Interleukin 12
Encyclopedia
Interleukin 12 is an interleukin
that is naturally produced by dendritic cells, macrophage
s and human B-lymphoblastoid cells (NC-37) in response to antigenic stimulation.
encoded by two separate genes, IL-12A (p35) and IL-12B
(p40). The active heterodimer, and a homodimer of p40 are formed following protein synthesis.
s into Th0 cells, which will further develop into either Th1 cells or Th2 cells. It is known as a T cell-stimulating factor, which can stimulate the growth and function of T cells. It stimulates the production of interferon-gamma
(IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) from T and natural killer (NK) cells, and reduces IL-4
mediated suppression of IFN-γ. T cells that produce IL-12 have a coreceptor, CD30
, which is associated with IL-12 activity.
IL-12 plays an important role in the activities of natural killer cells and T lymphocytes. IL-12 mediates enhancement of the cytotoxic activity of NK cells and CD8
+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. There also seems to be a link between IL-2 and the signal transduction of IL-12 in NK cells. IL-2 stimulates the expression of two IL-12 receptors, IL-12R-β1 and IL-12R-β2, maintaining the expression of a critical protein involved in IL-12 signaling in NK cells. Enhanced functional response is demonstrated by IFN-γ
production and killing of target cells.
IL-12 also has anti-angiogenic activity, which means it can block the formation of new blood vessels. It does this by increasing production of interferon gamma, which in turn increases the production of a chemokine
called inducible protein-10 (IP-10 or CXCL10
). IP-10 then mediates this anti-angiogenic effect. Because of its ability to induce immune responses and its anti-angiogenic activity, there has been an interest in testing IL-12 as a possible anti-cancer
drug. However, it has not been shown to have substantial activity in the tumors tested to this date. There is a link that may be useful in treatment between IL-12 and the diseases psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease.
proteins such as STAT4
that are implicated in IL-12 signaling in T cells and NK cells. This pathway is known as the JAK-STAT pathway.
. Administration of IL-12 to people suffering from autoimmune disease
s was shown to worsen the autoimmune phenomena. This is believed to be due to its key role in induction of Th1 immune responses. In contrast, IL-12 gene knock-out in mice or a treatment of mice with IL-12 specific antibodies ameliorated the disease.
Results published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology from a study where mice that were bred to be allergic to peanuts, Interleukin-12 has been shown to not be present, suggesting that the molecule normally stops allergies to food developing. Further investigation is underway, to determine whether
the results found in mice are as profound in humans.
Interleukin
Interleukins are a group of cytokines that were first seen to be expressed by white blood cells . The term interleukin derives from "as a means of communication", and "deriving from the fact that many of these proteins are produced by leukocytes and act on leukocytes"...
that is naturally produced by dendritic cells, macrophage
Macrophage
Macrophages are cells produced by the differentiation of monocytes in tissues. Human macrophages are about in diameter. Monocytes and macrophages are phagocytes. Macrophages function in both non-specific defense as well as help initiate specific defense mechanisms of vertebrate animals...
s and human B-lymphoblastoid cells (NC-37) in response to antigenic stimulation.
Gene and structure
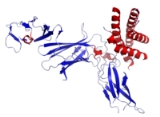
IL-12 is composed of a bundle of four alpha helices. It is a heterodimeric cytokineCytokine
Cytokines are small cell-signaling protein molecules that are secreted by the glial cells of the nervous system and by numerous cells of the immune system and are a category of signaling molecules used extensively in intercellular communication...
encoded by two separate genes, IL-12A (p35) and IL-12B
Interleukin-12 subunit beta
Subunit beta of interleukin 12 is a subunit of human interleukin 12.-Interactions:...
(p40). The active heterodimer, and a homodimer of p40 are formed following protein synthesis.
Functions
IL-12 is involved in the differentiation of naive T cellT cell
T cells or T lymphocytes belong to a group of white blood cells known as lymphocytes, and play a central role in cell-mediated immunity. They can be distinguished from other lymphocytes, such as B cells and natural killer cells , by the presence of a T cell receptor on the cell surface. They are...
s into Th0 cells, which will further develop into either Th1 cells or Th2 cells. It is known as a T cell-stimulating factor, which can stimulate the growth and function of T cells. It stimulates the production of interferon-gamma
Interferon-gamma
Interferon-gamma is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. This interferon was originally called macrophage-activating factor, a term now used to describe a larger family of proteins to which IFN-γ belongs...
(IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) from T and natural killer (NK) cells, and reduces IL-4
Interleukin 4
Interleukin-4, abbreviated IL-4, is a cytokine that induces differentiation of naive helper T cells to Th2 cells. Upon activation by IL-4, Th2 cells subsequently produce additional IL-4. The cell that initially produces IL-4, thus inducing Th0 differentiation, has not been identified, but recent...
mediated suppression of IFN-γ. T cells that produce IL-12 have a coreceptor, CD30
CD30
CD30, also known as TNFRSF8, is a cell membrane protein of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family and tumor marker.This receptor is expressed by activated, but not by resting, T and B cells. TRAF2 and TRAF5 can interact with this receptor, and mediate the signal transduction that leads to the...
, which is associated with IL-12 activity.
IL-12 plays an important role in the activities of natural killer cells and T lymphocytes. IL-12 mediates enhancement of the cytotoxic activity of NK cells and CD8
CD8
CD8 is a transmembrane glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T cell receptor . Like the TCR, CD8 binds to a major histocompatibility complex molecule, but is specific for the class I MHC protein. There are two isoforms of the protein, alpha and beta, each encoded by a different gene...
+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. There also seems to be a link between IL-2 and the signal transduction of IL-12 in NK cells. IL-2 stimulates the expression of two IL-12 receptors, IL-12R-β1 and IL-12R-β2, maintaining the expression of a critical protein involved in IL-12 signaling in NK cells. Enhanced functional response is demonstrated by IFN-γ
Interferon-gamma
Interferon-gamma is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. This interferon was originally called macrophage-activating factor, a term now used to describe a larger family of proteins to which IFN-γ belongs...
production and killing of target cells.
IL-12 also has anti-angiogenic activity, which means it can block the formation of new blood vessels. It does this by increasing production of interferon gamma, which in turn increases the production of a chemokine
Chemokine
Chemokines are a family of small cytokines, or proteins secreted by cells. Their name is derived from their ability to induce directed chemotaxis in nearby responsive cells; they are chemotactic cytokines...
called inducible protein-10 (IP-10 or CXCL10
CXCL10
C-X-C motif chemokine 10 also known as Interferon gamma-induced protein 10 or small-inducible cytokine B10 is an 8.7 kDa protein that in humans is encoded by the CXCL10 gene...
). IP-10 then mediates this anti-angiogenic effect. Because of its ability to induce immune responses and its anti-angiogenic activity, there has been an interest in testing IL-12 as a possible anti-cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
drug. However, it has not been shown to have substantial activity in the tumors tested to this date. There is a link that may be useful in treatment between IL-12 and the diseases psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Signal transduction
IL-12 binds to the IL-12 receptor, which is a heterodimeric receptor formed by IL-12R-β1 and IL-12R-β2. IL-12R-β2 is considered to play a key role in IL-12 function, since it is found on activated T cells and is stimulated by cytokines that promote Th1 cells development and inhibited by those that promote Th2 cells development. Upon binding, IL-12R-β2 becomes tyrosine phosphorylated and provides binding sites for kinases, Tyk2 and Jak2. These are important in activating critical transcription factorTranscription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
proteins such as STAT4
STAT4
STAT4 is a human gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the STAT protein family of transcription factors....
that are implicated in IL-12 signaling in T cells and NK cells. This pathway is known as the JAK-STAT pathway.
IL-12 and autoimmunity
IL-12 is linked with autoimmunityAutoimmunity
Autoimmunity is the failure of an organism to recognize its own constituent parts as self, which allows an immune response against its own cells and tissues. Any disease that results from such an aberrant immune response is termed an autoimmune disease...
. Administration of IL-12 to people suffering from autoimmune disease
Autoimmune disease
Autoimmune diseases arise from an overactive immune response of the body against substances and tissues normally present in the body. In other words, the body actually attacks its own cells. The immune system mistakes some part of the body as a pathogen and attacks it. This may be restricted to...
s was shown to worsen the autoimmune phenomena. This is believed to be due to its key role in induction of Th1 immune responses. In contrast, IL-12 gene knock-out in mice or a treatment of mice with IL-12 specific antibodies ameliorated the disease.
Results published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology from a study where mice that were bred to be allergic to peanuts, Interleukin-12 has been shown to not be present, suggesting that the molecule normally stops allergies to food developing. Further investigation is underway, to determine whether
the results found in mice are as profound in humans.

