
Zener diode
Encyclopedia
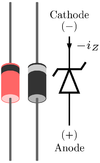
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
which allows current to flow in the forward direction in the same manner as an ideal diode, but will also permit it to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value known as the breakdown voltage
Breakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to become electrically conductive.The breakdown voltage of a diode is the minimum reverse voltage to make the diode conduct in reverse...
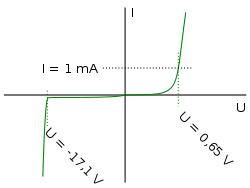
, "Zener knee voltage" or "Zener voltage." The device was named after Clarence Zener
Clarence Zener
Clarence Melvin Zener was the American physicist who first described the property concerning the breakdown of electrical insulators. These findings were later exploited by Bell Labs in the development of the Zener diode, which was duly named after him...
, who discovered this electrical property.
A conventional solid-state diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
will not allow significant current if it is reverse-biased below its reverse breakdown voltage. When the reverse bias breakdown voltage is exceeded, a conventional diode is subject to high current due to avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
. Unless this current is limited by circuitry, the diode will be permanently damaged due to overheating. In the case of a large forward bias (current in the direction of the arrow), the diode exhibits a voltage drop due to its junction built-in voltage and internal resistance. The amount of the voltage drop depends on the semiconductor material and the doping concentrations.
A Zener diode exhibits almost the same properties, except the device is specially designed so as to have a greatly reduced breakdown voltage, the so-called Zener voltage. By contrast with the conventional device, a reverse-biased Zener diode will exhibit a controlled breakdown and allow the current to keep the voltage across the Zener diode close to the Zener breakdown voltage. For example, a diode with a Zener breakdown voltage of 3.2 V will exhibit a voltage drop of very nearly 3.2 V across a wide range of reverse currents. The Zener diode is therefore ideal for applications such as the generation of a reference voltage (e.g. for an amplifier
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
stage), or as a voltage stabilizer for low-current applications.
The Zener diode's operation depends on the heavy doping
Doping (semiconductor)
In semiconductor production, doping intentionally introduces impurities into an extremely pure semiconductor for the purpose of modulating its electrical properties. The impurities are dependent upon the type of semiconductor. Lightly and moderately doped semiconductors are referred to as extrinsic...
of its p-n junction
P-n junction
A p–n junction is formed at the boundary between a P-type and N-type semiconductor created in a single crystal of semiconductor by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy .If two separate pieces of material were used, this would...
allowing electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s to tunnel from the valence band of the p-type material to the conduction band of the n-type material. In the atomic scale, this tunneling corresponds to the transport of valence band electrons into the empty conduction band states; as a result of the reduced barrier between these bands and high electric fields that are induced due to the relatively high levels of dopings on both sides. The breakdown voltage can be controlled quite accurately in the doping process. While tolerances within 0.05% are available, the most widely used tolerances are 5% and 10%. Breakdown voltage for commonly available zener diodes can vary widely from 1.2 volts to 200 volts.
Another mechanism that produces a similar effect is the avalanche effect as in the avalanche diode
Avalanche diode
In electronics, an avalanche diode is a diode that is designed to go through avalanche breakdown at a specified reverse bias voltage. The junction of an avalanche diode is designed to prevent current concentration at hot spots, so that the diode is undamaged by the breakdown...
. The two types of diode are in fact constructed the same way and both effects are present in diodes of this type. In silicon diodes up to about 5.6 volts, the Zener effect
Zener effect
The Zener effect is a type of electrical breakdown in a reverse biased P-N junction diode in which the electric field across the diode breaks some of the covalent bonds of the semiconductor atoms leading to a large number of free minority carriers, which suddenly increase the reverse current...
is the predominant effect and shows a marked negative temperature coefficient
Temperature coefficient
The temperature coefficient is the relative change of a physical property when the temperature is changed by 1 K.In the following formula, let R be the physical property to be measured and T be the temperature at which the property is measured. T0 is the reference temperature, and ΔT is the...
. Above 5.6 volts, the avalanche effect
Avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
becomes predominant and exhibits a positive temperature coefficient. In a 5.6 V diode, the two effects occur together and their temperature coefficients nearly cancel each other out, thus the 5.6 V diode is the component of choice in temperature-critical applications. Modern manufacturing techniques have produced devices with voltages lower than 5.6 V with negligible temperature coefficients, but as higher voltage devices are encountered, the temperature coefficient rises dramatically. A 75 V diode has 10 times the coefficient of a 12 V diode.
All such diodes, regardless of breakdown voltage, are usually marketed under the umbrella term of "Zener diode".
