
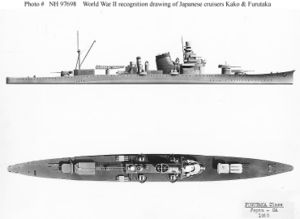
Japanese cruiser Kako
Encyclopedia
was the second vessel in the two-vessel Furutaka-class
of heavy cruiser
s in the Imperial Japanese Navy
. It was named after the Kakogawa River in Hyogo prefecture
, Japan.
Furutaka were the first generation of high speed heavy cruisers in the Japanese navy, intended to counter the US Navy Omaha class
and Royal Navy
Hawkins class
scout cruisers.
at Kobe
on July 20, 1926. Assigned to the Fifth Squadron (Sentai) from then until 1933, she served in Japanese and Chinese waters, participating in fleet maneuvers and combat operations off the China coast. Kako was given a major refit in 1929–30, improving her machinery and slightly changing her appearance. Briefly operating with CruDiv6 in 1933, Kako was in the naval review off Yokohama
in late August. She went into guard ship status in November of that year and into reserve in 1934.
In July 1936, Kako began an extensive reconstruction at Sasebo Navy Yard, which was completed by December 27, 1937. At this time, its six single 200 mm (7.9-inch) main gun turrets were replaced by three 203.2 mm (8-inch) twin turrets.
In late 1941, Kako was in CruDiv6 under Rear Admiral
Aritomo Goto
in the First Fleet with the Aoba
, Furutaka and Kinugasa
. At the time of the attack on Pearl Harbor
, it was engaged in support for the invasion of Guam
.
After the failed first invasion of Wake
CruDiv 6 was assigned to the larger second invasion force, and after the fall of Wake, returned to its forward base in Truk, Caroline Islands
.
From January 18, 1942, CruDiv 6 was assigned to support Japanese troop landings at Rabaul
, New Britain
and Kavieng
, New Ireland
and in patrols around the Marshall Islands
in unsuccessful pursuit of the American fleet. In March and April 1942, CruDiv6 provided support to CruDiv 18 in covering the landings of Japanese troops in the Solomon Islands
and New Guinea
at Buka
, Shortland
, Kieta
, Manus Island
, Admiralty Islands
and Tulagi
from a forward base at Rabaul. While at Shortland on May 6, 1942, Kako was unsuccessfully attacked by four USAAF Boeing
B-17 Flying Fortresses, but was not damaged.
, CruDiv 6 departed Shortland and effected a rendezvous at sea with light carrier Shoho
. At 1100 on May 7, 1942, north of Tulagi
, Shoho was attacked and sunk by 93 Douglas SBD Dauntless
dive-bombers and Douglas TBD Devastator torpedo-bombers from USS Yorktown
and USS Lexington
.
 The following day, May 8, 1942 46 SBDs, 21 TBDs and 15 Grumman F4F Wildcat
The following day, May 8, 1942 46 SBDs, 21 TBDs and 15 Grumman F4F Wildcat
s from Yorktown and Lexington damaged Shokaku
severely above the waterline and forced her retirement. As Furutaka and Kinugasa, undamaged in the battle, escorted Shokaku back to Truk, Kako and Aoba continued to cover the withdrawing Port Moresby
invasion convoy.
After refueling at Shortland on May 9, Kako was stranded on a reef entering Queen Carola Harbor, but was soon re-floated.
Kako returned to Kure Naval Arsenal
on May 22, 1942 for repairs, and returned to Truk on June 23, and from Truk to Rekata Bay
, Santa Isabel Island
, where it was assigned patrols through July.
In a major reorganization of the Japanese navy on July 14, 1942, Kako was assigned to the newly created Eighth Fleet
under Vice Admiral Mikawa Gunichi and was assigned to patrols around the Solomon Islands, New Britain and New Ireland.
a three-seat Aichi E13A
1 "Jake" reconnaissance floatplane launched from Kako was shot down by an SBD Dauntless of VS-72 from the USS Wasp
. This was the prelude to the Battle of Savo Island
the following day.
