Interspersed repeat
Encyclopedia
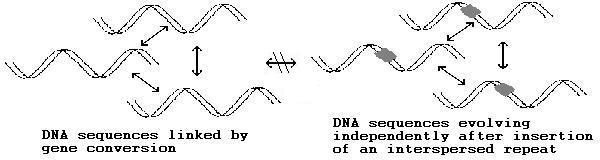
Interspersed repetitive DNA is found in all eukaryotic genomes. Certain classes of these sequences propagate themselves by RNA mediated transposition, and they have been called retrotransposon
s. Interspersed repetitive DNA elements allow new genes to evolve. They do this by uncoupling similar DNA sequences from gene conversion
during meiosis
. The recombinational events of meiosis create heteroduplexes composed of strands from each parental chromosome. These heteroduplexes lead to mismatch repair. The net result is the homogenization and elimination of sequence differences during meiosis. Gene conversion can be viewed as the force acting to create sequence identity within the gene pool
of a species
. This is a cohesive force acting to match up DNA sequences of individual organisms that comprise a species
. In effect the gene conversion causes the DNA sequences to clump together within a species and by doing so creates the natural boundaries between species
. The gene pool
of a species
consists of DNA sequences linked in a network by gene conversion
events.
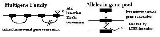
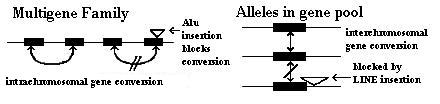
positions on their respective chromosomes or even that the homologies lie on different chromosomes. Gene conversion events can occur between different members of a gene family
situated on the same chromosome. When this happens, it is called intrachromosomal gene conversion as distinguished from interchromosomal gene conversion. The effect of homogenizing DNA sequences is the same.
or SINE
repetitive DNA are specialized for uncoupling intrachromosomal gene conversion while the longer LINE repetitive DNA are specialized for uncoupling interchromosomal gene conversion. In both cases, the interspersed repeats block gene conversion by inserting regions of non-homology within otherwise similar DNA sequences. The homogenizing forces linking DNA sequences are thereby broken and the DNA sequences are free to evolve independently. This leads to the creation of new genes and new species during evolution
. By breaking the links that would otherwise overwrite novel DNA sequence variations, interspersed repeats catalyse evolution, allowing the new genes and new species to develop.
enabling new genes to evolve without interference from the progenitor gene. Because insertion of an interspersed repeat is a saltatory event the evolution of the new gene will also be saltatory. Because speciation
ultimately depends on the creation of new genes, this naturally causes punctuated equilibria
. Interspersed repeats are thus responsible for punctuated evolution and rapid modes of evolution
.
Retrotransposon
Retrotransposons are genetic elements that can amplify themselves in a genome and are ubiquitous components of the DNA of many eukaryotic organisms. They are a subclass of transposon. They are particularly abundant in plants, where they are often a principal component of nuclear DNA...
s. Interspersed repetitive DNA elements allow new genes to evolve. They do this by uncoupling similar DNA sequences from gene conversion
Gene conversion
Gene conversion is an event in DNA genetic recombination, which occurs at high frequencies during meiotic division but which also occurs in somatic cells. It is a process by which DNA sequence information is transferred from one DNA helix to another DNA helix, whose sequence is altered.It is one...
during meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
. The recombinational events of meiosis create heteroduplexes composed of strands from each parental chromosome. These heteroduplexes lead to mismatch repair. The net result is the homogenization and elimination of sequence differences during meiosis. Gene conversion can be viewed as the force acting to create sequence identity within the gene pool
Gene pool
In population genetics, a gene pool is the complete set of unique alleles in a species or population.- Description :A large gene pool indicates extensive genetic diversity, which is associated with robust populations that can survive bouts of intense selection...