Uses
Shunt (electrical)
In electronics, a shunt is a device which allows electric current to pass around another point in the circuit. The term is also widely used in photovoltaics to describe an unwanted short circuit between the front and back surface contacts of a solar cell, usually caused by wafer damage.-Defective...
regulator
Voltage regulator
A voltage regulator is an electrical regulator designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage level. A voltage regulator may be a simple "feed-forward" design or may include negative feedback control loops. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components...
s to regulate the voltage across small circuits. When connected in parallel with a variable voltage source so that it is reverse biased, a Zener diode conducts when the voltage reaches the diode's reverse breakdown voltage. From that point on, the relatively low impedance of the diode keeps the voltage across the diode at that value.
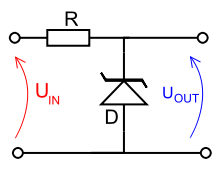
In the case of this simple reference, the current flowing in the diode is determined using Ohms law and the known voltage drop across the resistor R. IDiode = (UIN - UOUT) / RΩ
The value of R must satisfy two conditions:
- R must be small enough that the current through D keeps D in reverse breakdown. The value of this current is given in the data sheet for D. For example, the common BZX79C5V6 device, a 5.6 V 0.5 W Zener diode, has a recommended reverse current of 5 mA. If insufficient current exists through D, then UOUT will be unregulated, and less than the nominal breakdown voltage (this differs to voltage regulator tubeVoltage regulator tubeA voltage-regulator tube is an electronic component used as a shunt regulator to hold a voltage constant at a pre-determined level.Physically, these devices resemble vacuum tubes, but there are two main differences:...
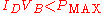
s where the output voltage will be higher than nominal and could rise as high as UIN). When calculating R, allowance must be made for any current through the external load, not shown in this diagram, connected across UOUT. - R must be large enough that the current through D does not destroy the device. If the current through D is ID, its breakdown voltage VB and its maximum power dissipation PMAX, then
 .
.
A load may be placed across the diode in this reference circuit, and as long as the zener stays in reverse breakdown, the diode will provide a stable voltage source to the load.
Shunt regulators are simple, but the requirements that the ballast resistor be small enough to avoid excessive voltage drop during worst-case operation (low input voltage concurrent with high load current) tends to leave a lot of current flowing in the diode much of the time, making for a fairly wasteful regulator with high quiescent power dissipation, only suitable for smaller loads.
Zener diodes in this configuration are often used as stable references for more advanced voltage regulator circuits.
These devices are also encountered, typically in series with a base-emitter junction, in transistor stages where selective choice of a device centered around the avalanche/Zener point can be used to introduce compensating temperature co-efficient balancing of the transistor PN junction. An example of this kind of use would be a DC error amplifier
Error amplifier (electronics)
An error amplifier is most commonly encountered in feedback unidirectional voltage control circuits where the sampled output voltage of the circuit under control is fed back and compared to a stable reference voltage...
used in a regulated power supply circuit feedback loop system.
Zener diodes are also used in surge protector
Surge protector
A surge protector is an appliance designed to protect electrical devices from voltage spikes. A surge protector attempts to limit the voltage supplied to an electric device by either blocking or by shorting to ground any unwanted voltages above a safe threshold...
s to limit transient voltage spikes.
Another notable application of the zener diode is the use of noise caused by its avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown
Avalanche breakdown is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche...
in a random number generator
Hardware random number generator
In computing, a hardware random number generator is an apparatus that generates random numbers from a physical process. Such devices are often based on microscopic phenomena that generate a low-level, statistically random "noise" signal, such as thermal noise or the photoelectric effect or other...
that never repeats.
See also
- Avalanche diodeAvalanche diodeIn electronics, an avalanche diode is a diode that is designed to go through avalanche breakdown at a specified reverse bias voltage. The junction of an avalanche diode is designed to prevent current concentration at hot spots, so that the diode is undamaged by the breakdown...
- Backward diodeBackward diodeIn semiconductor devices, a backward diode is a variation on a Zener diode or tunnel diode having a better conduction for small reverse biases than for forward bias voltages....
- Transient voltage suppression diodeTransient voltage suppression diodeA transient-voltage-suppression diode is an electronic component used to protect sensitive electronics from voltage spikes induced on connected wires....
- Voltage regulatorVoltage regulatorA voltage regulator is an electrical regulator designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage level. A voltage regulator may be a simple "feed-forward" design or may include negative feedback control loops. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components...
- Voltage regulator tubeVoltage regulator tubeA voltage-regulator tube is an electronic component used as a shunt regulator to hold a voltage constant at a pre-determined level.Physically, these devices resemble vacuum tubes, but there are two main differences:...