On August 9, the four heavy cruisers of CruDiv 6 (Aoba
, Kako, Furutaka
and Kinugasa
), the heavy cruiser Chōkai, light cruisers Tenryū
and Yubari
and destroyer Yūnagi
engaged the Allied forces in a night gun and torpedo action. At about 2300, Chōkai, Furutaka and Kako all launched their reconnaissance floatplane
s. The circling floatplanes dropped flares illuminating the targets and all the Japanese ships opened fire. USS Astoria
, Quincy
, Vincennes
and HMAS Canberra were sunk. USS Chicago
was damaged as were USS Ralph Talbot
and USS Patterson
. Kako's gunfire hit Vincennes in the hangar and destroyed all of her Curtiss SOC Seagull
floatplanes. On the Japanese side, Chōkai was hit three times, Kinugasa twice, Aoba once; Furutaka and Kako were not damaged.
On August 10, CruDiv 6's four cruisers were ordered unescorted to Kavieng, while the remainder of the striking force returned to Rabaul. At 0650 American submarine USS S-44
sighted CruDiv 6 on a track less than 900 yards (823 m) away and fired four Mark 10 torpedo
es from 700 yards (640.1 m) at the rear ship in the group, which happened to be Kako. At 0708, three torpedoes hit Kako. The first struck to starboard abreast the No. 1 turret. The other torpedoes hit further aft, in the vicinity of the forward magazines and boiler rooms 1 and 2. Kako rolled over on her starboard side and exploded as sea water reached her boilers. At 0715, Kako disappeared bow first in the sea off Simbari Island at 02°28′S 152°11′E in about 130 feet of water. Aoba, Furutaka and Kinugasa rescued Captain Takahashi and most of Kako's crew, but thirty-four crewmen were killed.
Kako was removed from the navy list
on September 15, 1942.
Furutaka class cruiser
The were a class of two Japanese heavy cruisers which saw service during World War II, both were sunk in 1942.-Description:The Furutaka class cruisers were the first heavy cruisers in the Japanese Imperial Navy....
of heavy cruiser
Heavy cruiser
The heavy cruiser was a type of cruiser, a naval warship designed for long range, high speed and an armament of naval guns roughly 203mm calibre . The heavy cruiser can be seen as a lineage of ship design from 1915 until 1945, although the term 'heavy cruiser' only came into formal use in 1930...
s in the Imperial Japanese Navy
Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1869 until 1947, when it was dissolved following Japan's constitutional renunciation of the use of force as a means of settling international disputes...
. It was named after the Kakogawa River in Hyogo prefecture
Hyogo Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kansai region on Honshū island. The capital is Kobe.The prefecture's name was previously alternately spelled as Hiogo.- History :...
, Japan.
Background
Kako and her sister shipSister ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same class as, or of virtually identical design to, another ship. Such vessels share a near-identical hull and superstructure layout, similar displacement, and roughly comparable features and equipment...
Furutaka were the first generation of high speed heavy cruisers in the Japanese navy, intended to counter the US Navy Omaha class
Omaha class cruiser
The Omaha-class cruisers were a class of light cruisers built for the United States Navy. The oldest class of cruiser still in service with the Navy at the outbreak of World War II, the Omaha class was an immediate post-World War I design....
and Royal Navy
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
Hawkins class
Hawkins class cruiser
The Hawkins class was a class of five heavy cruisers of the Royal Navy designed in 1915 and constructed throughout the First World War. All ships were named after Elizabethan sea captains...
scout cruisers.
Early career
Kako was completed at Kawasaki Shipbuilding CorporationKawasaki Shipbuilding Corporation
-External links:*...
at Kobe
Kobe
, pronounced , is the fifth-largest city in Japan and is the capital city of Hyōgo Prefecture on the southern side of the main island of Honshū, approximately west of Osaka...
on July 20, 1926. Assigned to the Fifth Squadron (Sentai) from then until 1933, she served in Japanese and Chinese waters, participating in fleet maneuvers and combat operations off the China coast. Kako was given a major refit in 1929–30, improving her machinery and slightly changing her appearance. Briefly operating with CruDiv6 in 1933, Kako was in the naval review off Yokohama
Yokohama
is the capital city of Kanagawa Prefecture and the second largest city in Japan by population after Tokyo and most populous municipality of Japan. It lies on Tokyo Bay, south of Tokyo, in the Kantō region of the main island of Honshu...
in late August. She went into guard ship status in November of that year and into reserve in 1934.
