
Latite
Encyclopedia

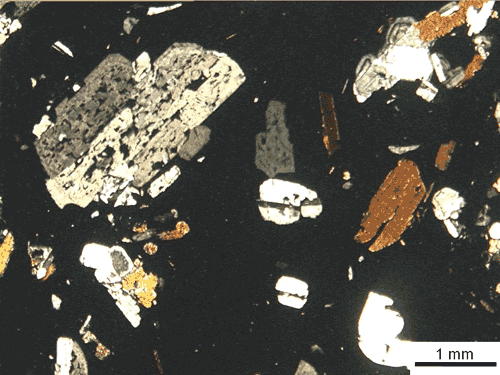
Igneous rock
Igneous rock is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic rock. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava...
, volcanic rock
Volcanic rock
Volcanic rock is a rock formed from magma erupted from a volcano. In other words, it is an igneous rock of volcanic origin...
, with aphanitic-aphyric to aphyric-porphyritic
Porphyritic
Porphyritic is an adjective used in geology, specifically for igneous rocks, for a rock that has a distinct difference in the size of the crystals, with at least one group of crystals obviously larger than another group...
texture. Its mineral
Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
assemblage is usually alkali feldspar
Feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming tectosilicate minerals which make up as much as 60% of the Earth's crust....
and plagioclase
Plagioclase
Plagioclase is an important series of tectosilicate minerals within the feldspar family. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a solid solution series, more properly known as the plagioclase feldspar series...
in approximately equal amounts. Quartz
Quartz
Quartz is the second-most-abundant mineral in the Earth's continental crust, after feldspar. It is made up of a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall formula SiO2. There are many different varieties of quartz,...
is less than five percent and is absent in a feldspathoid
Feldspathoid
The feldspathoids are a group of tectosilicate minerals which resemble feldspars but have a different structure and much lower silica content. They occur in rare and unusual types of igneous rocks....
-bearing latite, and olivine
Olivine
The mineral olivine is a magnesium iron silicate with the formula 2SiO4. It is a common mineral in the Earth's subsurface but weathers quickly on the surface....
is absent in a quartz
Quartz
Quartz is the second-most-abundant mineral in the Earth's continental crust, after feldspar. It is made up of a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall formula SiO2. There are many different varieties of quartz,...
-bearing latite. When quartz content is greater than five percent the rock is classified as quartz latite
Quartz latite
A quartz latite is a volcanic rock or fine grained intrusive rock equivalent to a latite with a phenocryst modal composition containing 5-20% quartz. Above 20% quartz, the rock would be classified as a rhyolite. It is the fine grained equivalent of a quartz monzonite containing approximately equal...
. Biotite
Biotite
Biotite is a common phyllosilicate mineral within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula . More generally, it refers to the dark mica series, primarily a solid-solution series between the iron-endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more aluminous endmembers...
, hornblende
Hornblende
Hornblende is a complex inosilicate series of minerals .It is not a recognized mineral in its own right, but the name is used as a general or field term, to refer to a dark amphibole....
, pyroxene
Pyroxene
The pyroxenes are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. They share a common structure consisting of single chains of silica tetrahedra and they crystallize in the monoclinic and orthorhombic systems...
and scarce olivine
Olivine
The mineral olivine is a magnesium iron silicate with the formula 2SiO4. It is a common mineral in the Earth's subsurface but weathers quickly on the surface....
or quartz
Quartz
Quartz is the second-most-abundant mineral in the Earth's continental crust, after feldspar. It is made up of a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall formula SiO2. There are many different varieties of quartz,...
are common accessory minerals.
Rhomb porphyries are an unusual variety with gray-white porphyritic
Porphyritic
Porphyritic is an adjective used in geology, specifically for igneous rocks, for a rock that has a distinct difference in the size of the crystals, with at least one group of crystals obviously larger than another group...
rhomb
Rhombus
In Euclidean geometry, a rhombus or rhomb is a convex quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length. The rhombus is often called a diamond, after the diamonds suit in playing cards, or a lozenge, though the latter sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 45° angle.Every...
shaped phenocrysts embedded in a very fine grained red-brown matrix
Matrix (geology)
The matrix or groundmass of rock is the finer grained mass of material in which larger grains, crystals or clasts are embedded.The matrix of an igneous rock consists of finer grained, often microscopic, crystals in which larger crystals are embedded. This porphyritic texture is indicative of...
. The composition of rhomb porphyry places it in the trachyte
Trachyte
Trachyte is an igneous volcanic rock with an aphanitic to porphyritic texture. The mineral assemblage consists of essential alkali feldspar; relatively minor plagioclase and quartz or a feldspathoid such as nepheline may also be present....
- latite classification of the QAPF diagram
QAPF diagram
A QAPF diagram is a double triangle diagram which is used to classify igneous rocks based on mineralogic composition. The acronym, QAPF, stands for "Quartz, Alkali feldspar, Plagioclase, Feldspathoid ". These are the mineral groups used for classification in QAPF diagram...
.