of a species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
. This is a cohesive force acting to match up DNA sequences of individual organisms that comprise a species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
. In effect the gene conversion causes the DNA sequences to clump together within a species and by doing so creates the natural boundaries between species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
. The gene pool
Gene pool
In population genetics, a gene pool is the complete set of unique alleles in a species or population.- Description :A large gene pool indicates extensive genetic diversity, which is associated with robust populations that can survive bouts of intense selection...
of a species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
consists of DNA sequences linked in a network by gene conversion
Gene conversion
Gene conversion is an event in DNA genetic recombination, which occurs at high frequencies during meiotic division but which also occurs in somatic cells. It is a process by which DNA sequence information is transferred from one DNA helix to another DNA helix, whose sequence is altered.It is one...
events.
Intrachromosomal and interchromosomal gene conversion
Gene conversion acts on DNA sequence homology as its substrate. There is no requirement that the sequence homologies lie at the allelicAllele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
positions on their respective chromosomes or even that the homologies lie on different chromosomes. Gene conversion events can occur between different members of a gene family
Gene family
A gene family is a set of several similar genes, formed by duplication of a single original gene, and generally with similar biochemical functions...
situated on the same chromosome. When this happens, it is called intrachromosomal gene conversion as distinguished from interchromosomal gene conversion. The effect of homogenizing DNA sequences is the same.
Role of Interspersed Repetitive DNA
Repetitive sequences play the role of uncoupling the gene conversion network, thereby allowing new genes to evolve. The shorter AluAlu sequence
An Alu element is a short stretch of DNA originally characterized by the action of the Alu restriction endonuclease. Alu elements of different kinds occur in large numbers in primate genomes. In fact, Alu elements are the most abundant mobile elements in the human genome. They are derived from the...
or SINE
Siné
Maurice Sinet , known as Siné, is a French cartoonist.As a young man he studied drawing and graphic arts, while earning a living as a cabaret singer. After his military service he started publishing his drawings and also worked as a photo-retoucher for porn magazines. His first published drawing...
repetitive DNA are specialized for uncoupling intrachromosomal gene conversion while the longer LINE repetitive DNA are specialized for uncoupling interchromosomal gene conversion. In both cases, the interspersed repeats block gene conversion by inserting regions of non-homology within otherwise similar DNA sequences. The homogenizing forces linking DNA sequences are thereby broken and the DNA sequences are free to evolve independently. This leads to the creation of new genes and new species during evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
. By breaking the links that would otherwise overwrite novel DNA sequence variations, interspersed repeats catalyse evolution, allowing the new genes and new species to develop.

Interspersed DNA elements catalyze the evolution of new genes
DNA sequences are linked together in a gene pool by gene conversion events. Insertion of an interspersed DNA element breaks this linkage, allowing independent evolution of a new gene. The interspersed repeat is an isolating mechanismReproductive isolation
The mechanisms of reproductive isolation or hybridization barriers are a collection of mechanisms, behaviors and physiological processes that prevent the members of two different species that cross or mate from producing offspring, or which ensure that any offspring that may be produced is not...
enabling new genes to evolve without interference from the progenitor gene. Because insertion of an interspersed repeat is a saltatory event the evolution of the new gene will also be saltatory. Because speciation
Speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which new biological species arise. The biologist Orator F. Cook seems to have been the first to coin the term 'speciation' for the splitting of lineages or 'cladogenesis,' as opposed to 'anagenesis' or 'phyletic evolution' occurring within lineages...
ultimately depends on the creation of new genes, this naturally causes punctuated equilibria
Punctuated equilibrium
Punctuated equilibrium is a theory in evolutionary biology which proposes that most species will exhibit little net evolutionary change for most of their geological history, remaining in an extended state called stasis...
. Interspersed repeats are thus responsible for punctuated evolution and rapid modes of evolution
Rapid modes of evolution
Rapid modes of evolution have been proposed by several notable biologists ever since Charles Darwin proposed his theory of evolutionary descent by natural selection...
.


