
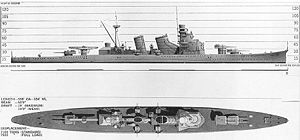
Japanese cruiser Kinugasa
Encyclopedia
was the second vessel in the two-vessel Aoba-class
of heavy cruiser
s in the Imperial Japanese Navy
. It was named after Mount Kinugasa, located in Yokosuka, Kanagawa
, Japan
.
Aoba were originally planned as the third and fourth vessels in the Furutaka-class of heavy cruisers. However, design issues with the Furutaka-class resulted in modifications including double turrets
and an aircraft catapult. These modifications created yet more weight to an already top-heavy design, causing stability problems. Nevertheless, Kinugasa played an important role in the opening stages of World War II
.
in Kobe
. Her early service was as flagship of the Fifth Squadron (Sentai), and she operated for virtually her entire career with that unit and the Sixth and Seventh Squadrons. In 1928, she became the first Japanese combat ship to carry an aircraft catapult
.
Kinugasa served off the China
coast from 1928 and 1929 and on several occasions during the 1930s. Placed in reserve in September 1937, she was extensively modernized at the Sasebo Navy Yard and not recommissioned until the end of October 1940.
of Rear Admiral
Aritomo Goto
as part of the First Fleet under overall command of Vice Admiral
Takasu Shiro. CruDiv 6 consisted of Kinugasa, Aoba
, Furutaka
and Kako
. At the time of the attack on Pearl Harbor
, CruDiv6 was engaged in the invasion of Guam
, following which it participated in the second invasion of Wake Island
.
From January through May 1942, Kinugasa was based out of Truk, in the Caroline Islands
where it provided protection for the landings of Japanese troops in the Solomon Islands
and New Guinea
at Rabaul
, Kavieng
, Buka
, Shortland
, Kieta
, Manus Island
, Admiralty Islands
and Tulagi
.
, CruDiv 6 departed Shortland and effected a rendezvous at sea with light carrier Shōhō
. At 1100 on 7 May 1942, north of Taguli Island, Shoho was attacked and sunk by 93 SBD Dauntless
dive-bombers and TBD Devastator
torpedo-bombers from USS Yorktown
and Lexington
.
The following day, 8 May 1942 46 SBDs, 21 TBDs and 15 Grumman F4F Wildcat
s from Yorktown and Lexington damaged Shōkaku
severely above the waterline and force her retirement. Furutaka and Kinugasa, undamaged in the battle, escorted Shōkaku back to Truk.
 Kinugasa was withdrawn to Japan in June 1942 for repairs, and returned to Truk by 4 July. Following the major reorganization of 14 July 1942, Kinugasa came under the newly created Eighth Fleet
Kinugasa was withdrawn to Japan in June 1942 for repairs, and returned to Truk by 4 July. Following the major reorganization of 14 July 1942, Kinugasa came under the newly created Eighth Fleet
under Vice Admiral Gunichi Mikawa
, based at Rabaul.
on 9 August 1942, the four heavy cruisers of CruDiv 6 (Aoba
, Kako
, Furutaka
and Kinugasa), the heavy cruiser Chōkai, light cruisers Tenryū
and Yubari
and destroyer Yūnagi
engaged the Allied forces in a night gun and torpedo action. At about 2300, Chōkai, Furutaka and Kako all launched their reconnaissance floatplane
s. The circling floatplanes dropped flares illuminating the targets and all the Japanese ships opened fire. US Ships Astoria
, Quincy
, Vincennes
and HMAS Canberra were sunk. USS Chicago
was damaged as were the USS Ralph Talbot
and USS Patterson
. On the Japanese side, Chōkai was hit three times, Kinugasa twice (once in her No. 1 Engine Room by a 5-inch shell from Patterson and her port steering gear by a shell from Vincennes), Aoba once, and Furutaka was not damaged.
