
Invariant extended Kalman filter
Encyclopedia
The invariant extended Kalman filter (IEKF) is a new version of the extended Kalman filter
(EKF) for nonlinear systems possessing symmetries (or invariances). It combines the advantages of both the EKF and the recently introduced symmetry-preserving filters. Indeed, instead of using a linear correction term based on a linear output error, it uses a geometrically adapted correction term based on an invariant output error; in the same way the gain matrix is not updated from a linear state error, but from an invariant state error. The main benefit is that the gain and covariance equations converge to constant values on a much bigger set of trajectories than equilibrium points than is the case for the EKF, which results in a better convergence of the estimation.
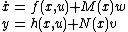
where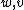 are independent white Gaussian noises.
are independent white Gaussian noises.
Consider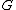 a Lie group
a Lie group
with identity , and
, and
(local) transformation groups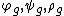 (
(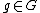 ) such that
) such that 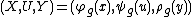 . The previous system with noise is said to be invariant if it is left unchanged by the action the transformations groups
. The previous system with noise is said to be invariant if it is left unchanged by the action the transformations groups 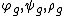 ; that is, if
; that is, if
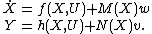
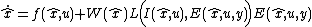
where
To analyze the error convergence, an invariant state error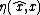 is defined, which is different from the standard output error
is defined, which is different from the standard output error 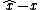 , since the standard output error usually does not preserve the symmetries of the system.
, since the standard output error usually does not preserve the symmetries of the system.
Given the considered system and associated transformation group, there exists a constructive method to determine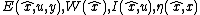 , based on the moving frame method.
, based on the moving frame method.
Similarly to the EKF, the gain matrix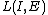 is determined from the equations
is determined from the equations
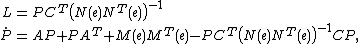
where the matices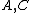 depend here only on the known invariant vector
depend here only on the known invariant vector 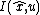 , rather than on
, rather than on 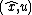 as in the standard EKF. This much simpler dependence and its consequences are the main interests of the IEKF. Indeed, the matices
as in the standard EKF. This much simpler dependence and its consequences are the main interests of the IEKF. Indeed, the matices 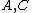 are then constant on a much bigger set of trajectories (so-called permanent trajectories) than equilibrium points as it is the case for the EKF. Near such trajectories, we are back to the "true", i.e. linear, Kalman filter where convergence is guaranteed. Informally, this means the IEKF converges in general at least around any slowly-varying permanent trajectory, rather than just around any slowly-varying equilibrium point for the EKF.
are then constant on a much bigger set of trajectories (so-called permanent trajectories) than equilibrium points as it is the case for the EKF. Near such trajectories, we are back to the "true", i.e. linear, Kalman filter where convergence is guaranteed. Informally, this means the IEKF converges in general at least around any slowly-varying permanent trajectory, rather than just around any slowly-varying equilibrium point for the EKF.
. In such systems the orientation, velocity and/or position of a moving rigid body,
e.g. an aircraft, are estimated from different embedded sensors, such as inertial sensors, magnetometers, GPS or sonars. The use of an IEKF naturally leads to consider the quaternion
error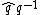 , which is often used as an ad-hoc trick to preserve the constraints of the quaternion group. The benefits of the IEKF compared to the EKF are experimentally shown for a large set of trajectories.
, which is often used as an ad-hoc trick to preserve the constraints of the quaternion group. The benefits of the IEKF compared to the EKF are experimentally shown for a large set of trajectories.
Extended Kalman filter
In estimation theory, the extended Kalman filter is the nonlinear version of the Kalman filter which linearizes about the current mean and covariance...
(EKF) for nonlinear systems possessing symmetries (or invariances). It combines the advantages of both the EKF and the recently introduced symmetry-preserving filters. Indeed, instead of using a linear correction term based on a linear output error, it uses a geometrically adapted correction term based on an invariant output error; in the same way the gain matrix is not updated from a linear state error, but from an invariant state error. The main benefit is that the gain and covariance equations converge to constant values on a much bigger set of trajectories than equilibrium points than is the case for the EKF, which results in a better convergence of the estimation.
