
Bandgap voltage reference
Encyclopedia
A bandgap voltage reference is a temperature independent voltage
reference circuit widely used in integrated circuit
s, usually with an output voltage around 1.25 V, close to the theoretical 1.22 eV bandgap of silicon
at 0 K
. This circuit concept was first published by David Hilbiber in 1964. Bob Widlar
, Paul Brokaw and others followed up with other commercially successful versions.
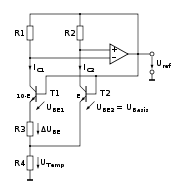
 The voltage difference between two p-n junctions (e.g. diode
The voltage difference between two p-n junctions (e.g. diode
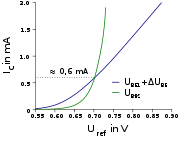
s), operated at different current densities, is used to generate a proportional to absolute temperature (PTAT) current in a first resistor. This current is used to generate a voltage in a second resistor. This voltage in turn is added to the voltage of one of the junctions (or a third one, in some implementations). The voltage across a diode operated at constant current, or here with a PTAT current, is complementary to absolute temperature (CTAT—reduces with increasing temperature), with approx. −2 mV/K. If the ratio between the first and second resistor is chosen properly, the first order effects of the temperature dependency of the diode and the PTAT current will cancel out. The resulting voltage is about 1.2–1.3 V, depending on the particular technology and circuit design, and is close to the theoretical 1.22 eV bandgap of silicon
at 0 K
. The remaining voltage change over the operating temperature
of typical integrated circuits is on the order of a few millivolts. This temperature dependency has a typical parabolic
behavior.
Because the output voltage is by definition fixed around 1.25 V for typical bandgap reference circuits, the minimum operating voltage is about 1.4 V, as in a CMOS
circuit at least one drain-source voltage of a FET (field effect transistor) has to be added. Therefore, recent work concentrates on finding alternative solutions, in which for example currents are summed instead of voltages, resulting in a lower theoretical limit for the operating voltage (Banba, 1999).
Note that sometimes confusion arises when using the abbreviation CTAT, where the "C" is incorrectly taken to mean "constant" rather than "complementary". To avoid this confusion, although not in widespread use, the term constant with temperature (CWT
) is sometimes used.
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
reference circuit widely used in integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
s, usually with an output voltage around 1.25 V, close to the theoretical 1.22 eV bandgap of silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
at 0 K
Absolute zero
Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. The laws of thermodynamics state that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means....
. This circuit concept was first published by David Hilbiber in 1964. Bob Widlar
Bob Widlar
Robert John Widlar was an American electronic engineer and a pioneer of linear integrated circuit design. Widlar invented the basic building blocks of linear ICs like the Widlar current source, the Widlar bandgap voltage reference and the Widlar output stage...
, Paul Brokaw and others followed up with other commercially successful versions.
Operation


Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
s), operated at different current densities, is used to generate a proportional to absolute temperature (PTAT) current in a first resistor. This current is used to generate a voltage in a second resistor. This voltage in turn is added to the voltage of one of the junctions (or a third one, in some implementations). The voltage across a diode operated at constant current, or here with a PTAT current, is complementary to absolute temperature (CTAT—reduces with increasing temperature), with approx. −2 mV/K. If the ratio between the first and second resistor is chosen properly, the first order effects of the temperature dependency of the diode and the PTAT current will cancel out. The resulting voltage is about 1.2–1.3 V, depending on the particular technology and circuit design, and is close to the theoretical 1.22 eV bandgap of silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
at 0 K
Absolute zero
Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. The laws of thermodynamics state that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means....
. The remaining voltage change over the operating temperature
Operating temperature
An operating temperature is the temperature at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the device function and application context, and ranges from the minimum operating temperature to the...
of typical integrated circuits is on the order of a few millivolts. This temperature dependency has a typical parabolic
Parabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
behavior.
Because the output voltage is by definition fixed around 1.25 V for typical bandgap reference circuits, the minimum operating voltage is about 1.4 V, as in a CMOS
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits...
circuit at least one drain-source voltage of a FET (field effect transistor) has to be added. Therefore, recent work concentrates on finding alternative solutions, in which for example currents are summed instead of voltages, resulting in a lower theoretical limit for the operating voltage (Banba, 1999).
Note that sometimes confusion arises when using the abbreviation CTAT, where the "C" is incorrectly taken to mean "constant" rather than "complementary". To avoid this confusion, although not in widespread use, the term constant with temperature (CWT
CWT
CWT or cwt may refer to:* Continuous wavelet transform* Complex wavelet transform* Centum weight , or hundredweight, 100 pounds or 112 pounds * Cadwalader, Wickersham & Taft, a prominent law firm...
) is sometimes used.
External links
- The Design of Band-Gap Reference Circuits: Trials and Tribulations – Robert Pease, National Semiconductor
- Features and Limitations of CMOS Voltage References
- ECE 327: LM317 Bandgap Voltage Reference Example – Brief explanation of the temperature-independent bandgap reference circuit within the LM317.