In July 1936, Kako began an extensive reconstruction at Sasebo Navy Yard, which was completed by December 27, 1937. At this time, its six single 200 mm (7.9-inch) main gun turrets were replaced by three 203.2 mm (8-inch) twin turrets.
In late 1941, Kako was in CruDiv6 under Rear Admiral
Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a naval commissioned officer rank above that of a commodore and captain, and below that of a vice admiral. It is generally regarded as the lowest of the "admiral" ranks, which are also sometimes referred to as "flag officers" or "flag ranks"...
Aritomo Goto
Aritomo Goto
was an admiral in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II.-Early career:Gotō was born in Ibaraki prefecture in 1888. He graduated from the 38th class of the Imperial Japanese Naval Academy in 1910, ranked 30th out of a class of 149 cadets. As a midshipman, he served on the cruiser and...
in the First Fleet with the Aoba
Japanese cruiser Aoba
was the lead ship in the two-vessel Aoba-class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. It is named after Mount Aoba, a volcano located behind Maizuru, Kyoto.-Background:...
, Furutaka and Kinugasa
Japanese cruiser Kinugasa
was the second vessel in the two-vessel Aoba-class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. It was named after Mount Kinugasa, located in Yokosuka, Kanagawa, Japan.- Background :...
. At the time of the attack on Pearl Harbor
Attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike conducted by the Imperial Japanese Navy against the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on the morning of December 7, 1941...
, it was engaged in support for the invasion of Guam
Battle of Guam (1941)
The First Battle of Guam, was an engagement during the Pacific War in World War II, and took place on 8 December 1941 on Guam in the Mariana Islands between the Empire of Japan and the United States...
.
After the failed first invasion of Wake
Battle of Wake Island
The Battle of Wake Island began simultaneously with the Attack on Pearl Harbor and ended on 23 December 1941, with the surrender of the American forces to the Empire of Japan...
CruDiv 6 was assigned to the larger second invasion force, and after the fall of Wake, returned to its forward base in Truk, Caroline Islands
Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia in the eastern part of the group, and Palau at the extreme western end...
.
From January 18, 1942, CruDiv 6 was assigned to support Japanese troop landings at Rabaul
Rabaul
Rabaul is a township in East New Britain province, Papua New Guinea. The town was the provincial capital and most important settlement in the province until it was destroyed in 1994 by falling ash of a volcanic eruption. During the eruption, ash was sent thousands of metres into the air and the...
, New Britain
New Britain
New Britain, or Niu Briten, is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from the island of New Guinea by the Dampier and Vitiaz Straits and from New Ireland by St. George's Channel...
and Kavieng
Kavieng
Kavieng is the capital of the Papua New Guinean province of New Ireland and the largest town on the island of the same name. The town is located at Balgai Bay, on the northern tip of the island. As of 2000, it had a population of 10,600....
, New Ireland
New Ireland (island)
New Ireland is a large island in Papua New Guinea, approximately 7,404 km² in area. It is the largest island of the New Ireland Province, lying northeast of the island of New Britain. Both islands are part of the Bismarck Archipelago, named after Otto von Bismarck, and they are separated by...
and in patrols around the Marshall Islands
Marshall Islands
The Republic of the Marshall Islands , , is a Micronesian nation of atolls and islands in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, just west of the International Date Line and just north of the Equator. As of July 2011 the population was 67,182...
in unsuccessful pursuit of the American fleet. In March and April 1942, CruDiv6 provided support to CruDiv 18 in covering the landings of Japanese troops in the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is a sovereign state in Oceania, east of Papua New Guinea, consisting of nearly one thousand islands. It covers a land mass of . The capital, Honiara, is located on the island of Guadalcanal...
and New Guinea
New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
at Buka
Buka, Papua New Guinea
Buka is situated on Buka Island, Bougainville Province, Papua New Guinea. It has been the capital of the province during the Bougainville civil war...
, Shortland
Shortland Island
Shortland Island is the largest island of the Shortland Islands, Solomon Islands, at . Named by John Shortland....
, Kieta
Kieta
Kieta is a port town located on the eastern coast of the island of Bougainville in Papua New Guinea, near the township of Arawa. After extensive destruction during the 1990 Civil Uprising on Bougainville, Kieta has few inhabitants now, and is known mainly for its transport connections .-History:On...