The heavily-laden American invasion transports off Guadalcanal were unprotected, but Admiral Mikawa, unaware that Admiral Fletcher
had withdrawn his aircraft carriers covering the invasion, feared an air attack at daybreak and ordered a retirement. Captain Sawa of Kinugasa, frustrated, launched a spread of torpedoes from Kinugasa's starboard tubes at the Allied
transports 13 miles (20.9 km) distant, but all missed. The following day as CruDiv6 approached Kavieng, Kako was torpedoed and sunk by the US submarine S 44
.
on 11 October 1942, CruDiv 6's (Aoba, Furutaka and Kinugasa), and destroyers Fubuki
and Hatsuyuki
departed Shortland to provide cover for a troop reinforcement convoy by shelling Henderson Field on Guadalcanal. The fleet was spotted by two Vought
OS2U Kingfisher
reconnaissance planes coming down the "Slot" at 30 knots (58.8 km/h).
So alerted, the radar-equipped American cruisers USS San Francisco
, Boise
, Salt Lake City
, and Helena
and five destroyers steamed around the end of Guadalcanal to block the entrance to Savo Sound.
At 2235, the Helena's radar spotted the Japanese fleet, and the Americans successfully cross the Japanese "T"
. Both fleets open fire, but Admiral Goto, thinking that he was under friendly-fire, ordered a 180-degree turn that exposed each of his ships to the American broadsides.
Aoba was damaged heavily, and Admiral Goto mortally wounded. Furutaka was hit by a torpedo that flooded her forward engine room and was sunk by Salt Lake City and Duncan
.
Kinugasa straddled Boise and Salt Lake City with 8-inch salvos knocking out Boise's No. 1 and 2 turrets. Kinugasa sustained four hits in the engagement. The following morning, Kinugasa was attacked by five American planes but not damaged, and returned to Shortland.
From 24-26 October and 1-5 November, Kinugasa and Chōkai provided cover for replacement convoys of troops and equipment to bolster Japanese defenses at Guadalcanal. On 14 November 1942, during the Naval Battle of Guadalcanal
, Kinugasa was attacked by TBF Avenger
torpedo-bombers and SBD Dauntless
dive bombers from the USS Enterprise
and USMC
Avengers from Guadalcanal. At 0936 a 500-pound bomb hit Kinugasa's 13.2-mm machine gun mount in front of the bridge, starting a fire in the forward gasoline storage area. Captain Sawa and his Executive Officer
were killed by the bomb, and Kinugasa gradually began to list to port. Near-misses caused additional fires and flooding and a second attack by 17 more Dauntless bombers knocked out Kinugasa's engines and rudder and opened more compartments to the sea. At 1122, Kinugasa capsized and sank southwest of Rendova Island
at 08°45′S 157°00′E, taking 511 crewmen with her.
Kinugasa was removed from the Navy list on 15 December 1942.
Aoba class cruiser
The were a class of two Japanese heavy cruisers which saw service during World War II.-Ships in class:The ships in the class were Aoba and Kinugasa .-External links:* Shares page with Furutaka-Class cruisers...
of heavy cruiser
Heavy cruiser
The heavy cruiser was a type of cruiser, a naval warship designed for long range, high speed and an armament of naval guns roughly 203mm calibre . The heavy cruiser can be seen as a lineage of ship design from 1915 until 1945, although the term 'heavy cruiser' only came into formal use in 1930...
s in the Imperial Japanese Navy
Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1869 until 1947, when it was dissolved following Japan's constitutional renunciation of the use of force as a means of settling international disputes...
. It was named after Mount Kinugasa, located in Yokosuka, Kanagawa
Yokosuka, Kanagawa
is a city located in Kanagawa, Japan. As of 2010, the city had an estimated population of 419,067 and a population density of 4,160 people per km². It covered an area of 100.62 km²...
, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
.
Background
Kinugasa and her sister shipSister ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same class as, or of virtually identical design to, another ship. Such vessels share a near-identical hull and superstructure layout, similar displacement, and roughly comparable features and equipment...
Aoba were originally planned as the third and fourth vessels in the Furutaka-class of heavy cruisers. However, design issues with the Furutaka-class resulted in modifications including double turrets
Gun turret
A gun turret is a weapon mount that protects the crew or mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in many directions.The turret is also a rotating weapon platform...
and an aircraft catapult. These modifications created yet more weight to an already top-heavy design, causing stability problems. Nevertheless, Kinugasa played an important role in the opening stages of World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
.
