voltage references are used in power supply voltage regulators, analog-to-digital converters and...
or voltage source
Voltage source
In electric circuit theory, an ideal voltage source is a circuit element where the voltage across it is independent of the current through it. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. In analysis, a voltage source supplies a constant DC or AC potential between its terminals for any current...
circuits). Once R1 has been calculated, removing R2 will cause the full load current (plus the Zener current) to flow through the diode and may exceed the diode's maximum current rating thereby damaging it. The regulation of this circuit is also not very good because the Zener current (and hence the Zener voltage) will vary depending on VS and inversely depending on the load current.
Simple series regulator

Common collector
In electronics, a common-collector amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor amplifier topologies, typically used as a voltage buffer...
stage to the simple Zener regulator forms a simple series voltage regulator and substantially improves the regulation of the circuit. Here, the load current IR2 is supplied by the transistor whose base is now connected to the Zener diode. Thus the transistor's base current (IB) forms the load current for the Zener diode and is much smaller than the current through R2. This regulator is classified as "series" because the regulating element, viz., the transistor, appears in series with the load.
R1 sets the Zener current (IZ) and is determined as -
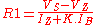 where, VZ is the Zener voltage, IB is the transistor's base current and K = 1.2 to 2 (to ensure that R1 is low enough for adequate IB).
where, VZ is the Zener voltage, IB is the transistor's base current and K = 1.2 to 2 (to ensure that R1 is low enough for adequate IB). where,
where,IR2 is the required load current and is also the transistor's emitter current (assumed to be equal to the collector current) and hFE(min) is the minimum acceptable DC current gain for the transistor.
This circuit has much better regulation than the simple Zener regulator, since the base current of the transistor forms a very light load on the Zener, thereby minimising variation in Zener voltage due to variation in the load. Note that the output voltage will always be about 0.65V less than the Zener due to the transistor's VBE drop. Although this circuit has good regulation, it is still sensitive to the load and supply variation. This can be resolved by incorporating negative feedback circuitry into it. This regulator is often used as a "pre-regulator" in more advanced series voltage regulator circuits.
The circuit is readily made adjustable by adding a pot across the Zener, moving the transistor base connection from the top of the Zener to the pot wiper. It may be made step adjustable by switching in different Zeners. Finally it is occasionally made microadjustable by adding a low value pot in series with the Zener; this allows a little voltage adjustment, but degrades regulation.
Using a linear regulator
Linear regulators can be constructed using discrete components but are usually encountered in integrated circuitIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
forms. The most common linear regulators are three-terminal integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
s in the TO220
TO220
The TO-220 is a style of electronic component package, commonly used for transistors, silicon-controlled rectifiers, and integrated circuits. The "TO" designation stands for "transistor outline". TO-220 packages have three leads. Similar packages with two, four, five or seven leads are also...
package. (The TO-220 package is the same kind that many medium-power transistors commonly come in: three legs in a straight line protruding from a black plastic molded case with a metal backplate which has a hole for bolting to a heatsink).
Common solid-state series voltage regulators are the LM78xx
78xx
The 78xx is a family of self-contained fixed linear voltage regulator integrated circuits. The 78xx family is commonly used in electronic circuits requiring a regulated power supply due to their ease-of-use and low cost...
(for positive voltages) and LM79xx (for negative voltages), and common fixed voltages are 5 V (for transistor-transistor logic
Transistor-transistor logic
Transistor–transistor logic is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function and the amplifying function are performed by transistors .TTL is notable for being a widespread...
circuits) and 12 V (for communications circuits and peripheral devices such as disk drives). In fixed voltage regulators the reference pin is tied to ground
Ground (electricity)
In electrical engineering, ground or earth may be the reference point in an electrical circuit from which other voltages are measured, or a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the Earth....
, whereas in variable regulators the reference pin is connected to the centre point of a fixed or variable voltage divider fed by the regulator's output. A variable voltage divider (such as a potentiometer
Potentiometer
A potentiometer , informally, a pot, is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used , it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat. Potentiometers are commonly used to control electrical devices such as volume controls on...
) allows the user to adjust the regulated voltage.
Fixed regulators