, Manus Island
Manus Island
Manus Island is part of Manus Province in northern Papua New Guinea and is the largest island of the Admiralty Islands. It is the fifth largest island in Papua New Guinea with an area of 2,100 km², measuring around 100 km × 30 km. According to the 2000 census, Manus Island had a...
, Admiralty Islands
Admiralty Islands
The Admiralty Islands are a group of eighteen islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the south Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island. These rainforest-covered islands form part of Manus Province, the smallest and...
and Tulagi
Tulagi
Tulagi, less commonly Tulaghi, is a small island in the Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Florida Island. The town of the same name on the island Tulagi, less commonly Tulaghi, is a small island (5.5 km by 1 km) in the Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Florida...
from a forward base at Rabaul. While at Shortland on May 6, 1942, Kako was unsuccessfully attacked by four USAAF Boeing
Boeing
The Boeing Company is an American multinational aerospace and defense corporation, founded in 1916 by William E. Boeing in Seattle, Washington. Boeing has expanded over the years, merging with McDonnell Douglas in 1997. Boeing Corporate headquarters has been in Chicago, Illinois since 2001...
B-17 Flying Fortresses, but was not damaged.
Battle of the Coral Sea
At the Battle of the Coral SeaBattle of the Coral Sea
The Battle of the Coral Sea, fought from 4–8 May 1942, was a major naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II between the Imperial Japanese Navy and Allied naval and air forces from the United States and Australia. The battle was the first fleet action in which aircraft carriers engaged...
, CruDiv 6 departed Shortland and effected a rendezvous at sea with light carrier Shoho
Japanese aircraft carrier Shoho
Shōhō , the lead ship of her class, was a light aircraft carrier of the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II...
. At 1100 on May 7, 1942, north of Tulagi
Tulagi
Tulagi, less commonly Tulaghi, is a small island in the Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Florida Island. The town of the same name on the island Tulagi, less commonly Tulaghi, is a small island (5.5 km by 1 km) in the Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Florida...
, Shoho was attacked and sunk by 93 Douglas SBD Dauntless
SBD Dauntless
The Douglas SBD Dauntless was a naval dive bomber made by Douglas during World War II. The SBD was the United States Navy's main dive bomber from mid-1940 until late 1943, when it was largely replaced by the SB2C Helldiver...
dive-bombers and Douglas TBD Devastator torpedo-bombers from USS Yorktown
USS Yorktown (CV-5)
was an aircraft carrier commissioned in the United States Navy from 1937 until she was sunk at the Battle of Midway in June 1942. She was named after the Battle of Yorktown in 1781 and the lead ship of the Yorktown class which was designed after lessons learned from operations with the large...
and USS Lexington
USS Lexington (CV-2)
USS Lexington , nicknamed the "Gray Lady" or "Lady Lex," was an early aircraft carrier of the United States Navy. She was the lead ship of the , though her sister ship was commissioned a month earlier...
.

F4F Wildcat
The Grumman F4F Wildcat was an American carrier-based fighter aircraft that began service with both the United States Navy and the British Royal Navy in 1940...
s from Yorktown and Lexington damaged Shokaku
Japanese aircraft carrier Shokaku
Shōkaku was an aircraft carrier of the Imperial Japanese Navy, the lead ship of her class. Along with her sister ship , she took part in several key naval battles during the Pacific War, including the attack on Pearl Harbor, the Battle of the Coral Sea and the Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands...
severely above the waterline and forced her retirement. As Furutaka and Kinugasa, undamaged in the battle, escorted Shokaku back to Truk, Kako and Aoba continued to cover the withdrawing Port Moresby
Port Moresby
Port Moresby , or Pot Mosbi in Tok Pisin, is the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea . It is located on the shores of the Gulf of Papua, on the southeastern coast of the island of New Guinea, which made it a prime objective for conquest by the Imperial Japanese forces during 1942–43...
invasion convoy.
After refueling at Shortland on May 9, Kako was stranded on a reef entering Queen Carola Harbor, but was soon re-floated.