Early career
Kinugasa was completed on 30 September 1927 at the Kawasaki shipyardsKawasaki Heavy Industries
is an international corporation based in Japan. It has headquarters in both Chūō-ku, Kobe and Minato, Tokyo.The company is named after its founder Shōzō Kawasaki and has no connection with the city of Kawasaki, Kanagawa....
in Kobe
Kobe
, pronounced , is the fifth-largest city in Japan and is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture on the southern side of the main island of Honshū, approximately west of Osaka...
. Her early service was as flagship of the Fifth Squadron (Sentai), and she operated for virtually her entire career with that unit and the Sixth and Seventh Squadrons. In 1928, she became the first Japanese combat ship to carry an aircraft catapult
Aircraft catapult
An aircraft catapult is a device used to launch aircraft from ships—in particular aircraft carriers—as a form of assisted take off. It consists of a track built into the flight deck, below which is a large piston or shuttle that is attached through the track to the nose gear of the aircraft, or in...
.
Kinugasa served off the China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
coast from 1928 and 1929 and on several occasions during the 1930s. Placed in reserve in September 1937, she was extensively modernized at the Sasebo Navy Yard and not recommissioned until the end of October 1940.
Early stages of the Pacific War
In 1941, Kinugasa was assigned to Cruiser Division 6 (CruDiv6), as flagshipFlagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, reflecting the custom of its commander, characteristically a flag officer, flying a distinguishing flag...
of Rear Admiral
Rear admiral (United States)
Rear admiral is a naval commissioned officer rank above that of a commodore and captain, and below that of a vice admiral. The uniformed services of the United States are unique in having two grades of rear admirals.- Rear admiral :...
Aritomo Goto
Aritomo Goto
was an admiral in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.-Early career:Gotō was born in Ibaraki prefecture in 1888. He graduated from the 38th class of the Imperial Japanese Naval Academy in 1910, ranked 30th out of a class of 149 cadets. As a midshipman, he served on the cruiser and...
as part of the First Fleet under overall command of Vice Admiral
Vice admiral (United States)
In the United States Navy, the United States Coast Guard, the United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Commissioned Corps, and the United States Maritime Service, vice admiral is a three-star flag officer, with the pay grade of...
Takasu Shiro. CruDiv 6 consisted of Kinugasa, Aoba
Japanese cruiser Aoba
was the lead ship in the two-vessel Aoba-class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. It is named after Mount Aoba, a volcano located behind Maizuru, Kyoto.-Background:...
, Furutaka
Japanese cruiser Furutaka
was the lead ship in the two-vessel Furutaka-class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. It was named after Mount Furutaka, located on Etajima, Hiroshima immediately behind the Imperial Japanese Navy Academy.-Design:...
and Kako
Japanese cruiser Kako
was the second vessel in the two-vessel Furutaka-class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. It was named after the Kakogawa River in Hyogo prefecture, Japan.-Background:...
. At the time of the attack on Pearl Harbor
Attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike conducted by the Imperial Japanese Navy against the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on the morning of December 7, 1941...
, CruDiv6 was engaged in the invasion of Guam
Battle of Guam (1941)
The First Battle of Guam, was an engagement during the Pacific War in World War II, and took place on 8 December 1941 on Guam in the Mariana Islands between the Empire of Japan and the United States...
, following which it participated in the second invasion of Wake Island
Wake Island
Wake Island is a coral atoll having a coastline of in the North Pacific Ocean, located about two-thirds of the way from Honolulu west to Guam east. It is an unorganized, unincorporated territory of the United States, administered by the Office of Insular Affairs, U.S. Department of the Interior...
.
From January through May 1942, Kinugasa was based out of Truk, in the Caroline Islands
Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia in the eastern part of the group, and Palau at the extreme western end...
where it provided protection for the landings of Japanese troops in the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is a sovereign state in Oceania, east of Papua New Guinea, consisting of nearly one thousand islands. It covers a land mass of . The capital, Honiara, is located on the island of Guadalcanal...
and New Guinea
New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
at Rabaul
Rabaul
Rabaul is a township in East New Britain province, Papua New Guinea. The town was the provincial capital and most important settlement in the province until it was destroyed in 1994 by falling ash of a volcanic eruption. During the eruption, ash was sent thousands of metres into the air and the...