when the load is less than 1.5 ampere
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
s.
The "78xx
78xx
The 78xx is a family of self-contained fixed linear voltage regulator integrated circuits. The 78xx family is commonly used in electronic circuits requiring a regulated power supply due to their ease-of-use and low cost...
" series (7805, 7812, etc.) regulate positive voltages while the "79xx" series (7905, 7912, etc.) regulate negative voltages. Often, the last two digits of the device number are the output voltage; e.g., a 7805 is a +5 V regulator, while a 7915 is a -15 V regulator. There are variants on the 78xx series ICs, such as 78L and 78S, some of which can supply up to 1.5 Amps.
Adjusting fixed regulators
Several ways are used to make fixed IC regulators adjustable.A Zener diode or resistor is added between the IC's ground terminal and ground. Resistors are acceptable where ground current is constant, but are ill-suited to regulators with varying ground current. Switching in different Zeners, diodes or resistors can be used to obtain stepwise adjustment.
A potentiometer can be placed in series with the ground terminal to variably increase the output voltage. This degrades regulation, and is not suitable for regulators with varying ground current.
Product Launch
The adjustable linear regulator IC still in use today first debuted on April 12, 1977 in an Electronic DesignElectronic Design Magazine
First published 55 years ago, Electronic Design is the largest published print magazine for the electronic design industry published in the USA by Penton Media....
article entitled "Break Loose from Fixed IC Regulators". The article was written by Robert Dobkin, an IC
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
designer then working for National Semiconductor
National Semiconductor
National Semiconductor was an American semiconductor manufacturer, that specialized in analog devices and subsystems,formerly headquartered in Santa Clara, California, USA. The products of National Semiconductor included power management circuits, display drivers, audio and operational amplifiers,...
. Dobkin later left National in 1981 to found Linear Technology
Linear Technology
Linear Technology Corporation designs, manufactures and markets a broad line of standard high performance analog integrated circuits. Applications for the company's products include telecommunications, cellular telephones, networking products, notebook and desktop computers, video/multimedia,...
where he is currently chief technology officer.
Operation
For output voltages not provided by standard fixed regulators and load currents of less than 7 ampereAmpere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
s, commonly available "adjustable" three-terminal linear regulators may be used. An adjustable regulator generates a fixed low nominal voltage between its output and its 'adjust' terminal (equivalent to the ground terminal in a fixed regulator). The "317
LM317
The LM317 is a popular variable voltage regulator. It was invented by Robert C. Dobkin and Robert J. Widlar in 1970 while they worked at National Semiconductor.-Specifications:-See also:...
" series (+1.25V) regulates positive voltages while the "337" series (-1.25V) regulates negative voltages.

Complex power requirements (e.g., op-amp circuits needing matched positive and negative DC supplies) are more difficult, but single IC dual tracking adjustable regulators are available. Some even have selectable current limiting as well. An example is the 419x series.
Note that some regulators, like the LM317, require a minimum load.
Protection
Linear IC voltage regulators may include a variety of protection methods:- current limiting
- foldbackFoldback (power supply design)Foldback is a design feature that functions as follows. When overcurrent is drawn by the load, the supply reduces output voltage and current to well below the current limit. This approach has been used in power supplies and power amplifiers....
- thermal shutdown
- safe area protection
Sometimes external protection is used, such as crowbar protection
Crowbar (circuit)
A crowbar circuit is an electrical circuit used to prevent an overvoltage condition of a power supply unit from damaging the circuits attached to the power supply. It operates by putting a short circuit or low resistance path across the voltage source, much as if one dropped a tool of the same name...
Other devices
More complex regulators are available in packages with more than three pins, including dual in-line packageDual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package is an electronic device package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board or inserted in a socket.A DIP is usually referred to as a DIPn, where n is...
s.
See also
- Voltage regulatorVoltage regulatorA voltage regulator is an electrical regulator designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage level. A voltage regulator may be a simple "feed-forward" design or may include negative feedback control loops. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components...
- Bandgap voltage referenceBandgap voltage referenceA bandgap voltage reference is a temperature independent voltage reference circuit widely used in integrated circuits, usually with an output voltage around 1.25 V, close to the theoretical 1.22 eV bandgap of silicon at 0 K. This circuit concept was first published by David Hilbiber in 1964...
- LM317LM317The LM317 is a popular variable voltage regulator. It was invented by Robert C. Dobkin and Robert J. Widlar in 1970 while they worked at National Semiconductor.-Specifications:-See also:...
- Brokaw bandgap referenceBrokaw bandgap referenceBrokaw bandgap reference is a voltage reference circuit widely used in integrated circuits, with an output voltage around 1.25 V with only little temperature dependence...
- Switched-mode power supplySwitched-mode power supplyA switched-mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator in order to be highly efficient in the conversion of electrical power...
- Low-dropout regulator
External links
- "Zener regulator" at Hyperphysics
- Linear voltage regulator tutorial video in HD Includes practical examples.
- ECE 327: LM317 Bandgap Voltage Reference Example — Brief explanation of the temperature-independent bandgap reference circuit within the LM317.
- ECE 327: Procedures for Voltage Regulators Lab — Gives schematics, explanations, and analyses for Zener shunt regulator, series regulator, feedback series regulator, feedback series regulator with current limiting, and feedback series regulator with current foldback. Also discusses the proper use of the LM317LM317The LM317 is a popular variable voltage regulator. It was invented by Robert C. Dobkin and Robert J. Widlar in 1970 while they worked at National Semiconductor.-Specifications:-See also:...
integrated circuitIntegrated circuitAn integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
bandgap voltage referenceBandgap voltage referenceA bandgap voltage reference is a temperature independent voltage reference circuit widely used in integrated circuits, usually with an output voltage around 1.25 V, close to the theoretical 1.22 eV bandgap of silicon at 0 K. This circuit concept was first published by David Hilbiber in 1964...
and bypass capacitorCapacitorA capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
s.- ECE 327: Report Strategies for Voltage Regulators Lab — Gives more-detailed quantitative analysis of behavior of several shunt and series regulators in and out of normal operating ranges.
- "7A SPX1580 regulator"