Kako returned to Kure Naval Arsenal
Kure Naval Arsenal
was one of four principal naval shipyards owned and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. -History:The Kure Naval District was established at Kure, Hiroshima in 1889, as the second of the naval districts responsible for the defense of the Japanese home islands along with the establishment of the...
on May 22, 1942 for repairs, and returned to Truk on June 23, and from Truk to Rekata Bay
Rekata Bay
Rekata Bay, also known as Suavanau, is a bay located on the northeast coast of Santa Isabel Island in the Solomon Islands between Santa Isabel and Papatura Island.-History:...
, Santa Isabel Island
Santa Isabel Island
Santa Isabel Island is the longest in the Solomon Islands, South Pacific, and the largest in the group of islands in Isabel Province.-Location and geographic data:...
, where it was assigned patrols through July.
In a major reorganization of the Japanese navy on July 14, 1942, Kako was assigned to the newly created Eighth Fleet
IJN 8th Fleet
The was a fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy established during World War II.-History:Established on 14 July 1942, the IJN 8th Fleet was a headquarters unit established to direct Japanese naval operations in the Solomon Islands and New Guinea...
under Vice Admiral Mikawa Gunichi and was assigned to patrols around the Solomon Islands, New Britain and New Ireland.
Battle of Savo Island
On August 8, 1942, north of GuadalcanalGuadalcanal
Guadalcanal is a tropical island in the South-Western Pacific. The largest island in the Solomons, it was discovered by the Spanish expedition of Alvaro de Mendaña in 1568...
a three-seat Aichi E13A
Aichi E13A
-See also:-References:NotesBibliography* Dorr, Robert E. and Chris Bishop. Vietnam Air War Debrief. London: Aerospace Publishing, 1996. ISBN 1-874023-78-6....
1 "Jake" reconnaissance floatplane launched from Kako was shot down by an SBD Dauntless of VS-72 from the USS Wasp
USS Wasp (CV-7)
USS Wasp was a United States Navy aircraft carrier. The eighth Navy ship of that name, she was the sole ship of her class. Built to use up the remaining tonnage allowed to the U.S. for aircraft carriers under the treaties of the time, she was built on a reduced-size version of the Yorktown-class...
. This was the prelude to the Battle of Savo Island
Battle of Savo Island
The Battle of Savo Island, also known as the First Battle of Savo Island and, in Japanese sources, as the , was a naval battle of the Pacific Campaign of World War II, between the Imperial Japanese Navy and Allied naval forces...
the following day.
On August 9, the four heavy cruisers of CruDiv 6 (Aoba
Japanese cruiser Aoba
was the lead ship in the two-vessel Aoba-class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. It is named after Mount Aoba, a volcano located behind Maizuru, Kyoto.-Background:...
, Kako, Furutaka
Japanese cruiser Furutaka
was the lead ship in the two-vessel Furutaka-class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. It was named after Mount Furutaka, located on Etajima, Hiroshima immediately behind the Imperial Japanese Navy Academy.-Design:...
and Kinugasa
Japanese cruiser Kinugasa
was the second vessel in the two-vessel Aoba-class of heavy cruisers in the Imperial Japanese Navy. It was named after Mount Kinugasa, located in Yokosuka, Kanagawa, Japan.- Background :...
), the heavy cruiser Chōkai, light cruisers Tenryū
Japanese cruiser Tenryu
was the lead ship in the two-ship of light cruisers of the Imperial Japanese Navy. Tenryū was named after the Tenryū River in Nagano and Shizuoka prefectures.-Background:...
and Yubari
Japanese cruiser Yubari
was a light cruiser built between 1922 and 1923 for the Imperial Japanese Navy. She fought in World War II and was sunk by the US Navy.-Design:The ship originated as an experimental scout cruiser, which would have the combat potential of the standard Japanese light cruisers on a much lighter ship....
and destroyer Yūnagi
Japanese destroyer Yunagi (1924)
was the ninth and final vessel of the Kamikaze-class destroyers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy following World War I. Advanced for their time, these ships served as first-line destroyers through the 1930s, but were considered obsolescent by the start of the Pacific War.-History:Construction...
engaged the Allied forces in a night gun and torpedo action. At about 2300, Chōkai, Furutaka and Kako all launched their reconnaissance floatplane
Floatplane
A floatplane is a type of seaplane, with slender pontoons mounted under the fuselage; only the floats of a floatplane normally come into contact with water, with the fuselage remaining above water...
s. The circling floatplanes dropped flares illuminating the targets and all the Japanese ships opened fire. USS Astoria
USS Astoria (CA-34)
The second USS Astoria was a United States Navy New Orleans-class heavy cruiser that participated in both the Battle of the Coral Sea and the Battle of Midway, but was then sunk in August 1942 at the Battle of Savo Island...