, Kavieng
Kavieng
Kavieng is the capital of the Papua New Guinean province of New Ireland and the largest town on the island of the same name. The town is located at Balgai Bay, on the northern tip of the island. As of 2000, it had a population of 10,600....
, Buka
Buka, Papua New Guinea
Buka is situated on Buka Island, Bougainville Province, Papua New Guinea. It has been the capital of the province during the Bougainville civil war...
, Shortland
Shortland
-Geography:* Shortland Island* Shortland Islands* Shortlands, a ward of the London Borough of Bromley* Shortland, New South Wales* Shortland's Bluff, an old name for Queenscliff, Victoria, Australia-People:...
, Kieta
Kieta
Kieta is a port town located on the eastern coast of the island of Bougainville in Papua New Guinea, near the township of Arawa. After extensive destruction during the 1990 Civil Uprising on Bougainville, Kieta has few inhabitants now, and is known mainly for its transport connections .-History:On...
, Manus Island
Manus Island
Manus Island is part of Manus Province in northern Papua New Guinea and is the largest island of the Admiralty Islands. It is the fifth largest island in Papua New Guinea with an area of 2,100 km², measuring around 100 km × 30 km. According to the 2000 census, Manus Island had a...
, Admiralty Islands
Admiralty Islands
The Admiralty Islands are a group of eighteen islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the south Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island. These rainforest-covered islands form part of Manus Province, the smallest and...
and Tulagi
Tulagi
Tulagi, less commonly Tulaghi, is a small island in the Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Florida Island. The town of the same name on the island Tulagi, less commonly Tulaghi, is a small island (5.5 km by 1 km) in the Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Florida...
.
Battle of Coral Sea
At the Battle of the Coral SeaBattle of the Coral Sea
The Battle of the Coral Sea, fought from 4–8 May 1942, was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II between the Imperial Japanese Navy and Allied naval and air forces from the United States and Australia. The battle was the first fleet action in which aircraft carriers engaged...
, CruDiv 6 departed Shortland and effected a rendezvous at sea with light carrier Shōhō
Japanese aircraft carrier Shoho
Shōhō , the lead ship of her class, was a light aircraft carrier of the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II...
. At 1100 on 7 May 1942, north of Taguli Island, Shoho was attacked and sunk by 93 SBD Dauntless
SBD Dauntless
The Douglas SBD Dauntless was a naval dive bomber made by Douglas during World War II. The SBD was the United States Navy's main dive bomber from mid-1940 until late 1943, when it was largely replaced by the SB2C Helldiver...
dive-bombers and TBD Devastator
TBD Devastator
The Douglas TBD Devastator was a torpedo bomber of the United States Navy, ordered in 1934, first flying in 1935 and entering service in 1937. At that point, it was the most advanced aircraft flying for the USN and possibly for any navy in the world...
torpedo-bombers from USS Yorktown
USS Yorktown (CV-5)
was an aircraft carrier commissioned in the United States Navy from 1937 until she was sunk at the Battle of Midway in June 1942. She was named after the Battle of Yorktown in 1781 and the lead ship of the Yorktown class which was designed after lessons learned from operations with the large...
and Lexington
USS Lexington (CV-2)
USS Lexington , nicknamed the "Gray Lady" or "Lady Lex," was an early aircraft carrier of the United States Navy. She was the lead ship of the , though her sister ship was commissioned a month earlier...
.
The following day, 8 May 1942 46 SBDs, 21 TBDs and 15 Grumman F4F Wildcat
F4F Wildcat
The Grumman F4F Wildcat was an American carrier-based fighter aircraft that began service with both the United States Navy and the British Royal Navy in 1940...
s from Yorktown and Lexington damaged Shōkaku
Japanese aircraft carrier Shokaku
Shōkaku was an aircraft carrier of the Imperial Japanese Navy, the lead ship of her class. Along with her sister ship , she took part in several key naval battles during the Pacific War, including the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Battle of the Coral Sea and the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands...
severely above the waterline and force her retirement. Furutaka and Kinugasa, undamaged in the battle, escorted Shōkaku back to Truk.