Motivation
Most physical systems possess natural symmetries (or invariance), i.e. there exist transformations (e.g. rotations, translations, scalings) that leave the system unchanged. From mathematical and engineering viewpoint, it makes sense that a filter well-designed for the considered system should preserve the same invariance properties. The idea for the IEKF is a modification of the EKF equations to take advantage of the symmetries of the system.Definition
Consider the system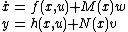
where
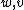 are independent white Gaussian noises.
are independent white Gaussian noises.Consider
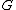 a Lie group
a Lie groupLie group
In mathematics, a Lie group is a group which is also a differentiable manifold, with the property that the group operations are compatible with the smooth structure...
with identity
 , and
, and(local) transformation groups
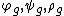 (
(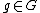 ) such that
) such that 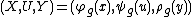 . The previous system with noise is said to be invariant if it is left unchanged by the action the transformations groups
. The previous system with noise is said to be invariant if it is left unchanged by the action the transformations groups 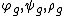 ; that is, if
; that is, if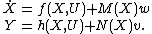
Filter equations and main result
Since it is a symmetry-preserving filter, the general form of an IEKF reads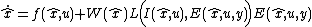
where
-
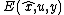 is an invariant output error, which is different to the usual output error
is an invariant output error, which is different to the usual output error 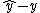
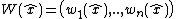 is an invariant frame
is an invariant frame
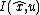 is an invariant vector
is an invariant vector
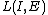 is a freely chosen gain matrix.
is a freely chosen gain matrix.
To analyze the error convergence, an invariant state error
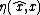 is defined, which is different from the standard output error
is defined, which is different from the standard output error 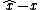 , since the standard output error usually does not preserve the symmetries of the system.
, since the standard output error usually does not preserve the symmetries of the system.Given the considered system and associated transformation group, there exists a constructive method to determine
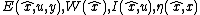 , based on the moving frame method.
, based on the moving frame method.Similarly to the EKF, the gain matrix
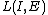 is determined from the equations
is determined from the equations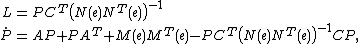
where the matices
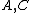 depend here only on the known invariant vector
depend here only on the known invariant vector 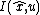 , rather than on
, rather than on 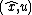 as in the standard EKF. This much simpler dependence and its consequences are the main interests of the IEKF. Indeed, the matices
as in the standard EKF. This much simpler dependence and its consequences are the main interests of the IEKF. Indeed, the matices 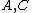 are then constant on a much bigger set of trajectories (so-called permanent trajectories) than equilibrium points as it is the case for the EKF. Near such trajectories, we are back to the "true", i.e. linear, Kalman filter where convergence is guaranteed. Informally, this means the IEKF converges in general at least around any slowly-varying permanent trajectory, rather than just around any slowly-varying equilibrium point for the EKF.
are then constant on a much bigger set of trajectories (so-called permanent trajectories) than equilibrium points as it is the case for the EKF. Near such trajectories, we are back to the "true", i.e. linear, Kalman filter where convergence is guaranteed. Informally, this means the IEKF converges in general at least around any slowly-varying permanent trajectory, rather than just around any slowly-varying equilibrium point for the EKF.Application example in aerospace engineering
Invariant extended Kaman filters are for instance used in attitude and heading reference systemsAttitude and Heading Reference Systems
An attitude heading reference system consists of sensors on three axes that provide heading, attitude and yaw information for aircraft. They are designed to replace traditional mechanical gyroscopic flight instruments and provide superior reliability and accuracy.AHRS consist of either solid-state...
. In such systems the orientation, velocity and/or position of a moving rigid body,
e.g. an aircraft, are estimated from different embedded sensors, such as inertial sensors, magnetometers, GPS or sonars. The use of an IEKF naturally leads to consider the quaternion
Quaternion
In mathematics, the quaternions are a number system that extends the complex numbers. They were first described by Irish mathematician Sir William Rowan Hamilton in 1843 and applied to mechanics in three-dimensional space...
error
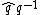 , which is often used as an ad-hoc trick to preserve the constraints of the quaternion group. The benefits of the IEKF compared to the EKF are experimentally shown for a large set of trajectories.
, which is often used as an ad-hoc trick to preserve the constraints of the quaternion group. The benefits of the IEKF compared to the EKF are experimentally shown for a large set of trajectories.