, Quincy
USS Quincy (CA-39)
USS Quincy was a United States Navy New Orleans-class heavy cruiser sunk at the Battle of Savo Island in 1942.Quincy, the second ship to carry the name, was laid down by the Bethlehem Shipbuilding Company, Quincy, Massachusetts on 15 November 1933, launched on 19 June 1935, sponsored by Mrs. Henry S...
, Vincennes
USS Vincennes (CA-44)
USS Vincennes was a United States Navy New Orleans-class heavy cruiser sunk at the Battle of Savo Island in 1942. She was the second ship to bear the name....
and HMAS Canberra were sunk. USS Chicago
USS Chicago (CA-29)
USS Chicago was a Northampton-class heavy cruiser of the United States Navy that served in the Pacific Theater in the early years of World War II. She was the second US Navy ship to be named after the city of Chicago, Illinois...
was damaged as were USS Ralph Talbot
USS Ralph Talbot (DD-390)
USS Ralph Talbot was a Bagley-class destroyer in the United States Navy, named for USMC Second Lieutenant Ralph Talbot , who was awarded the Medal of Honor during World War I...
and USS Patterson
USS Patterson (DD-392)
USS Patterson , a , was the 2nd ship of the United States Navy to be named for Daniel Todd Patterson, an officer of the US Navy that served in the Quasi-War with France, First Barbary War, and the War of 1812....
. Kako's gunfire hit Vincennes in the hangar and destroyed all of her Curtiss SOC Seagull
SOC Seagull
-See also:-References:NotesBibliography* Bowers, Peter M. Curtiss Aircraft, 1907-1947. London: Putnam & Company Ltd., 1979. ISBN 0-370-10029-8....
floatplanes. On the Japanese side, Chōkai was hit three times, Kinugasa twice, Aoba once; Furutaka and Kako were not damaged.
On August 10, CruDiv 6's four cruisers were ordered unescorted to Kavieng, while the remainder of the striking force returned to Rabaul. At 0650 American submarine USS S-44
USS S-44 (SS-155)
USS S-44 was a third-group S-class submarine of the United States Navy.Her keel was laid down on 19 February 1921 by the Bethlehem Shipbuilding Corporation in Quincy, Massachusetts. She was launched on 27 October 1923 sponsored by Mrs. H.E. Grieshaber, and was commissioned on 16 February 1925...
sighted CruDiv 6 on a track less than 900 yards (823 m) away and fired four Mark 10 torpedo
Mark 10 torpedo
The Mark 10 was a torpedo first put into use by the United States in 1915 and was used as the primary torpedo in the S-class submarine. It used alcohol-water steam propulsion. It was succeeded by the problematic Mark 14 torpedo, but remained in service in S-boats & fleet submarines through the...
es from 700 yards (640.1 m) at the rear ship in the group, which happened to be Kako. At 0708, three torpedoes hit Kako. The first struck to starboard abreast the No. 1 turret. The other torpedoes hit further aft, in the vicinity of the forward magazines and boiler rooms 1 and 2. Kako rolled over on her starboard side and exploded as sea water reached her boilers. At 0715, Kako disappeared bow first in the sea off Simbari Island at 02°28′S 152°11′E in about 130 feet of water. Aoba, Furutaka and Kinugasa rescued Captain Takahashi and most of Kako's crew, but thirty-four crewmen were killed.
Kako was removed from the navy list
Navy List
A Navy List or Naval Register is an official list of naval officers, their ranks and seniority, the ships which they command or to which they are appointed, etc., that is published by the government or naval authorities of a country....
on September 15, 1942.
External links
- Tabular record: CombinedFleet.com: Kako history (Retrieved January 26, 2007.)
- Gallery: US Navy Historical Center