IJN 8th Fleet
The was a fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy established during World War II.-History:Established on 14 July 1942, the IJN 8th Fleet was a headquarters unit established to direct Japanese naval operations in the Solomon Islands and New Guinea...
under Vice Admiral Gunichi Mikawa
Gunichi Mikawa
was a Vice-Admiral in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.Mikawa was the commander of a heavy cruiser force that carried out spectacular I.J.N. victory over the U.S. Navy and the Royal Australian Navy at the Battle of Savo Island in Ironbottom Sound on the night of August 1942. In...
, based at Rabaul.
The Battle of Savo Island
In the Battle of Savo IslandBattle of Savo Island
The Battle of Savo Island, also known as the First Battle of Savo Island and, in Japanese sources, as the , was a naval battle of the Pacific Campaign of World War II, between the Imperial Japanese Navy and Allied naval forces...
on 9 August 1942, the four heavy cruisers of CruDiv 6 (Aoba
Japanese cruiser Aoba
was the lead ship in the two-vessel Aoba-class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. It is named after Mount Aoba, a volcano located behind Maizuru, Kyoto.-Background:...
, Kako
Japanese cruiser Kako
was the second vessel in the two-vessel Furutaka-class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. It was named after the Kakogawa River in Hyogo prefecture, Japan.-Background:...
, Furutaka
Japanese cruiser Furutaka
was the lead ship in the two-vessel Furutaka-class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. It was named after Mount Furutaka, located on Etajima, Hiroshima immediately behind the Imperial Japanese Navy Academy.-Design:...
and Kinugasa), the heavy cruiser Chōkai, light cruisers Tenryū
Japanese cruiser Tenryu
was the lead ship in the two-ship of light cruisers of the Imperial Japanese Navy. Tenryū was named after the Tenryū River in Nagano and Shizuoka prefectures.-Background:...
and Yubari
Japanese cruiser Yubari
was a light cruiser built between 1922 and 1923 for the Imperial Japanese Navy. She fought in World War II and was sunk by the US Navy.-Design:The ship originated as an experimental scout cruiser, which would have the combat potential of the standard Japanese light cruisers on a much lighter ship....
and destroyer Yūnagi
Japanese destroyer Yunagi (1924)
was the ninth and final vessel of the Kamikaze-class destroyers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy following World War I. Advanced for their time, these ships served as first-line destroyers through the 1930s, but were considered obsolescent by the start of the Pacific War.-History:Construction...
engaged the Allied forces in a night gun and torpedo action. At about 2300, Chōkai, Furutaka and Kako all launched their reconnaissance floatplane
Floatplane
A floatplane is a type of seaplane, with slender pontoons mounted under the fuselage; only the floats of a floatplane normally come into contact with water, with the fuselage remaining above water...
s. The circling floatplanes dropped flares illuminating the targets and all the Japanese ships opened fire. US Ships Astoria
USS Astoria (CA-34)
The second USS Astoria was a United States Navy New Orleans-class heavy cruiser that participated in both the Battle of the Coral Sea and the Battle of Midway, but was then sunk in August 1942 at the Battle of Savo Island...
, Quincy
USS Quincy (CA-39)
USS Quincy was a United States Navy New Orleans-class heavy cruiser sunk at the Battle of Savo Island in 1942.Quincy, the second ship to carry the name, was laid down by the Bethlehem Shipbuilding Company, Quincy, Massachusetts on 15 November 1933, launched on 19 June 1935, sponsored by Mrs. Henry S...
, Vincennes
USS Vincennes (CA-44)
USS Vincennes was a United States Navy New Orleans-class heavy cruiser sunk at the Battle of Savo Island in 1942. She was the second ship to bear the name....
and HMAS Canberra were sunk. USS Chicago
USS Chicago (CA-29)
USS Chicago was a Northampton-class heavy cruiser of the United States Navy that served in the Pacific Theater in the early years of World War II. She was the second US Navy ship to be named after the city of Chicago, Illinois...
was damaged as were the USS Ralph Talbot
USS Ralph Talbot (DD-390)
USS Ralph Talbot was a Bagley-class destroyer in the United States Navy, named for USMC Second Lieutenant Ralph Talbot , who was awarded the Medal of Honor during World War I...
and USS Patterson
USS Patterson (DD-392)
USS Patterson , a , was the 2nd ship of the United States Navy to be named for Daniel Todd Patterson, an officer of the US Navy that served in the Quasi-War with France, First Barbary War, and the War of 1812....
