Kerr-lens modelocking
Encyclopedia
Kerr-lens modelocking is a method of modelocking
laser
s via a nonlinear optical
process known as the optical Kerr effect
. This method allows the generation of pulses of light with a duration as short as a few femtoseconds.
The optical Kerr effect is a process which results from the nonlinear response of an optical medium to the electric field
of an electromagnetic wave. The refractive index
of the medium is dependent on the field strength.
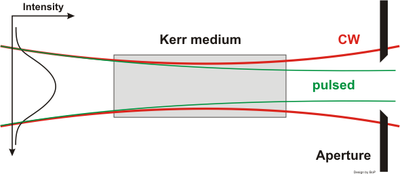
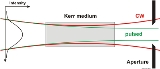
 Because of the non-uniform power density distribution in a Gaussian beam
Because of the non-uniform power density distribution in a Gaussian beam
(as found in laser resonators) the refractive index changes across the beam profile; the refractive index experienced by the beam is greater in the center of the beam than at the edge. Therefore a rod of an active Kerr medium works like a lens for high intensity light. This is called self-focusing
and in extreme cases leads to material destruction. In the laser cavity short bursts of light will then be focused differently to continuous waves (cw).
To favor the pulsed mode over cw, the cavity could be made unstable for cw-operation, but more often a low stability is a by-product of a cavity design putting emphasis on aperture effects. Older designs used a hard aperture, that simply cuts off, while modern designs use a soft aperture, that means the overlap between the pumped region of the gain medium and the pulse. While the effect of a lens on a free laser beam is quite obvious, inside a cavity the whole beam tries to adapt to this change. The standard cavity with flat mirrors and a thermal lens in the laser crystal has the smallest beam width on the end-mirrors. With the additional Kerr lens the width on the end-mirror gets even smaller. Therefore small end-mirrors (hard aperture) favor pulses. In Ti:Sapphire oscillators telescopes are inserted around the crystal to increase the intensity. For a soft aperture consider an infinite laser crystal with a thermal lens. A laser beam is guided like in a glass fiber. With an additional Kerr lens the beam width gets smaller. In a real laser the crystal is finite. The cavity on both sides features a concave mirror and then a relative long path to a flat mirror. The cw light exits the laser end face with a larger beam width and slight divergence. It illuminates a smaller area on the concave mirror, leading to a small beam-width on the way to the flat mirror. Thus diffraction
is stronger. Because of the divergence the light is effectively coming from a point farther apart and leads to more convergence after the concave mirror. This convergence is balanced with diffraction. The pulsed light exits the end face with a smaller beam width and no divergence. Thus it illuminates a larger area on the concave mirror and is less convergent afterwards. So both cw and pulses light fronts are mirrored back onto themselves. A cavity close to a confocal one means to be close to instability, which means the beam diameter is sensitive to cavity changes.
This emphasizes the modulation.
With a slightly asymmetric cavity prolonging the cavity emphasizes diffraction and even makes it unstable for cw-operation, while staying stable for pulsed operation.
The length of the medium used for KLM is limited by group velocity
dispersion.
KLM is used in Carrier envelope offset control.
Modelocking can also be started by shifting the optimum focus from the cw-operation to pulsed operation while changing the power density by kicking the end mirror of the resonator cavity (though a piezo mounted, synchronous oscillating end-mirror would be more 'turn key').
Other principles involve different nonlinear effects like saturable absorbers and saturable Bragg reflectors, which induce pulses short enough to initiate the Kerr-lensing process.
.
Laser media for ultrashort pulses (e.g. Ti:Sapphire
)
Dispersion management with prism sequences.
Chirped mirror
technology allows to compensate timing mismatch of different wavelengths inside the cavity due to material dispersion while keeping the stability high and the losses low.
The Kerr effect leads to the Kerr-lens and Self-phase modulation
at the same time. To a first approximation it is possible to consider them as independent effects.
These short pulses open the new field of ultrafast optics, which is a field of nonlinear optics
that gives access to a completely new class of phenomena like measurement of electron movements in an atom (attosecond phenomena), coherent broadband light generation (ultrabroad lasers) and thereby gives rise to many new applications in optical sensing (e.g. coherent laser radar, ultrahigh resolution optical coherence tomography
), material processing and other fields like metrology
(extremely exact frequency and time measurements).
Modelocking
Mode-locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds or femtoseconds ....
laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
s via a nonlinear optical
Nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
process known as the optical Kerr effect
Kerr effect
The Kerr effect, also called the quadratic electro-optic effect , is a change in the refractive index of a material in response to an applied electric field. The Kerr effect is distinct from the Pockels effect in that the induced index change is directly proportional to the square of the electric...
. This method allows the generation of pulses of light with a duration as short as a few femtoseconds.
The optical Kerr effect is a process which results from the nonlinear response of an optical medium to the electric field
Electric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
of an electromagnetic wave. The refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
of the medium is dependent on the field strength.


Gaussian beam
In optics, a Gaussian beam is a beam of electromagnetic radiation whose transverse electric field and intensity distributions are well approximated by Gaussian functions. Many lasers emit beams that approximate a Gaussian profile, in which case the laser is said to be operating on the fundamental...
(as found in laser resonators) the refractive index changes across the beam profile; the refractive index experienced by the beam is greater in the center of the beam than at the edge. Therefore a rod of an active Kerr medium works like a lens for high intensity light. This is called self-focusing
Nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
and in extreme cases leads to material destruction. In the laser cavity short bursts of light will then be focused differently to continuous waves (cw).