. On the Japanese side, Chōkai was hit three times, Kinugasa twice (once in her No. 1 Engine Room by a 5-inch shell from Patterson and her port steering gear by a shell from Vincennes), Aoba once, and Furutaka was not damaged.
The heavily-laden American invasion transports off Guadalcanal were unprotected, but Admiral Mikawa, unaware that Admiral Fletcher
Frank Jack Fletcher
Frank Jack Fletcher was an admiral in the United States Navy during World War II. Fletcher was the operational commander at the pivotal Battles of Coral Sea and of Midway. He was the nephew of Admiral Frank Friday Fletcher.-Early life and early Navy career:Fletcher was born in Marshalltown, Iowa...
had withdrawn his aircraft carriers covering the invasion, feared an air attack at daybreak and ordered a retirement. Captain Sawa of Kinugasa, frustrated, launched a spread of torpedoes from Kinugasa's starboard tubes at the Allied
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
transports 13 miles (20.9 km) distant, but all missed. The following day as CruDiv6 approached Kavieng, Kako was torpedoed and sunk by the US submarine S 44
USS S-44 (SS-155)
USS S-44 was a third-group S-class submarine of the United States Navy.Her keel was laid down on 19 February 1921 by the Bethlehem Shipbuilding Corporation in Quincy, Massachusetts. She was launched on 27 October 1923 sponsored by Mrs. H.E. Grieshaber, and was commissioned on 16 February 1925...
.
Battle of Cape Esperance
At the Battle of Cape EsperanceBattle of Cape Esperance
The Battle of Cape Esperance, also known as the Second Battle of Savo Island and, in Japanese sources, as the , took place on 11–12 October 1942, and was a naval battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II between the Imperial Japanese Navy and United States Navy...
on 11 October 1942, CruDiv 6's (Aoba, Furutaka and Kinugasa), and destroyers Fubuki
Japanese destroyer Fubuki
was the lead ship of twenty-four destroyers, built for the Imperial Japanese Navy following World War I. When introduced into services, these ships were the most powerful destroyers in the world. They served as first-line destroyers through the 1930s, and remained formidable weapons systems well...
and Hatsuyuki
Japanese destroyer Hatsuyuki
was a Fubuki class was the third of twenty-four destroyers, built for the Imperial Japanese Navy following World War I. When introduced into service, these ships were the most powerful destroyers in the world...
departed Shortland to provide cover for a troop reinforcement convoy by shelling Henderson Field on Guadalcanal. The fleet was spotted by two Vought
Vought
Vought is the name of several related aerospace firms. These have included, in the past, Lewis and Vought Corporation, Chance Vought, Vought Sikorsky, LTV Aerospace , Vought Aircraft Companies, and the current Vought Aircraft Industries. The first incarnation of Vought was established by Chance M...
OS2U Kingfisher
OS2U Kingfisher
The Vought OS2U Kingfisher was an American catapult-launched observation floatplane. It was a compact mid-wing monoplane, with a large central float and small stabilizing floats. Performance was modest, because of its light engine...
reconnaissance planes coming down the "Slot" at 30 knots (58.8 km/h).
So alerted, the radar-equipped American cruisers USS San Francisco
USS San Francisco (CA-38)
USS San Francisco , a New Orleans-class heavy cruiser, was the second ship of the United States Navy named after the city of San Francisco, California. She saw extensive action during World War II....
, Boise
USS Boise (CL-47)
USS Boise was a United States Navy Brooklyn-class light cruiser. The cruiser was named for Boise, the capital city of the state of Idaho....
, Salt Lake City
USS Salt Lake City (CA-25)
USS Salt Lake City of the United States Navy was a Pensacola-class heavy cruiser sometimes known as "Swayback Maru". She had the distinction of having taken part in more engagements than any other ship in the fleet...
, and Helena
USS Helena (CL-50)
USS Helena was a St. Louis-class light cruiser of the United States Navy, damaged in the attack on Pearl Harbor, and subsequently active in the Pacific War until she was sunk at the battle of Kula Gulf in 1943...
and five destroyers steamed around the end of Guadalcanal to block the entrance to Savo Sound.
At 2235, the Helena's radar spotted the Japanese fleet, and the Americans successfully cross the Japanese "T"
Crossing the T
Crossing the T or Capping the T is a classic naval warfare tactic attempted from the late 19th to mid 20th century, in which a line of warships crossed in front of a line of enemy ships, allowing the crossing line to bring all their guns to bear while receiving fire from only the forward guns of...
. Both fleets open fire, but Admiral Goto, thinking that he was under friendly-fire, ordered a 180-degree turn that exposed each of his ships to the American broadsides.
Aoba was damaged heavily, and Admiral Goto mortally wounded. Furutaka was hit by a torpedo that flooded her forward engine room and was sunk by Salt Lake City and Duncan
USS Duncan (DD-485)
|...
.
Kinugasa straddled Boise and Salt Lake City with 8-inch salvos knocking out Boise's No. 1 and 2 turrets. Kinugasa sustained four hits in the engagement. The following morning, Kinugasa was attacked by five American planes but not damaged, and returned to Shortland.
Naval Battle of Guadalcanal
On 14 October 1942, Kinugasa was designated flagship of Crudiv 6. The following day, Kinugasa and Chōkai bombarded Henderson Field on Guadalcanal with a total of 752 8-inch shells.From 24-26 October and 1-5 November, Kinugasa and Chōkai provided cover for replacement convoys of troops and equipment to bolster Japanese defenses at Guadalcanal. On 14 November 1942, during the Naval Battle of Guadalcanal
Naval Battle of Guadalcanal
The Naval Battle of Guadalcanal, sometimes referred to as the Third and Fourth Battles of Savo Island, the Battle of the Solomons, The Battle of Friday the 13th, or, in Japanese sources, as the , took place from 12–15 November 1942, and was the decisive engagement in a series of naval battles...
, Kinugasa was attacked by TBF Avenger
TBF Avenger
The Grumman TBF Avenger was a torpedo bomber developed initially for the United States Navy and Marine Corps, and eventually used by several air or naval arms around the world....
torpedo-bombers and SBD Dauntless
SBD Dauntless
The Douglas SBD Dauntless was a naval dive bomber made by Douglas during World War II. The SBD was the United States Navy's main dive bomber from mid-1940 until late 1943, when it was largely replaced by the SB2C Helldiver...
dive bombers from the USS Enterprise
USS Enterprise (CV-6)
USS Enterprise , colloquially referred to as the "Big E," was the sixth aircraft carrier of the United States Navy and the seventh U.S. Navy ship to bear the name. Launched in 1936, she was a ship of the Yorktown class, and one of only three American carriers commissioned prior to World War II to...
and USMC
United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps is a branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for providing power projection from the sea, using the mobility of the United States Navy to deliver combined-arms task forces rapidly. It is one of seven uniformed services of the United States...
Avengers from Guadalcanal. At 0936 a 500-pound bomb hit Kinugasa's 13.2-mm machine gun mount in front of the bridge, starting a fire in the forward gasoline storage area. Captain Sawa and his Executive Officer
Executive officer
An executive officer is generally a person responsible for running an organization, although the exact nature of the role varies depending on the organization.-Administrative law:...
were killed by the bomb, and Kinugasa gradually began to list to port. Near-misses caused additional fires and flooding and a second attack by 17 more Dauntless bombers knocked out Kinugasa's engines and rudder and opened more compartments to the sea. At 1122, Kinugasa capsized and sank southwest of Rendova Island
Rendova Island
Rendova Island is an island, part of the New Georgia Islands of Solomon Islands in the South Pacific, east of Papua New Guinea. There are two indigenous languages spoken on Rendova Island: the Austronesian language Ughele in the north, and the Papuan language Touo in the south.The black-sand...
at 08°45′S 157°00′E, taking 511 crewmen with her.
Kinugasa was removed from the Navy list on 15 December 1942.
External links
- Tabular record: CombinedFleet.com: Kinugasa history (Retrieved 26 January 2007.)
- Gallery: US Navy Historical Center