To favor the pulsed mode over cw, the cavity could be made unstable for cw-operation, but more often a low stability is a by-product of a cavity design putting emphasis on aperture effects. Older designs used a hard aperture, that simply cuts off, while modern designs use a soft aperture, that means the overlap between the pumped region of the gain medium and the pulse. While the effect of a lens on a free laser beam is quite obvious, inside a cavity the whole beam tries to adapt to this change. The standard cavity with flat mirrors and a thermal lens in the laser crystal has the smallest beam width on the end-mirrors. With the additional Kerr lens the width on the end-mirror gets even smaller. Therefore small end-mirrors (hard aperture) favor pulses. In Ti:Sapphire oscillators telescopes are inserted around the crystal to increase the intensity. For a soft aperture consider an infinite laser crystal with a thermal lens. A laser beam is guided like in a glass fiber. With an additional Kerr lens the beam width gets smaller. In a real laser the crystal is finite. The cavity on both sides features a concave mirror and then a relative long path to a flat mirror. The cw light exits the laser end face with a larger beam width and slight divergence. It illuminates a smaller area on the concave mirror, leading to a small beam-width on the way to the flat mirror. Thus diffraction
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
is stronger. Because of the divergence the light is effectively coming from a point farther apart and leads to more convergence after the concave mirror. This convergence is balanced with diffraction. The pulsed light exits the end face with a smaller beam width and no divergence. Thus it illuminates a larger area on the concave mirror and is less convergent afterwards. So both cw and pulses light fronts are mirrored back onto themselves. A cavity close to a confocal one means to be close to instability, which means the beam diameter is sensitive to cavity changes.
This emphasizes the modulation.
With a slightly asymmetric cavity prolonging the cavity emphasizes diffraction and even makes it unstable for cw-operation, while staying stable for pulsed operation.
The length of the medium used for KLM is limited by group velocity
Group velocity
The group velocity of a wave is the velocity with which the overall shape of the wave's amplitudes — known as the modulation or envelope of the wave — propagates through space....
dispersion.
KLM is used in Carrier envelope offset control.
Starting a Kerr-lens modelocked laser
Initiation of Kerr-lens modelocking depends on the strength of the nonlinear effect involved. If the laser field builds up in a cavity the laser has to overcome the region of cw operation, which often is favoured by the pumping mechanism. This can be achieved by a very strong Kerr-lensing that is strong enough to modelock due to small changes of the laser field strength (laser field build-up or stochastic fluctuations).Modelocking can also be started by shifting the optimum focus from the cw-operation to pulsed operation while changing the power density by kicking the end mirror of the resonator cavity (though a piezo mounted, synchronous oscillating end-mirror would be more 'turn key').
Other principles involve different nonlinear effects like saturable absorbers and saturable Bragg reflectors, which induce pulses short enough to initiate the Kerr-lensing process.
Modelocking - evolution of the pulse
Intensity changes with lengths of nanoseconds are amplified by the Kerr-lensing process and the pulselength further shrinks to achieve higher field strengths in the center of the pulse. This sharpening process is only limited by the bandwidth achievable with the laser material and the cavity-mirrors as well as the dispersion of the cavity. The shortest pulse achievable with a given spectrum is called the bandwidth-limited pulseBandwidth-limited pulse
A bandwidth-limited pulse is a pulse of a wave that has the minimum possible duration for a given spectral bandwidth. Optical pulses of this type can be generated by mode-locked lasers...
.
Laser media for ultrashort pulses (e.g. Ti:Sapphire
Ti-sapphire laser
Ti:sapphire lasers are tunable lasers which emit red and near-infrared light in the range from 650 to 1100 nanometers. These lasers are mainly used in scientific research because of their tunability and their ability to generate ultrashort pulses...
)
Dispersion management with prism sequences.
Chirped mirror
Chirped mirror
A chirped mirror is a dielectric mirror with chirped spaces—spaces of varying depth designed to reflect varying wavelengths of lights—between the dielectric layers ....
technology allows to compensate timing mismatch of different wavelengths inside the cavity due to material dispersion while keeping the stability high and the losses low.
The Kerr effect leads to the Kerr-lens and Self-phase modulation
Self-phase modulation
Self-phase modulation is a nonlinear optical effect of light-matter interaction.An ultrashort pulse of light, when travelling in a medium, will induce a varying refractive index of the medium due to the optical Kerr effect...
at the same time. To a first approximation it is possible to consider them as independent effects.
Applications
Since Kerr-lens modelocking is an effect that directly reacts on the electric field, the response time is fast enough to produce light pulses in the visible and near infrared with lengths of less than 5 femtoseconds. Due to the high electrical field strength focused ultrashort laser beams can overcome the threshold of 1014 W cm-2, which surpasses the field strength of the electron-ion bond in atoms.These short pulses open the new field of ultrafast optics, which is a field of nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
that gives access to a completely new class of phenomena like measurement of electron movements in an atom (attosecond phenomena), coherent broadband light generation (ultrabroad lasers) and thereby gives rise to many new applications in optical sensing (e.g. coherent laser radar, ultrahigh resolution optical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography is an optical signal acquisition and processing method. It captures micrometer-resolution, three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media . Optical coherence tomography is an interferometric technique, typically employing near-infrared light...
), material processing and other fields like metrology
Metrology
Metrology is the science of measurement. Metrology includes all theoretical and practical aspects of measurement. The word comes from Greek μέτρον , "measure" + "λόγος" , amongst others meaning "speech, oration, discourse, quote, study, calculation, reason"...
(extremely exact frequency and time measurements).

